Join the Begins With a Bang publication
Commute the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the most important questions of all
Right here in our Universe, it can be the standard subject that we will immediately come across, measure, manipulate, experiment with, and follow, however it’s the darkish subject that represents lots of the mass within the Universe. While the entire “stuff” that the planets, stars, fuel, plasma, and dirt are composed of represents about 4.9% of the full calories within the Universe, the mysterious darkish subject — whose nature is unknown however for which the observational astrophysical proof is overwhelming — makes up a whopping 27% of the cosmic calories finances. Best darkish calories, making up 68% of the Universe, is extra essential from an calories density standpoint.And but, darkish subject is handiest ever present in diffuse halos, by no means in collapsed clumps like customary subject. Why is that? That’s the topic of this week’s query, coming the entire means from Barry Lewis in New Zealand, who needs to grasp:“How does darkish subject, whilst being gravitational, no longer cave in? I will be able to’t bring to mind any dialogue I’ve come throughout that addresses this obvious want for it to enjoy some form of mutual repulsive pressure.”It’s a difficult query, as it comes in conjunction with two commonplace misconceptions. First, that merely gravitating is enough to result in cave in, despite the fact that we use the time period “gravitational cave in” at all times in astrophysics. And 2d, {that a} loss of cave in signifies some form of repulsive pressure. Let’s dive into the puzzle and unpack what’s in reality occurring. In line with fashions and simulations, all galaxies will have to be embedded in darkish subject haloes, whose densities top on the galactic facilities. On lengthy sufficient timescales, of most likely one thousand million years, a unmarried darkish subject particle from the outskirts of the halo will whole one orbit. With out a huge darkish subject halo, galaxies could be smaller, decrease in mass, and not able to carry onto the ejecta from stellar cataclysms.
In line with fashions and simulations, all galaxies will have to be embedded in darkish subject haloes, whose densities top on the galactic facilities. On lengthy sufficient timescales, of most likely one thousand million years, a unmarried darkish subject particle from the outskirts of the halo will whole one orbit. With out a huge darkish subject halo, galaxies could be smaller, decrease in mass, and not able to carry onto the ejecta from stellar cataclysms.
Credit score: NASA, ESA, and T. Brown and J. Tumlinson (STScI)
One of the simplest ways to grasp what occurs — and what doesn’t occur — to darkish subject is to believe the stuff we’re extra acquainted with first: customary subject. Most conventional subject that we all know is within the type of atoms: atomic nuclei, made up of both naked protons or certain mixtures of protons and neutrons, surrounded and orbited by means of a lot lighter debris referred to as electrons. Impartial atoms have the similar choice of electrons orbiting them because the choice of protons of their nucleus, while ions have both extra (for negatively charged) or fewer (for undoubtedly charged) electrons in comparison to the choice of protons of their nucleus.As a result of those bodily houses inherent to customary subject, there are in fact 3 major categories of pressure we want to believe for traditional subject.
There’s gravitation, which impacts any particle with calories and/or mass, the place mass is a type of rest-energy, possessed by means of all of standard subject’s major constituents: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
There’s electromagnetism, which impacts any particle both with a web electrical fee or whose constituent elements include an electrical fee, particularly once they’re in movement or in touch with admire to each other.
And there are the nuclear forces, which permit protons and neutrons to bind in combination, which allow fusion and fission reactions, and which govern the radioactive decays of risky atomic nuclei.
