Join the Begins With a Bang publication
Go back and forth the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the most important questions of all
There are some outstanding and unexpected details concerning the Universe, however 3 of them, put in combination, pressure us right into a profound set of restrictions on life itself.
The Universe, at the biggest scales, seems to be isotropic, or the similar in all instructions. Regardless of how a ways away we glance, no course seems to be “most well-liked” or to showcase other homes than every other.
Additionally, at the biggest cosmic scales, the Universe seems to be homogeneous, or the similar in any respect places. Whether or not we glance “right here” or “there” or “any place else,” we see kind of the similar temperatures, densities, numbers of galaxies, and many others., as long as we pattern a big sufficient area of house.
And in the end, the farther away we glance when it comes to distance — once more, similarly in all instructions — the farther again we’re seeing in time: seeing the Universe because it was once at previous and previous moments.
The ones 3 details, of isotropy, homogeneity, and evolution in time, are one of the hallmarks of recent cosmology: each theoretically and observationally. However what does that imply for the Universe as a complete, and what does that suggest for our position inside of it? That’s what Bob MacKendrick needs to grasp, as he writes in to invite:“How are we able to glance again in time and spot a smaller extra primitive universe in each and every course except the Earth is the middle of the universe?”Observationally, it’s true that after we glance again in time, we do see a smaller and extra primitive Universe in each and every course. However is Earth the middle of the Universe? It’s a very easy entice to fall for, but it surely’s no longer one thing that may be true throughout the context of our very best idea of gravity: Einstein’s normal relativity. Right here’s why. In the back of the dome of a chain of Eu Southern Observatory telescopes, the Milky Manner towers within the southern skies, flanked by means of the Massive and Small Magellanic Clouds, at proper. Even if there are a number of thousand stars and the airplane of the Milky Manner all visual to human eyes, there are best 4 galaxies past our personal that the standard unaided human eye can hit upon. We didn’t know they have been positioned outdoor of the Milky Manner till the Nineteen Twenties: after Einstein’s normal relativity has already outmoded Newtonian gravity.
In the back of the dome of a chain of Eu Southern Observatory telescopes, the Milky Manner towers within the southern skies, flanked by means of the Massive and Small Magellanic Clouds, at proper. Even if there are a number of thousand stars and the airplane of the Milky Manner all visual to human eyes, there are best 4 galaxies past our personal that the standard unaided human eye can hit upon. We didn’t know they have been positioned outdoor of the Milky Manner till the Nineteen Twenties: after Einstein’s normal relativity has already outmoded Newtonian gravity.
Credit score: ESO/Z. Bardon (www.bardon.cz)/ProjectSoft (www.projectsoft.cz)
If we move all of the long ago in time to 1915 — again when Einstein first put forth his normal idea of relativity — it’s arduous to fathom how little we knew concerning the Universe on the time. We have been in a position to peer stars throughout the Milky Manner that have been masses and even hundreds of light-years far-off, however knew of no option to measure the distances to stars more than that. We did see nebulae, together with spiral and elliptical nebulae, but it surely was once no longer but typically permitted that they have been galaxies, or “island universes” as they have been then known as, past the level of the Milky Manner itself. We didn’t know that the Universe was once increasing, and the Giant Bang had no longer but been formulated.However with a brand new idea of gravity, normal relativity, Einstein found out an incredible theoretical downside that arose by means of evaluating his working out of the Universe with the predictions of his idea. If, as Einstein idea, the Universe was once:
homogeneous, or the similar density in all places,
static, or no longer increasing/evolving through the years,
and obeyed the regulations of normal relativity, which he strongly suspected was once the case,
there was once a pathological downside that arose: the Universe should be volatile. Below Einstein’s legislation of gravity, the presence and distribution of topic and effort made up our minds the curvature of spacetime, and for those who had a uniform distribution of topic in a static Universe, you discovered that the Universe wouldn’t stay static in any respect. As a substitute, on account of all that topic, the Universe would inevitably cave in, contracting and ultimately resulting in a singularity: what we now know as a black hollow. In a Universe that isn’t increasing, you’ll be able to fill it with desk bound topic in any configuration you favor, however it’s going to all the time cave in right down to a black hollow. One of these Universe is volatile within the context of Einstein’s gravity, and should be increasing to be solid, or we should settle for its inevitable destiny.
