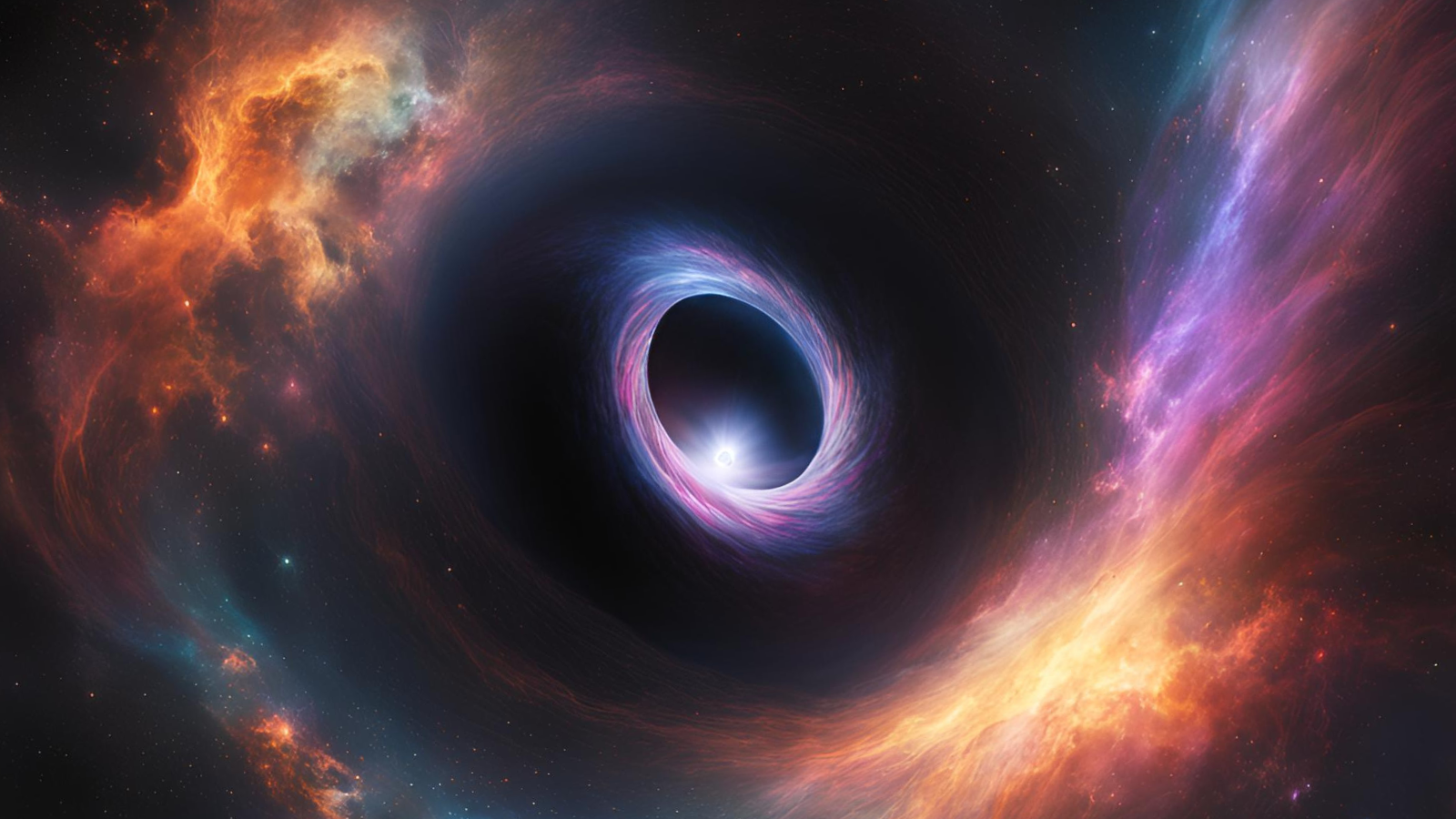
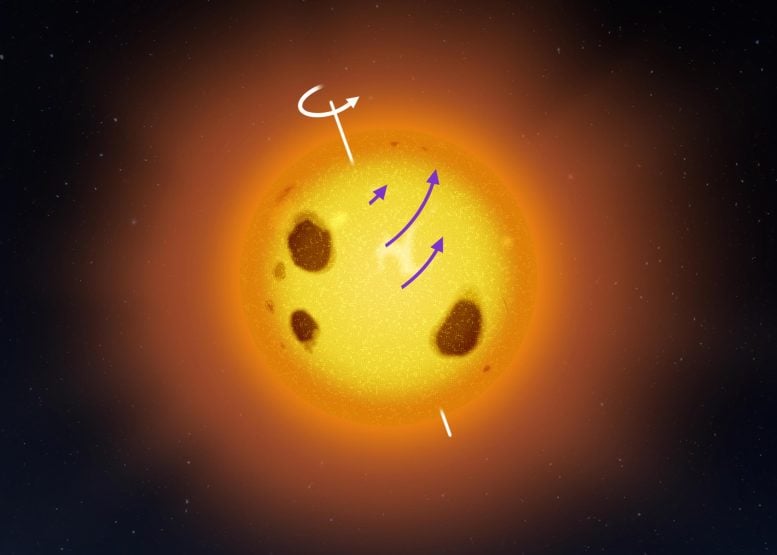
 A close-by celebrity V889 Herculis rotates the quickest at a latitude of about 40 levels. This unconventional rotational profile demanding situations established stellar fashions. Credit score: Jani Närhi, College of HelsinkiResearchers on the College of Helsinki have found out that the celebrity V889 Herculis rotates in some way this is in contrast to our Solar.Whilst the Solar spins quickest at its equator, V889 Herculis rotates quickest at a latitude of about 40 levels. This distinctive discovering is helping scientists higher perceive the complexities of ways stars just like the Solar function, in particular when it comes to floor exercise like sunspots and sun eruptions.Ordinary Stellar Rotation Seen in V889 HerculisThe Solar rotates the quickest on the equator and the rotation fee slows down at upper latitudes, changing into the slowest within the polar areas. However a close-by Solar-like celebrity V889 Herculis, some 115 light-years away within the constellation of Hercules, rotates the quickest at a latitude of about 40 levels, whilst each the equator and polar areas rotate extra slowly.A identical rotational profile has now not been noticed for another celebrity. The result’s surprising as a result of stellar rotation has been thought to be a well-understood elementary bodily parameter however any such rotational profile has now not been predicted even in pc simulations.