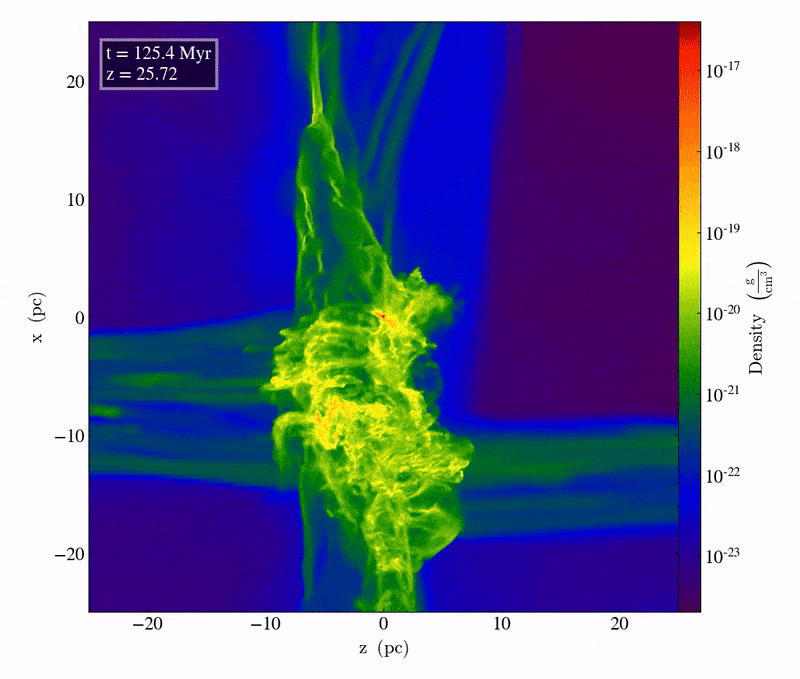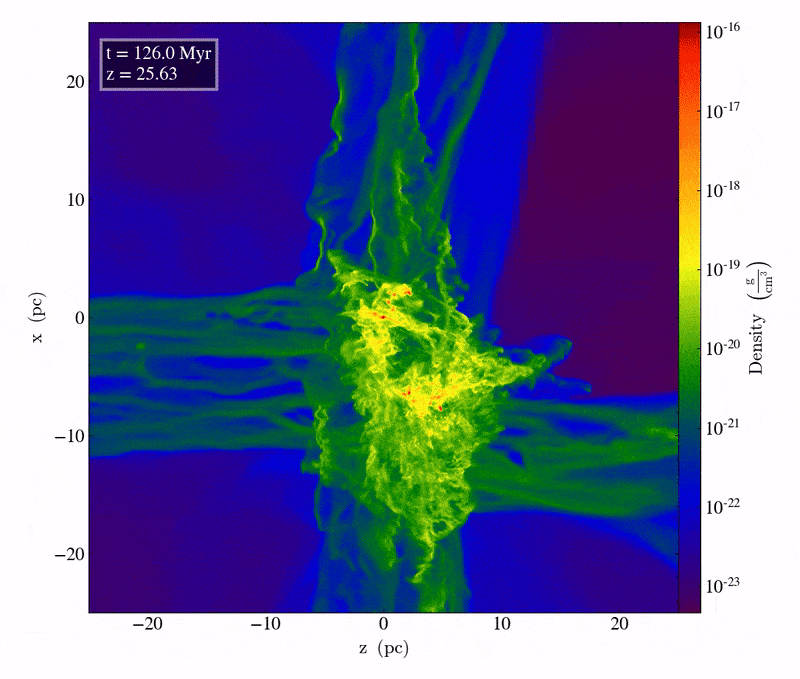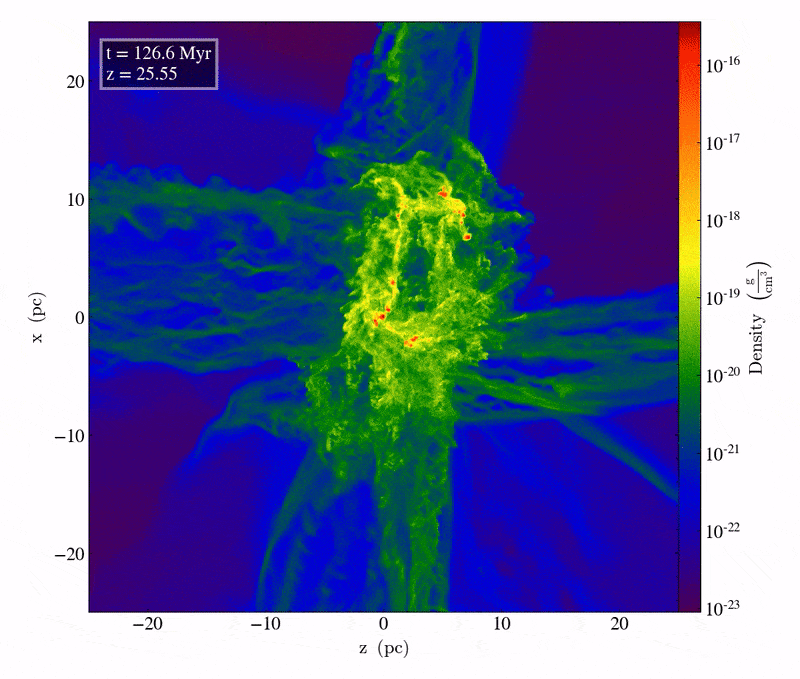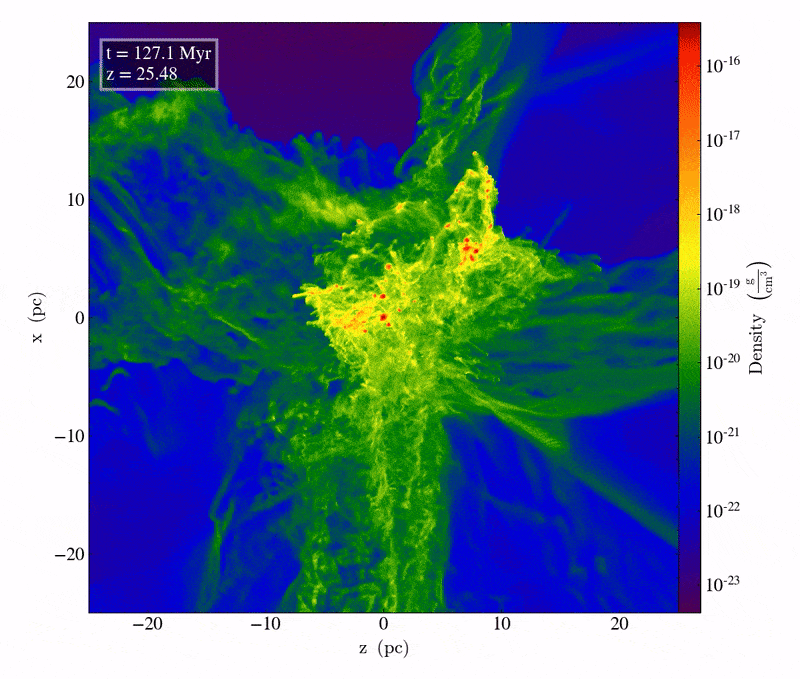 This snippet from a supercomputer simulation displays simply over 1 million years of cosmic evolution between two converging chilly streams of fuel. It’s handiest in the course of the electromagnetic interplay that those streams of fuel can radiate warmth away, turning into, and ultimate, chilly. On this brief period, just a bit over 100 million years after the Large Bang, clumps of subject develop to own particular person stars containing tens of 1000’s of sun plenty each and every within the densest areas, and may result in direct cave in black holes of an estimated ~40,000 sun plenty.Credit score: M.A. Latif et al., Nature, 2022
This snippet from a supercomputer simulation displays simply over 1 million years of cosmic evolution between two converging chilly streams of fuel. It’s handiest in the course of the electromagnetic interplay that those streams of fuel can radiate warmth away, turning into, and ultimate, chilly. On this brief period, just a bit over 100 million years after the Large Bang, clumps of subject develop to own particular person stars containing tens of 1000’s of sun plenty each and every within the densest areas, and may result in direct cave in black holes of an estimated ~40,000 sun plenty.Credit score: M.A. Latif et al., Nature, 2022
One of the crucial commonplace issues we see within the Universe that standard subject can do is solely to cave in — below its personal gravity, as we frequently say — and result in the formation of latest stars. It might be completely cheap to invite, “What’s using this cave in?” and to get a hold of an easy solution: gravity.That’s partly proper! For those who took a cloud