In a Universe that isn’t increasing, you’ll be able to fill it with desk bound topic in any configuration you favor, however it’s going to all the time cave in right down to a black hollow. One of these Universe is volatile within the context of Einstein’s gravity, and should be increasing to be solid, or we should settle for its inevitable destiny.
Credit score: E. Siegel/Past the Galaxy
Obviously, this each hasn’t already came about and, observationally, wasn’t within the technique of going down. Einstein himself knew there should be one thing fighting it, and so — in both a stroke of genius or in desperation to save lots of his idea — Einstein offered a brand new time period to his equations: a cosmological consistent. This cosmological consistent wasn’t a typical type of power like topic and radiation, which can be composed of debris and will both unfold out or grow to be denser below the affect of forces, however slightly the cosmological consistent was once a type of power that was once inherent to house itself, and all the time driven outward: appearing as a internet impetus to push items inside of house clear of one every other.Einstein reasoned that best by means of counteracting the inward pull of gravity on topic and radiation with the outward “push” of a cosmological consistent may a static Universe be completed, as some type of “stability” state should be completed. However within the coming decade of the Nineteen Twenties, each theoretical and observational concerns would display that this line of pondering by means of Einstein may no longer perhaps be right kind. In reality, many criticized Einstein’s creation of the cosmological consistent for this objective for one essential explanation why: it was once a conceptual resolution, however intimately, it was once an volatile one. In case your Universe had any tiny imperfections, or inhomogeneities inside of it in any respect, similar to stars, planets, or Einsteins, it couldn’t stay balanced, and portions of it could be doomed to cave in whilst others could be pressured to extend. A mural of the Einstein box equations, with an indication of sunshine bending across the eclipsed Solar: the important thing observations that first validated normal relativity 4 years after it was once first theoretically put forth: again in 1919. The Einstein tensor is proven decomposed, at left, into the Ricci tensor and Ricci scalar, with the cosmological consistent time period added in after that. If that consistent weren’t incorporated, an increasing (or collapsing) Universe would were an inevitable result.
A mural of the Einstein box equations, with an indication of sunshine bending across the eclipsed Solar: the important thing observations that first validated normal relativity 4 years after it was once first theoretically put forth: again in 1919. The Einstein tensor is proven decomposed, at left, into the Ricci tensor and Ricci scalar, with the cosmological consistent time period added in after that. If that consistent weren’t incorporated, an increasing (or collapsing) Universe would were an inevitable result.
