An asteroid that tore throughout the surroundings over Germany in January was once spinning sooner than every other near-Earth object ever recorded, new analysis suggests.The distance rock, dubbed 2024 BX1, was a fireball and exploded over Berlin within the early hours of Jan. 21. Despite the fact that small asteroids on collision classes with Earth are in most cases detected best after they crash into the ambience, scientists noticed this one kind of 3 hours sooner than have an effect on.That is not the one approach 2024 BX1 was once ordinary, in line with a paper printed to the preprint database arXiv on April 5. Researchers assume the asteroid, which was once touring 31,000 mph (50,000 km/h), was once rotating as soon as each and every 2.6 seconds — the quickest spin ever observed for an asteroid. Comparable: Watch 2 bus-size asteroids make shut flybys of Earth this week (video)Prior to now, the file for the fastest-spinning asteroid belonged to a flying rock known as 2020 HS7, which confirmed a rotation duration of two.99 seconds. That asteroid measured between 13 and 24 ft (4 to eight meters) in diameter, which is fairly larger than 2024 BX1 and would possibly give an explanation for why the latter spun sooner.Asteroids spin for a number of causes, comparable to being propelled again into area after a collision. As a result of they’re extra compact, smaller asteroids generally tend to spin sooner than higher ones. “They have got interior energy, so they may be able to rotate sooner,” lead creator Maxime Devogèle, a physicist on the College of Central Florida who works with the Ecu Area Company, instructed New Scientist.Devogèle and his colleagues studied the rotational speeds of 3 asteroids, together with 2024 BX1, the usage of photographs they took because the gadgets approached Earth. The opposite two asteroids, 2023 CX1 and 2024 EF, had been described in keeping with shut calls with our planet recorded on Feb. 13, 2023, and March 4, 2024, respectively.Breaking area information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!The researchers evolved a brand new approach to visualize the asteroids’ dizzying rotational speeds. The process concerned adjusting the scale of the aperture — the opening mild passes thru to go into a digital camera — to stay the starry background sharp and let the asteroid seem as a path of sunshine.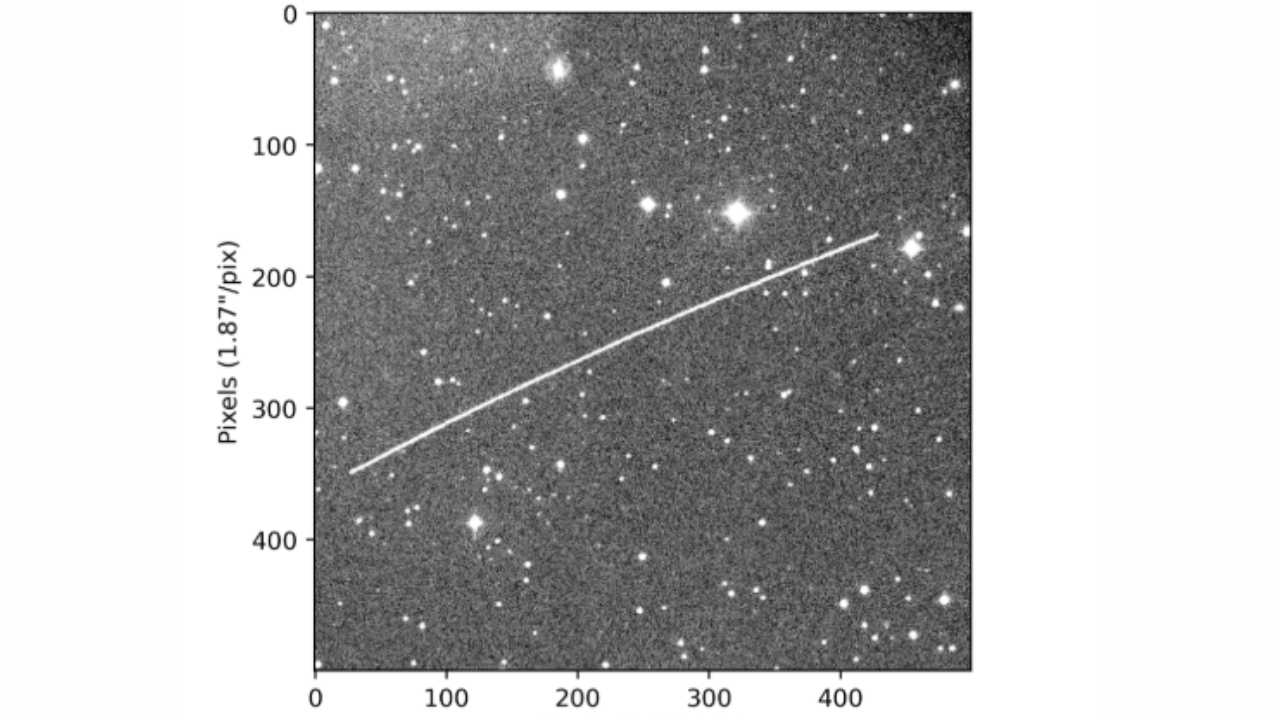 Statement of the asteroid 2023 CX1 9 mins sooner than have an effect on from the Schiaparelli Observatory in Italy. The curvature of CX1’s path is attributed to its very shut proximity to the observer (roughly 4,350 miles, or 7,000 km) and the fast variation of its relative movement within the sky. (Symbol credit score: Devogèle et al. (2024))When photographing asteroids, scientists can in most cases music the publicity time in order that each the flying rock and the area of area in the back of it stay quite crisp. However near-Earth gadgets like 2024 BX1 trip so rapid that they require impossibly brief publicity instances to look transparent.”As an alternative of monitoring the asteroid