of fuel that used to be massive and large, and all the debris inside of that fuel had been first of all at relaxation, after which grew to become off all the non-gravitational forces whilst letting gravity do its factor, you may get gravitational cave in. If truth be told, as used to be proven again within the 1910s, in a while after normal relativity used to be first put forth in its present (ultimate) shape, you wouldn’t simply get gravitational cave in happening; you’d get gravitational cave in that introduced you the entire solution to the formation of a black hollow!It doesn’t subject what the preliminary configuration of your debris are, both. They might be round, cylindrical, cube-like, dispensed in a circle, and even totally random: like some form of wild-grown potato. None of that issues. If the entire debris get started off at relaxation, and there’s not anything else occurring within the Universe apart from for gravity on this native, huge particle-dominated area of area, that’s the one imaginable end result: gravitational cave in, the entire means down, immediately, to a black hollow. In a Universe that isn’t increasing, you’ll fill it with desk bound subject in any configuration you favor, however it is going to at all times cave in right down to a black hollow. This sort of Universe is risky within the context of Einstein’s gravity, and will have to be increasing to be solid, or we will have to settle for its inevitable destiny.
In a Universe that isn’t increasing, you’ll fill it with desk bound subject in any configuration you favor, however it is going to at all times cave in right down to a black hollow. This sort of Universe is risky within the context of Einstein’s gravity, and will have to be increasing to be solid, or we will have to settle for its inevitable destiny.