Credit score: Vysotsky / Wikimedia Commons
The primary revolution was once theoretical, and started with Alexander Friedmann in 1922. Operating with the Einstein box equations, Friedmann become the primary particular person to turn how a Universe that was once uniformly full of:
topic,
radiation,
a cosmological consistent,
and/or every other type of power that you’ll be able to write down,
would evolve through the years. First off, it’s outstanding to notice that this kind of Universe would, or should, evolve with time; that’s obviously no longer one thing that looked as if it would align with what we practice. However, Friedmann no longer best continued, however went so far as to turn exactly how this kind of Universe would evolve, and what components would decide its long run evolution.What Friedmann discovered was once outstanding: a suite of equations that comparable, on one hand, the entire quantity of topic and effort provide on one aspect, to the velocity at which the separation between any two arbitrary issues in house would alternate. I’ll say that once more in a relatively other means in order that you realize how profound that is: when you have topic and/or power provide for your Universe and uniformly allotted all the way through it, then the separation distance between any two issues in house will alternate through the years, and the velocity at which that distance adjustments is made up our minds immediately by means of the entire topic and effort density. In different phrases, house can’t be static inside of a uniformly-filled Universe, as Einstein firstly concocted.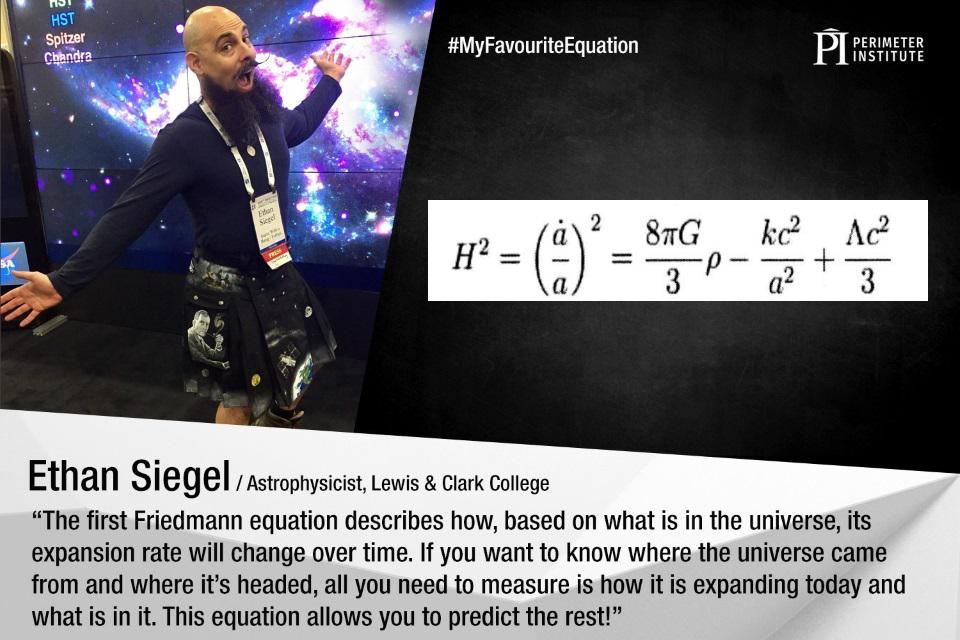 A photograph of Ethan Siegel on the American Astronomical Society’s hyperwall in 2017, at the side of the primary Friedmann equation at proper. The primary Friedmann equation main points the Hubble enlargement charge squared at the left hand aspect, which governs the evolution of spacetime. The proper aspect comprises all of the other kinds of topic and effort, at the side of spatial curvature (within the ultimate time period), which determines how the Universe evolves at some point. This has been known as a very powerful equation in all of cosmology and was once derived by means of Friedmann in necessarily its trendy shape again in 1922.
A photograph of Ethan Siegel on the American Astronomical Society’s hyperwall in 2017, at the side of the primary Friedmann equation at proper. The primary Friedmann equation main points the Hubble enlargement charge squared at the left hand aspect, which governs the evolution of spacetime. The proper aspect comprises all of the other kinds of topic and effort, at the side of spatial curvature (within the ultimate time period), which determines how the Universe evolves at some point. This has been known as a very powerful equation in all of cosmology and was once derived by means of Friedmann in necessarily its trendy shape again in 1922.
Credit score: Harley Thronson ({photograph}) and Perimeter Institute (composition)
What Friedmann’s equations don’t inform you, then again, is what course that distance alternate goes to be in: certain or adverse. In different phrases, the Universe can’t stay static, but it surely has two choices for the way it can evolve: it could possibly extend, with the space between any two issues lengthening with time, or it could possibly contract, with the space between any two issues shrinking with time. This occurs always in physics: we’ve equations that govern how the Universe works, however they don’t provide you with distinctive answers, however slightly a host (two or extra) of conceivable answers. Mathematically, there are more than one solutions. However in our bodily Universe, there’s just one exact result that ever happens.How are we able to inform which result applies to our Universe?You must glance to the Universe itself, and decide which of the conceivable answers is if truth be told bodily related. The solution to this could come from the mix of 3 other observations.