movement, resulting in stars showing trailed at the photographs, we noticed the asteroid the usage of sidereal monitoring and let the asteroid sweep throughout the box,” the researchers wrote within the paper, which has now not been peer-reviewed.Because of a protracted publicity time, the ensuing photographs display the asteroid 2024 BX1 trailing in opposition to the starry sky. Adjustments in brightness alongside the trail spotlight the place the thing turned around and counsel it had an elongated form, in line with the paper. The researchers measured the gap between those shiny spots and located that it corresponded to a rotation time of two.588 seconds, amounting to round 33,000 rotations in keeping with day.”The good thing about this system is that it permits [us] to extract the brightness of the thing over the years in unmarried photographs,” the researchers wrote. “We display that this system works and is very efficient in detecting rapid rotating asteroids.”Understanding the rotational speeds of asteroids flying with regards to Earth may well be helpful in mitigating the danger such gadgets pose to people and infrastructure, they added.
Statement of the asteroid 2023 CX1 9 mins sooner than have an effect on from the Schiaparelli Observatory in Italy. The curvature of CX1’s path is attributed to its very shut proximity to the observer (roughly 4,350 miles, or 7,000 km) and the fast variation of its relative movement within the sky. (Symbol credit score: Devogèle et al. (2024))When photographing asteroids, scientists can in most cases music the publicity time in order that each the flying rock and the area of area in the back of it stay quite crisp. However near-Earth gadgets like 2024 BX1 trip so rapid that they require impossibly brief publicity instances to look transparent.”As an alternative of monitoring the asteroid movement, resulting in stars showing trailed at the photographs, we noticed the asteroid the usage of sidereal monitoring and let the asteroid sweep throughout the box,” the researchers wrote within the paper, which has now not been peer-reviewed.Because of a protracted publicity time, the ensuing photographs display the asteroid 2024 BX1 trailing in opposition to the starry sky. Adjustments in brightness alongside the trail spotlight the place the thing turned around and counsel it had an elongated form, in line with the paper. The researchers measured the gap between those shiny spots and located that it corresponded to a rotation time of two.588 seconds, amounting to round 33,000 rotations in keeping with day.”The good thing about this system is that it permits [us] to extract the brightness of the thing over the years in unmarried photographs,” the researchers wrote. “We display that this system works and is very efficient in detecting rapid rotating asteroids.”Understanding the rotational speeds of asteroids flying with regards to Earth may well be helpful in mitigating the danger such gadgets pose to people and infrastructure, they added.
Asteroid that exploded over Berlin was once fastest-spinning area rock ever recorded