Credit score: E. Siegel/Past the Galaxy
However what if there are different houses at play?Positive, you may suppose the very first thing to do could be to show at the nuclear forces, and due to this fact — since those debris are atoms, with atomic nuclei at their cores — you’d reason why that gravitational cave in would continue handiest till the atomic nuclei were given shut sufficient to cause nuclear fusion, resulting in the formation of stars.Alternatively, ahead of you were given to that level, you may understand that you simply did your self a disservice by means of ignoring a very powerful bodily truth: nuclear fusion, the method that governs the calories manufacturing in stars, isn’t made up our minds by means of the density of debris within the celebrity’s core by myself, however somewhat depends on each the density of debris and likewise the temperature of the debris throughout the celebrity’s core. Particularly, the most typical form of nuclear fusion present in stars — the place naked protons fuse into heavier atomic nuclei — can handiest continue at temperatures attaining 4 million Ok or above. That’s an overly top temperature certainly!There have been two issues that we ignored that grow to be vastly essential, then, in relation to how what we name “gravitational cave in” in fact works: the calories (together with the energy-of-motion, or kinetic calories) of the debris that is going into forming those stars, and the pressure that governs the heating, cooling, radiation, and interplay of those debris: the electromagnetic pressure.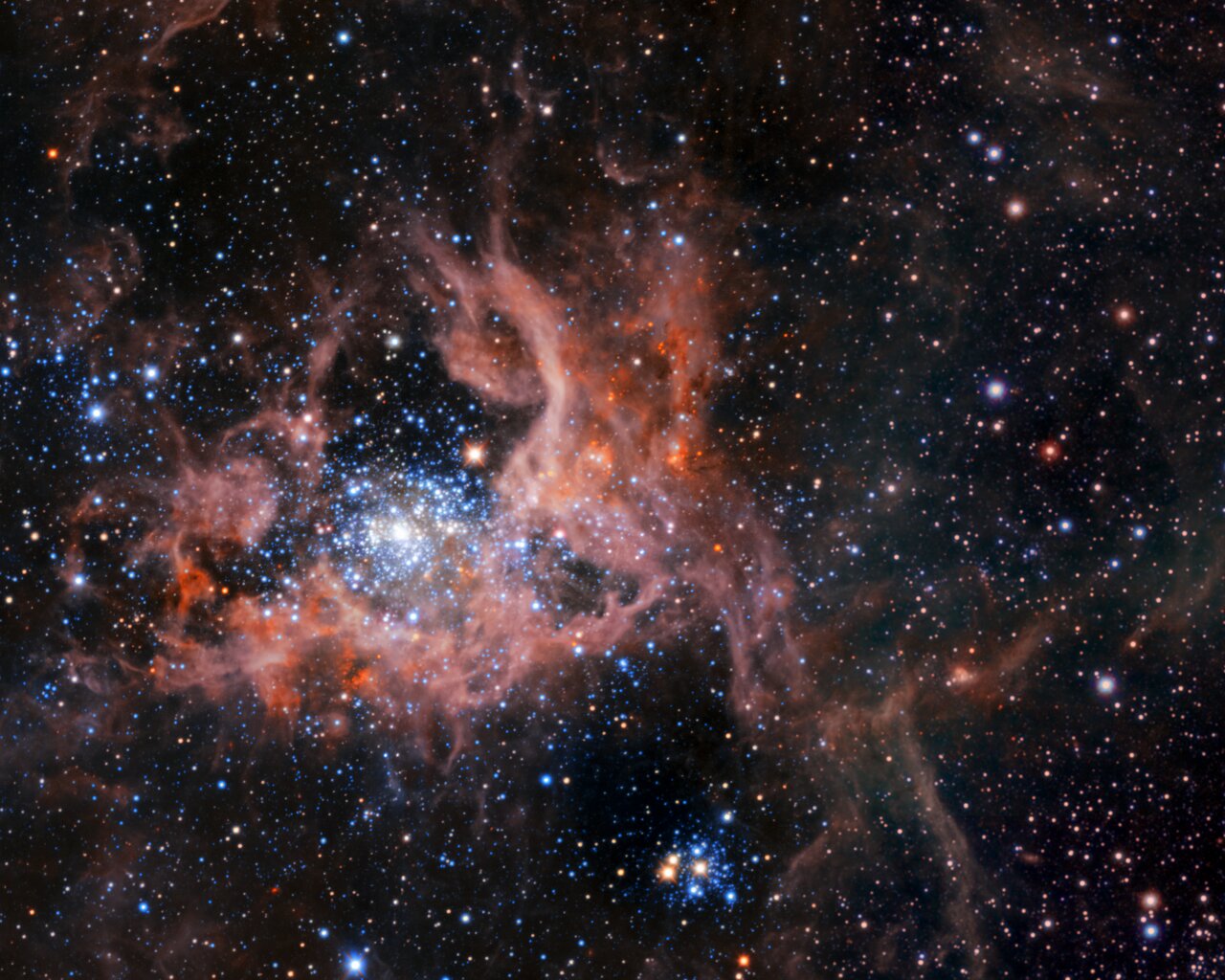 This infrared symbol displays the star-forming area 30 Doradus, sometimes called the Tarantula Nebula, highlighting its brilliant stars and light-weight, pinkish clouds of scorching fuel. The younger stars which can be visual throughout this symbol, in large part in blue, may handiest have shaped from chilly fuel, another way it wouldn’t have collapsed sufficiently to permit the formation of stars.Credit score: ESO, M.-R. Cioni/VISTA Magellanic Cloud survey. Acknowledgment: Cambridge Astronomical Survey Unit
This infrared symbol displays the star-forming area 30 Doradus, sometimes called the Tarantula Nebula, highlighting its brilliant stars and light-weight, pinkish clouds of scorching fuel. The younger stars which can be visual throughout this symbol, in large part in blue, may handiest have shaped from chilly fuel, another way it wouldn’t have collapsed sufficiently to permit the formation of stars.Credit score: ESO, M.-R. Cioni/VISTA Magellanic Cloud survey. Acknowledgment: Cambridge Astronomical Survey Unit
In our actual Universe, it isn’t imaginable to have a big selection of huge debris which can be dispensed over a big quantity of area which can be all instantaneously at relaxation. As a substitute, the debris present in any fuel cloud each and every have an inherent velocity to them in accordance with the interactions they’ve skilled: we name this the kinetic principle of gases. Debris jump round and have interaction with one every other, exchanging calories and momentum till they achieve what’s referred to as thermal equilibrium: a state the place the typical warmth (or kinetic calories) of any a part of the device is the same as the typical warmth (or kinetic calories) of all the device itself.That is one thing that handiest happens for atoms and ions, the most typical sorts of customary subject within the Universe, on account of the electromagnetic interplay. When debris collide with one every other, they may be able to achieve this in two techniques:
