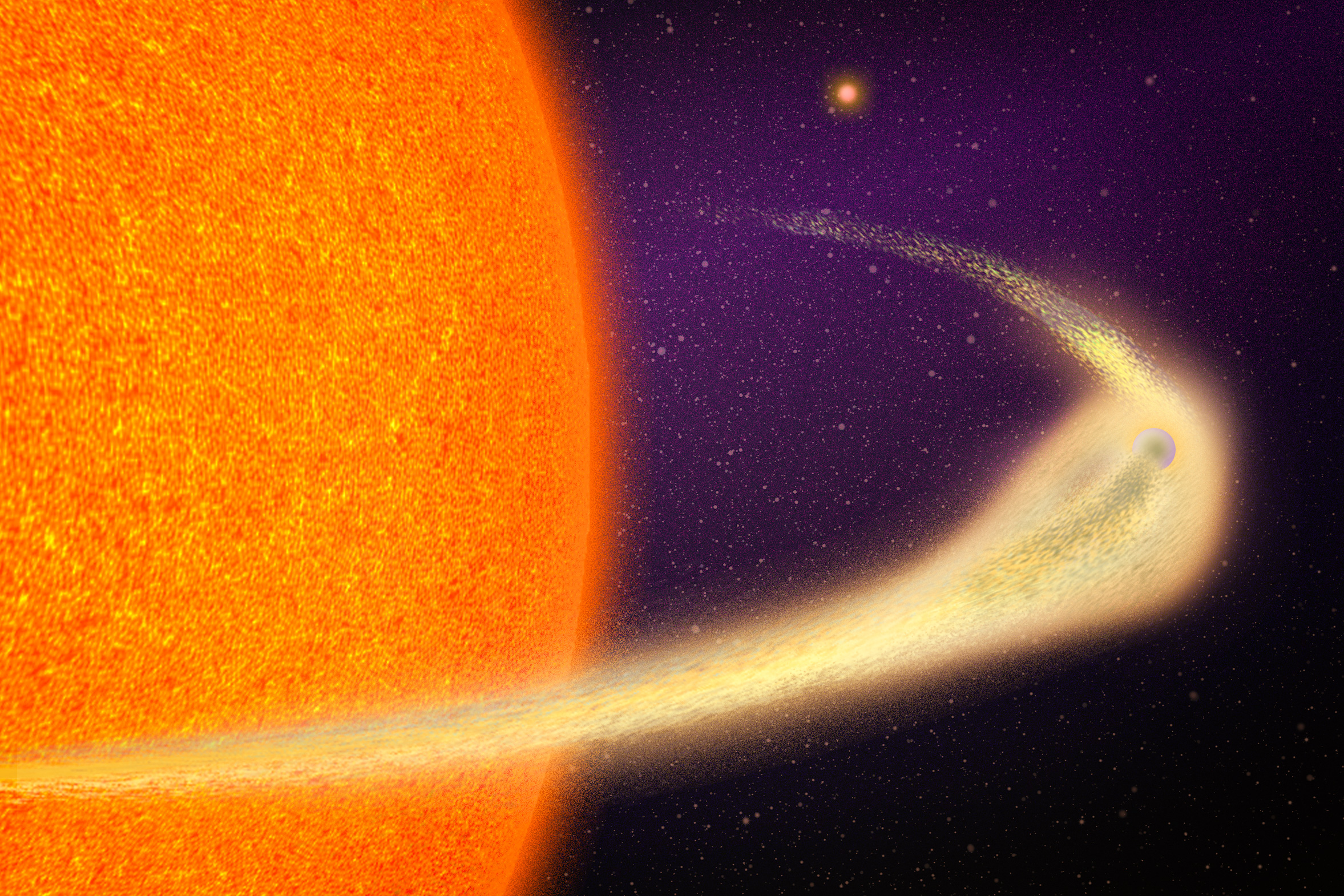
MIT astronomers have came upon a planet some 140 light-years from Earth this is hastily crumbling to items.The disintegrating international is concerning the mass of Mercury, even though it circles about 20 instances nearer to its big name than Mercury does to the solar, finishing an orbit each 30.5 hours. At such shut proximity to its big name, the planet is most likely lined in magma this is boiling off into house. Because the roasting planet whizzes round its big name, it’s losing a huge quantity of floor minerals and successfully evaporating away.The astronomers noticed the planet the usage of NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite tv for pc (TESS), an MIT-led project that screens the closest stars for transits, or periodic dips in starlight which may be indicators of orbiting exoplanets. The sign that tipped the astronomers off used to be a bizarre transit, with a dip that fluctuated extensive each orbit.The scientists showed that the sign is of a tightly orbiting rocky planet this is trailing an extended, comet-like tail of particles.“The level of the tail is gargantuan, stretching as much as 9 million kilometers lengthy, or more or less part of the planet’s complete orbit,” says Marc Hon, a postdoc in MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and House Analysis.It seems that that the planet is disintegrating at a dramatic charge, losing an quantity of subject matter identical to 1 Mount Everest every time it orbits its big name. At this tempo, given its small mass, the researchers are expecting that the planet might utterly fall apart in about 1 million to two million years.“We were given fortunate with catching it precisely when it’s in reality going away,” says Avi Shporer, a collaborator at the discovery who could also be on the TESS Science Place of business. “It’s like on its ultimate breath.”Hon and Shporer, at the side of their colleagues, have revealed their effects these days within the Astrophysical Magazine Letters. Their MIT co-authors come with Saul Rappaport, Andrew Vanderburg, Jeroen Audenaert, William Fong, Jack Haviland, Katharine Hesse, Daniel Muthukrishna, Glen Petitpas, Ellie Schmelzer, Sara Seager, and George Ricker, at the side of collaborators from more than one different establishments.Roasting awayThe new planet, which scientists have tagged as BD+05 4868 Ab, used to be detected nearly by way of happenstance.“We weren’t in search of this type of planet,” Hon says. “We had been doing the standard planet vetting, and I took place to identify this sign that seemed very strange.”The everyday sign of an orbiting exoplanet looks as if a short lived dip in a gentle curve, which repeats frequently, indicating {that a} compact frame similar to a planet is in short passing in entrance of, and briefly blocking off, the sunshine from its host big name.This standard trend used to be in contrast to what Hon and his colleagues detected from the host big name BD+05 4868 A, positioned within the constellation of Pegasus. Although a transit seemed each 30.5 hours, the brightness took for much longer to go back to standard, suggesting an extended trailing construction nonetheless blocking off starlight. Much more intriguing, the intensity of the dip modified with every orbit, suggesting that no matter used to be passing in entrance of the big name wasn’t at all times the similar form or blocking off an identical quantity of sunshine.