Henrietta Leavitt’s observations of the period-luminosity relation for Cepheid variable stars, which taught us that for those who measure how temporarily a Cepheid periodically brightens and dims, you’ll be able to know intrinsically how vibrant it’s.
Vesto Slipher’s observations of the spiral and elliptical nebulae within the sky, which confirmed — from how the wavelength in their mild was once shifted — they moved with extremely massive speeds, and with speeds that generally indicated a movement clear of us, slightly than towards us.
And Edwin Hubble’s (and his assistant, Milton Humason’s) observations of stars of that exact same elegance that Leavitt investigated and cataloged — Cepheid variable stars — in different galaxies, which gave the impression vastly faint in comparison to Cepheids throughout the Milky Manner and the Magellanic Clouds.
 As was once first famous by means of Vesto Slipher again within the 1910s, one of the items we practice display the spectral signatures of absorption or emission of specific atoms, ions, or molecules, however with a scientific shift towards both the crimson or blue finish of the sunshine spectrum. When blended with distance measurements for the ones items, this information gave upward push to the preliminary thought of the increasing Universe: the farther away a galaxy is, the bigger its mild will seem redshifted to our eyes and tools.
As was once first famous by means of Vesto Slipher again within the 1910s, one of the items we practice display the spectral signatures of absorption or emission of specific atoms, ions, or molecules, however with a scientific shift towards both the crimson or blue finish of the sunshine spectrum. When blended with distance measurements for the ones items, this information gave upward push to the preliminary thought of the increasing Universe: the farther away a galaxy is, the bigger its mild will seem redshifted to our eyes and tools.
Credit score: Vesto Slipher, 1917, Proc. Amer. Phil. Soc.
It didn’t take lengthy for other people to place those puzzle items in combination. Even if Hubble himself was once historically credited with the invention of the increasing Universe — and certainly, his observations have been important in making that choice — he wasn’t the primary to do it. Again in 1927, Georges Lemaître put the items along with initial information from Hubble and Humason’s research; then in 1928, Howard Robertson had the similar thought, independently, and drew the similar conclusion: the Universe was once increasing. Hubble’s first paper linking those concepts in combination didn’t seem till 1929, and it wasn’t till the Thirties that he, Einstein, and the vast majority of the astrophysical neighborhood came over to the inescapable conclusion: the Universe is increasing.Within the time since then, after all, we’ve realized a complete lot extra concerning the increasing Universe, which is simply one of the most 4 “cornerstones” of recent cosmology which have been in position starting within the Sixties. The opposite 3 are:
the invention of the cosmic microwave background, which issues to an early time period in our cosmic historical past the place it was once so sizzling that impartial atoms couldn’t stably shape,
the size of the primordial abundance of the sunshine components and their isotopes, indicating an excellent previous, warmer era the place protons and neutrons have been fused in combination in nuclear reactions,
and the evolving formation of construction in our Universe, which takes us from an early uniform state to a late-time state wealthy in stars, galaxies, clusters of galaxies, and ultimately a full-fledged cosmic internet of construction.
While you put all 4 of those cornerstones in combination, a transparent image emerges: the recent Giant Bang. The increasing Universe, filled with galaxies and the advanced construction we practice as of late, arose from a smaller, warmer, denser, extra uniform state. Even if the level of the observable Universe, as of late, takes us out some 46 billion light-years in all instructions, within the far-off cosmic previous, the whole thing in house was once a lot more compact, nearer in combination, and occupied a way smaller quantity, begging the query: what drives the growth of the Universe, each to begin with, in the beginning of the recent Giant Bang, and as of late, at past due cosmic instances, the place the growth is accelerating?