elastically, the place they jump off each and every different whilst retaining each calories and momentum, the place each and every elastic collision brings your device one step nearer to thermal equilibrium,
or inelastically, the place debris preserve momentum however lose calories by means of both partly or wholly sticking in combination, the place each and every inelastic collision reduces the full kinetic calories of your device on the expense of manufacturing a distinct type of calories: warmth.
 This simulation displays debris in a fuel of a random preliminary velocity/calories distribution colliding with one every other, thermalizing, and coming near the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. The state of attaining thermal equilibrium is when all portions of the device can trade calories, collide with, and have interaction with all different portions of the device freely, and is straightforward to succeed in for a closed, remoted, unchanging device. In contrast, the increasing Universe is wildly out of equilibrium.
This simulation displays debris in a fuel of a random preliminary velocity/calories distribution colliding with one every other, thermalizing, and coming near the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. The state of attaining thermal equilibrium is when all portions of the device can trade calories, collide with, and have interaction with all different portions of the device freely, and is straightforward to succeed in for a closed, remoted, unchanging device. In contrast, the increasing Universe is wildly out of equilibrium.
Credit score: Dswartz4/Wikimedia Commons
If all collisions had been elastic, you’d merely get a big mass of fuel that swirled and orbited round its general middle of mass, with houses just like the temperature and kinetic calories of each and every species of atom to your fuel made up our minds by means of a well-studied distribution: the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. As proven above, that is an frequently helpful approximation for one thing like a fuel heated to a definite temperature within a constant-volume calorimeter.Alternatively, in the event you had been to take that very same imaginary inhabitants of fuel, and also you reduced the quantity that it occupied — which is strictly what occurs when cave in happens — you’d in finding that the temperature of the fuel larger! Upper temperatures correspond to larger speeds and larger kinetic energies, and that results in every other end result as effectively: upper pressures.Whilst you build up the power of a fuel, it has a tendency to wish to develop outward. The one solution to get a fuel cloud to cave in, then, is to:
get started with a cloud that’s sufficiently chilly,
and when it begins to contract, it must be sufficiently environment friendly at dropping warmth away,
another way it gained’t cave in additional, and can as an alternative re-expand.