“The form of the transit is standard of a comet with an extended tail,” Hon explains. “Except for that it’s not likely that this tail comprises unstable gases and ice as anticipated from an actual comet — those would no longer live on lengthy at such shut proximity to the host big name. Mineral grains evaporated from the planetary floor, then again, can linger lengthy sufficient to give this sort of unique tail.”Given its proximity to its big name, the crew estimates that the planet is roasting at round 1,600 levels Celsius, or just about 3,000 levels Fahrenheit. Because the big name roasts the planet, any minerals on its floor are most likely boiling away and escaping into house, the place they cool into an extended and dusty tail.The dramatic dying of this planet is a result of its low mass, which is between that of Mercury and the moon. Extra huge terrestrial planets just like the Earth have a more potent gravitational pull and due to this fact can hang onto their atmospheres. For BD+05 4868 Ab, the researchers suspect there may be little or no gravity to carry the planet in combination.“This can be a very tiny object, with very vulnerable gravity, so it simply loses a large number of mass, which then additional weakens its gravity, so it loses much more mass,” Shporer explains. “It’s a runaway procedure, and it’s best getting worse and worse for the planet.”Mineral trailOf the just about 6,000 planets that astronomers have came upon thus far, scientists know of best 3 different disintegrating planets past our sun machine. Every of those crumbling worlds had been noticed over 10 years in the past the usage of information from NASA’s Kepler House Telescope. All 3 planets had been noticed with an identical comet-like tails. BD+05 4868 Ab has the longest tail and the private transits out of the 4 recognized disintegrating planets thus far.“That signifies that its evaporation is essentially the most catastrophic, and it is going to disappear a lot sooner than the opposite planets,” Hon explains.The planet’s host big name is slightly shut, and thus brighter than the celebs internet hosting the opposite 3 disintegrating planets, making the program preferrred for additional observations the usage of NASA’s James Webb House Telescope (JWST), which will lend a hand resolve the mineral make-up of the mud tail by way of figuring out which colours of infrared mild it absorbs.This summer time, Hon and graduate pupil Nicholas Tusay from Penn State College will lead observations of BD+05 4868 Ab the usage of JWST. “This might be a novel alternative to immediately measure the internal composition of a rocky planet, which might let us know so much concerning the range and attainable habitability of terrestrial planets outdoor our sun machine,” Hon says.The researchers additionally will glance via TESS information for indicators of different disintegrating worlds.“Infrequently with the meals comes the urge for food, and we are actually seeking to start up the seek for precisely a lot of these gadgets,” Shporer says. “Those are bizarre gadgets, and the form of the sign adjustments through the years, which is one thing that’s tricky for us to seek out. However it’s one thing we’re actively operating on.”This paintings used to be supported, partially, by way of NASA.