The increasing Universe, filled with galaxies and the advanced construction we practice as of late, arose from a smaller, warmer, denser, extra uniform state. Even if the level of the observable Universe, as of late, takes us out some 46 billion light-years in all instructions, within the far-off cosmic previous, the whole thing in house was once a lot more compact, nearer in combination, and occupied a way smaller quantity, begging the query: what drives the growth of the Universe, each to begin with, in the beginning of the recent Giant Bang, and as of late, at past due cosmic instances, the place the growth is accelerating?
Credit score: C.-A. Faucher-Giguere, A. Lidz, and L. Hernquist, Science, 2008
The recent Giant Bang has long gone by means of many names prior to now. Georges Lemaître known as it the “cosmic egg” when he first mentioned an early state from which the Universe as-we-know-it expanded from. George Gamow, who fleshed out many of those cornerstones within the Nineteen Forties, known as it the “primeval atom,” and due to this fact the cosmic microwave background’s authentic title was once the “primeval fireball,” because it was once known {that a} leftover thermal tub of radiation would have firstly been very popular within the early Universe. However it was once if truth be told the Giant Bang’s largest detractor, Fred Hoyle, who coined the time period Giant Bang derogatorily in 1949.However as soon as the cosmic microwave background was once found out round 15 years later, the reality of the topic may now not be not noted; the Giant Bang described our cosmic origins — and have compatibility the overall suite of information — while not one of the possible choices on the time may fit its successes. Even as of late, some 60 years after the cosmic microwave background’s discovery, the recent Giant Bang reigns unchallenged as our very best thought relating to our cosmic origins, even if it now possesses components that have been unknown to cosmologists and astrophysicists on the time: darkish topic, darkish power, and an epoch that precedes and units up the recent Giant Bang itself, cosmic inflation. This image, referred to as our concordance type of cosmology, is remarkably robust and powerful. The level of the visual Universe now is going on for 46.1 billion light-years: the space that mild emitted on the speedy of the Giant Bang could be positioned from us as of late, after a 13.8 billion 12 months adventure. As time marches on, mild that’s even farther away, this is nonetheless on its option to us, will ultimately arrive: from relatively bigger distances and with relatively bigger redshifts. We see into the previous after we glance out to nice distances since the mild emitted from far-off items should traverse the ones nice intergalactic distances at a finite pace: the rate of sunshine.
The level of the visual Universe now is going on for 46.1 billion light-years: the space that mild emitted on the speedy of the Giant Bang could be positioned from us as of late, after a 13.8 billion 12 months adventure. As time marches on, mild that’s even farther away, this is nonetheless on its option to us, will ultimately arrive: from relatively bigger distances and with relatively bigger redshifts. We see into the previous after we glance out to nice distances since the mild emitted from far-off items should traverse the ones nice intergalactic distances at a finite pace: the rate of sunshine.
Credit score: Pablo Carlos Budassi
So why is it, then, that after we glance again in time, we see a smaller, extra primitive Universe regardless of the place we glance? Why can we see that the Universe seems smaller and extra primitive by means of equivalent quantities, as we glance to ever-greater distances, in each and every course?It’s no longer as a result of Earth is the middle of the Universe. As a substitute, it’s since the Universe has a boundary: a boundary no longer in house, however in time, which corresponds to the instant that the recent Giant Bang framework started to explain our Universe.Right here, the place we’re presently within the Universe, a cumulative 13.8 billion years have elapsed for the reason that get started of the recent Giant Bang. This isn’t particular to us from right here at our vantage level; if shall we instantaneously “teleport” ourselves to every other location in house — however demanded that we no longer shuttle via time to do it — we’d to find the similar factor was once true: 13.8 billion years has elapsed for the reason that get started of the recent Giant Bang. That is true the place we’re, and it’s additionally true in every single place else. That’s since the Giant Bang wasn’t an tournament that happened at some extent, or one location in house. As a substitute, it was once an tournament that happened at a second in time, however that happened in every single place (a minimum of, in every single place throughout the a part of the Universe that we will be able to practice) unexpectedly. The observable Universe would possibly prolong for 46 billion light-years in all instructions from our viewpoint, however that’s no longer distinctive to our vantage level; all observers in any respect places would revel in the similar factor. There’s definitely extra, unobservable Universe identical to ours past the boundaries of what we will be able to see. It’s unfair to affiliate any specific level with the middle, as what we understand is made up our minds by means of the period of time that’s handed for the reason that mild seen as of late was once emitted, slightly than the geometry of the Universe.