So, how does customary subject shed its warmth away? Via heat-emitting inelastic collisions, via photon-emitting electromagnetic radiation, or via being in touch with a less warm inhabitants of subject material. This one small area close to the center of NGC 2014 showcases a mixture of evaporating gaseous globules and free-floating Bok globules, because the mud is going from scorching, tenuous filaments at most sensible to denser, cooler clouds the place new stars shape within under. The combo of colours displays a distinction in temperatures and emission strains from more than a few atomic signatures. It’s handiest on account of the electromagnetic interactions between customary subject that complicated, collapsed buildings, equivalent to those observed right here, can shape.(Credit score: NASA, ESA and STScI)
This one small area close to the center of NGC 2014 showcases a mixture of evaporating gaseous globules and free-floating Bok globules, because the mud is going from scorching, tenuous filaments at most sensible to denser, cooler clouds the place new stars shape within under. The combo of colours displays a distinction in temperatures and emission strains from more than a few atomic signatures. It’s handiest on account of the electromagnetic interactions between customary subject that complicated, collapsed buildings, equivalent to those observed right here, can shape.(Credit score: NASA, ESA and STScI)
For this reason we will’t shape new stars from populations of scorching fuel; the preliminary molecular cloud must be sufficiently chilly, or it gained’t have the ability to cave in. It’s why there are huge temperature gradients that shape throughout the hearts of protostars and different collapsing clouds of fuel: as a result of the place the debris are densest and feature collapsed essentially the most critically, the best quantity of warmth will get trapped, versus the less-dense outer layers that may extra simply radiate, convect, and thermally switch warmth away. For this reason massive fuel clouds generally tend to fragment into smaller clumps, and why we don’t simply shape “one massive celebrity” from maximum star-forming areas, however loads, 1000’s, and even better numbers of stars of all kinds of plenty.Alternatively, all of those techniques of “eliminating warmth” or “dropping kinetic calories” rely on that one interplay that makes radiation, thermal switch, and inelastic collisions imaginable: electromagnetism. If we grew to become the electromagnetic interplay off — which, most likely thankfully, we will’t do for traditional subject — then that fuel cloud may by no means cave in to shape stars. Additionally, customary subject couldn’t cave in right down to shape a disk for disk galaxies; subject material would by no means shape protoplanetary disks round newly forming stars, by no means resulting in planets; the Universe would fight to make any certain buildings in any respect. This set of illustrations explains how a big black hollow can shape from the direct cave in of an enormous cloud of fuel inside of a few hundred million years after the Large Bang. Streams of fuel, in the event that they’re sufficiently chilly, may end up in the direct cave in of a “seed” black hollow of a number of tens of 1000’s (no less than) of sun plenty, which will shape even previous to any stars forming within the surrounding younger galaxy. Because the galaxy and black hollow develop, in the end the stellar mass content material will outweigh the extra slowly-growing black hollow. Darkish subject, which will’t turn out to be “chilly” by means of dropping warmth in the similar means, can’t shape a black hollow in a similar fashion.
This set of illustrations explains how a big black hollow can shape from the direct cave in of an enormous cloud of fuel inside of a few hundred million years after the Large Bang. Streams of fuel, in the event that they’re sufficiently chilly, may end up in the direct cave in of a “seed” black hollow of a number of tens of 1000’s (no less than) of sun plenty, which will shape even previous to any stars forming within the surrounding younger galaxy. Because the galaxy and black hollow develop, in the end the stellar mass content material will outweigh the extra slowly-growing black hollow. Darkish subject, which will’t turn out to be “chilly” by means of dropping warmth in the similar means, can’t shape a black hollow in a similar fashion.
Credit score: NASA/STScI/Leah Hustak
However it would make diffuse, “puffy” buildings, on account of two major causes: there would nonetheless be huge debris, or debris with a favorable relaxation mass, in conjunction with the truth that the Universe is increasing. We generally take into accounts the increasing Universe as being essential for radiation: species like photons or gravitational waves. You probably have an increasing Universe and radiation travels via it, the wavelength of that radiation will get longer, and it loses calories, or “cools off.”Neatly, it seems that radiation isn’t the one stuff that loses calories and “cools off” because the Universe expands; huge debris, or subject, does too. Topic has two elements to its calories:
relaxation mass calories, which gained’t trade because the Universe expands,
and kinetic calories, which is able to trade because the Universe expands.
Even supposing our Universe began with a scorching Large Bang, it additionally has been increasing. Basically, for subject, when its kinetic calories is analogous to (or greater than) its relaxation mass calories, it strikes with reference to the rate of sunshine, behaving in a similar fashion to radiation. But if its kinetic calories is small in comparison to its relaxation mass calories, it strikes slowly and will begin to clump in combination.In different phrases, even supposing we crammed the Universe with customary subject with the electromagnetic interplay grew to become off, because it expanded, the subject would decelerate and clump in combination into massive, huge, diffuse buildings: halos and filaments. This snippet from a structure-formation simulation, with the growth of the Universe scaled out, represents billions of years of gravitational enlargement in a depressing matter-rich Universe. Over the years, overdense clumps of subject develop richer and extra huge, increasing into galaxies, teams, and clusters of galaxies, whilst the fewer dense areas than moderate preferentially surrender their subject to the denser surrounding spaces. The “void” areas between the certain buildings proceed to develop, however the buildings themselves don’t.
This snippet from a structure-formation simulation, with the growth of the Universe scaled out, represents billions of years of gravitational enlargement in a depressing matter-rich Universe. Over the years, overdense clumps of subject develop richer and extra huge, increasing into galaxies, teams, and clusters of galaxies, whilst the fewer dense areas than moderate preferentially surrender their subject to the denser surrounding spaces. The “void” areas between the certain buildings proceed to develop, however the buildings themselves don’t.
Credit score: Ralf Kaehler and Tom Abel (KIPAC)/Oliver Hahn
Does this sound acquainted?It will have to sound acquainted; that is exactly how darkish subject behaves: as customary subject with the electromagnetic interplay (and likewise, no less than, the sturdy nuclear interplay) grew to become off! Whilst customary subject can cave in to do such things as “cross splat” and “stick in combination” and “shed calories” and “go through inelastic collisions,” darkish subject can do none of the ones issues. It might handiest draw in different debris (together with different darkish subject debris) via gravitation, and lose kinetic calories in conjunction with the growth of the Universe.In different phrases, despite the fact that we, as astrophysicists — together with me, in my view, as an astrophysicist — frequently speak about customary subject “gravitationally collapsing,” it’s no longer that gravitation is the most important consider why our acquainted collapsed buildings shaped. Gravitation is what drives the cave in, however it’s the electromagnetic (and, to a far lesser extent, the nuclear) interactions which can be what allow “collapsed buildings” to shape. That’s the one reason customary subject can shape:
stars,
galaxies,
planets,
astrophysically actual black holes,
stellar remnants like neutron stars and white dwarfs,
and chilly collections of subject, together with fuel and dirt,
typically. With out the electromagnetic interplay, customary subject could be trapped the best way darkish subject is: in massive, diffuse, fluffy, halo-like buildings, not able to cave in additional.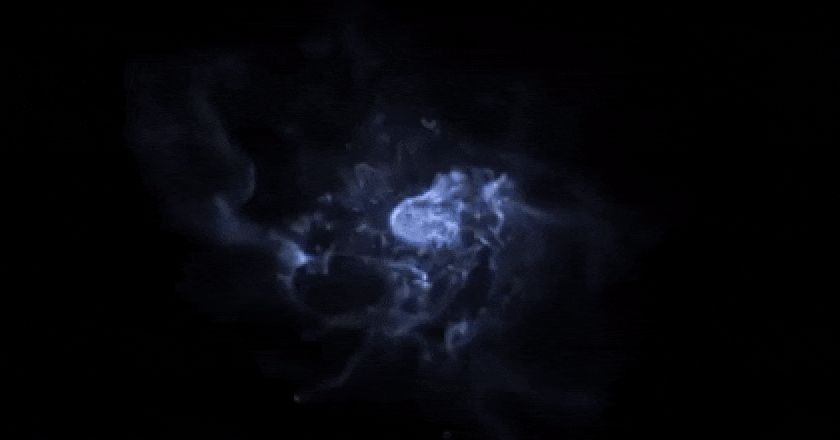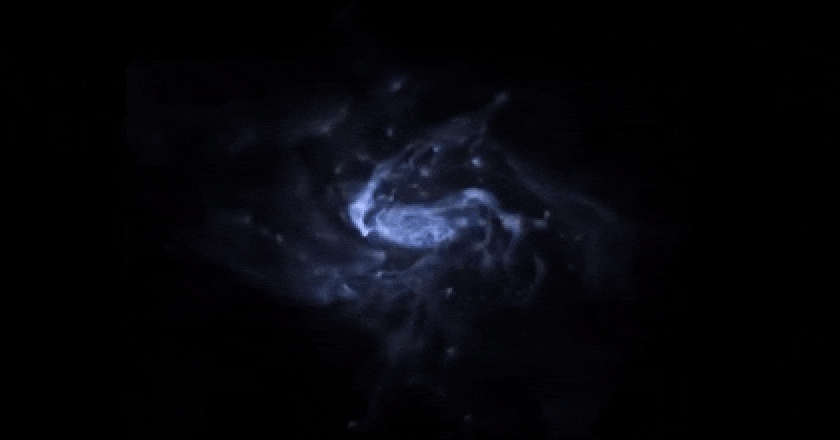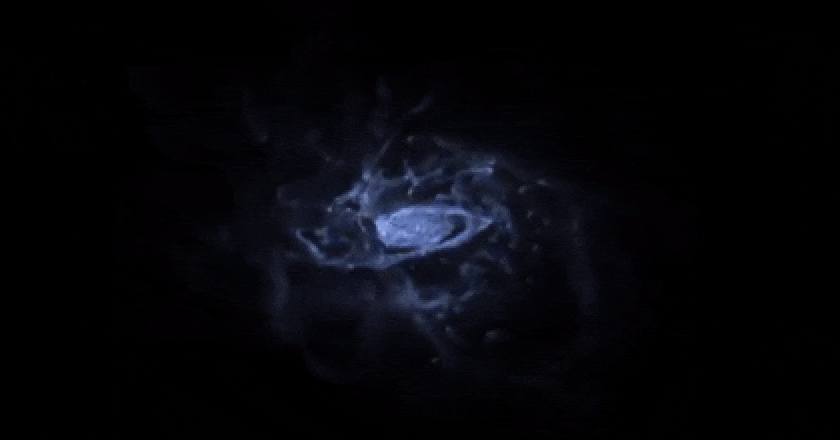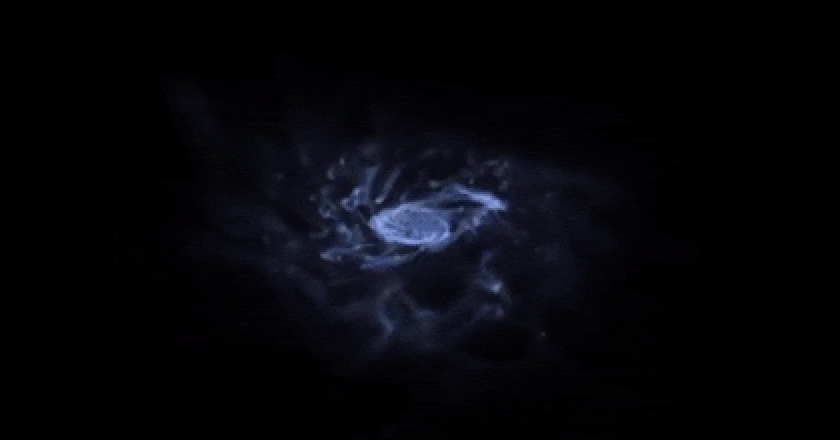 This supercomputer simulation displays the emergence of a rotating disk after loads of hundreds of thousands of years of cosmic evolution from fuel and dirt; the simulation additionally comprises stars and darkish subject, which aren’t proven right here. If the darkish subject had been visual, it could make a huge halo a lot greater, in radius, than all the dimension of the picture proven right here.