The observable Universe would possibly prolong for 46 billion light-years in all instructions from our viewpoint, however that’s no longer distinctive to our vantage level; all observers in any respect places would revel in the similar factor. There’s definitely extra, unobservable Universe identical to ours past the boundaries of what we will be able to see. It’s unfair to affiliate any specific level with the middle, as what we understand is made up our minds by means of the period of time that’s handed for the reason that mild seen as of late was once emitted, slightly than the geometry of the Universe.
Credit score: Frederic Michel and Andrew Z. Colvin/Wikimedia Commons; annotations by means of E. Siegel
Because of this there’s a tiny caveat to the perception that the Universe is homogeneous: it’s homogeneous — i.e., the similar in any respect places — in house, however no longer in time! In different phrases, we wish to alter our thought of homogeneity for the passing of cosmic time, and because of this, for the growth of the Universe over that elapsed time. That’s since the pace of sunshine is finite, and any emitted mild should shuttle in the course of the Universe, even because the Universe itself expands, prior to it arrives at our eyes. This is why why the sunshine that does arrive from far-off resources is not just redshifted, or stretched, by means of the growth of the Universe, however that the items we see don’t seem to be as they’re presently, however slightly as they have been when that mild that’s arriving now was once emitted: thousands and thousands and even billions of years in the past, relying on their distance.This isn’t distinctive to our vantage level right here on Earth. As an example, after we glance out on the maximum far-off galaxy within the identified Universe as of late, JADES-GS-z14-0, we’re seeing it at a time:
when the Universe was once best 285 million years outdated,
simply 2.1% of its present age,
when the space setting apart two issues in house was once simply 7% of what it’s as of late,
and the place the common density of the Universe was once virtually 3000 instances as nice as it’s as of late.
If we have been as an alternative positioned inside of that galaxy (or, slightly, no matter that galaxy has grown into over the next 13.52 billion years), we’d to find the similar factor after we seemed again in the wrong way: on the tiny protogalaxy that may ultimately grow to be the Milky Manner. We’d see the Milky Manner because it was once when the Universe was once best 285 million years outdated, simply 2.1% of its present age, when distances between two issues in house was once simply 7% of its provide worth and the place the density was once ~3000 instances as nice as it’s as of late.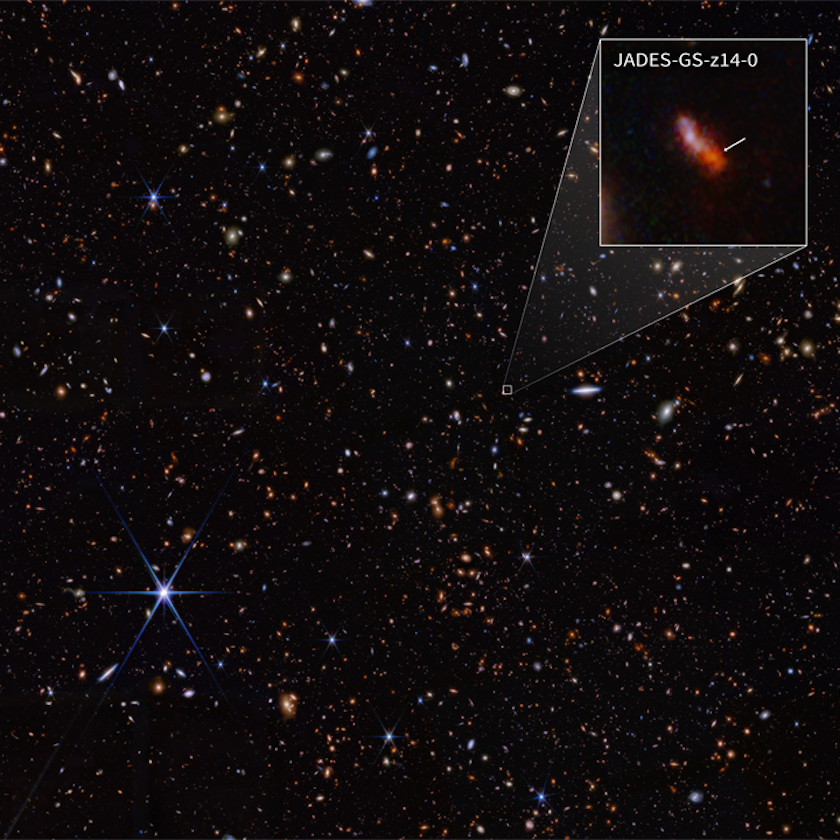 Proven throughout the context of the JWST JADES box, galaxy JADEs-GS-z14-0 is totally unremarkable, however nonetheless has simply damaged the cosmic distance file once more, changing into the primary galaxy ever discovered when the Universe was once below 300 million years outdated: simply 2.1% of its present age. From its vantage level throughout the increasing Universe, it could see our proto-Milky Manner because it was once some 13.52 billion years in the past: after we have been simply 2.1% of our present age.