This supercomputer simulation displays the emergence of a rotating disk after loads of hundreds of thousands of years of cosmic evolution from fuel and dirt; the simulation additionally comprises stars and darkish subject, which aren’t proven right here. If the darkish subject had been visual, it could make a huge halo a lot greater, in radius, than all the dimension of the picture proven right here.
Credit score: R. Crain (LJMU) and J. Geach (U. Herts)
That’s the approach to the massive puzzle. Positive, gravitation is the impetus for the mutual enchantment between all items that possess a relaxation mass, and the extra general mass you might have confined inside of a given quantity, the more potent the self-gravitational pressure goes to be for that selection of subject. However gravitation doesn’t violate calories conservation; it merely turns (gravitational) possible calories into kinetic calories when debris get drawn into the site the place gravitation is most powerful. Except there’s some mechanism for the ones transferring debris to do such things as:
radiate calories,
collide,
have interaction (via a non-gravitational pressure),
stick or fuse in combination,
“splat” into every other type of subject,
or switch warmth/calories away,
they’re by no means going to completely cave in, however somewhat will handiest stay certain in combination in a diffuse, fluffy, uncollapsed halo.The largest distinction between darkish subject and customary subject isn’t elements like “mass” or “gravitation” in any respect; in truth, the ones are two houses they very a lot no longer handiest have in commonplace, however enjoy identically. The large variations get up from the truth that customary subject interacts via different forces as effectively — by way of the electromagnetic pressure, specifically — which permits it to do all of the ones aforementioned issues, whilst darkish subject stories none of them, no less than so far as we will come across. Darkish subject doesn’t enjoy a repulsive pressure, nor does it want to. Simply the truth that it handiest interacts gravitationally, and no longer via another manner, guarantees that it gained’t ever cave in right down to shape compact, complicated buildings the best way customary subject so mechanically and unavoidably does.Ship to your Ask Ethan inquiries to startswithabang at gmail dot com!
Join the Begins With a Bang publication
Commute the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the most important questions of all