Proven throughout the context of the JWST JADES box, galaxy JADEs-GS-z14-0 is totally unremarkable, however nonetheless has simply damaged the cosmic distance file once more, changing into the primary galaxy ever discovered when the Universe was once below 300 million years outdated: simply 2.1% of its present age. From its vantage level throughout the increasing Universe, it could see our proto-Milky Manner because it was once some 13.52 billion years in the past: after we have been simply 2.1% of our present age.
Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, B. Robertson (UC Santa Cruz), B. Johnson (CfA), S. Tacchella (Cambridge), P. Cargile (CfA)
The concept Earth will be the middle of the Universe is rooted in two core misconceptions concerning the Giant Bang: that it came about at a selected location in house that each one items pace clear of, like an explosion, and that the truth that we see items transferring clear of us in all instructions manner we’re at, or very with reference to, the middle of that explosion. However that’s no longer true, and all of our observations point out that. If the Giant Bang have been an explosion, then:
there could be fewer items at bigger distances, which isn’t what’s seen,
densities could be decrease after we glance farther away, slightly than the bigger values seen,
and the Universe could be no hotter at nice distances than it’s within sight, as an alternative of the seen assets that temperature will increase the farther and farther away we glance.
As scientists, we don’t draw conclusions most probably, and we don’t achieve a systematic consensus about one thing as enormous because the foundation and historical past of our Universe except the proof supporting it’s similarly enormous. Relating to the recent Giant Bang, it completely is, and that’s why the germ of an concept took a long time to increase, didn’t grow to be broadly permitted till the important supporting proof arrived within the mid-Sixties, after which has withstood each and every problem — albeit, with slight changes — in always since. The Universe appears “more youthful” the farther away we glance as it’s best been round for a finite period of time. The Giant Bang, as Gamow put it goodbye in the past, was once “the day and not using a the previous day,” and the farther away we glance, the nearer again in time to that tournament we’re in a position to peer. With new observations and new features, we’re poised to probe nearer to that second of introduction than ever prior to.Ship for your Ask Ethan inquiries to startswithabang at gmail dot com!
Join the Begins With a Bang publication
Go back and forth the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the most important questions of all