“We implemented a newly evolved statistical strategy to the knowledge of a well-known celebrity that has been studied within the College of Helsinki for years. We didn’t be expecting to look such anomalies in stellar rotation. The anomalies within the rotational profile of V889 Herculis point out that our figuring out of stellar dynamics and magnetic dynamos is inadequate,” explains researcher Mikko Tuomi who coordinated the researchDynamics of a ball of plasmaThe goal celebrity V889 Herculis is just like a tender Solar, telling a tale in regards to the historical past and evolution of the Solar. Tuomi emphasizes that it is important to grasp stellar astrophysics with a view to, for example, expect activity-induced phenomena at the Sun floor, similar to spots and eruptions.Stars are round buildings the place subject is within the state of plasma, consisting of charged debris. They’re dynamic gadgets that dangle in a stability between the drive generated in nuclear reactions of their cores and their very own gravity. They’ve no cast surfaces, in contrast to many planets.The stellar rotation isn’t consistent for all latitudes – an impact referred to as differential rotation. It’s led to through the truth that scorching plasma rises to the celebrity’s floor by way of a phenomenon referred to as convection, which in flip has an impact at the native rotation fee. It is because angular momentum will have to be conserved and the convection happens perpendicular to the rotational axis close to the equator while it’s parallel to the axis close to the poles.On the other hand, many elements similar to stellar mass, age, chemical composition, rotation duration, and magnetic box have an affect on the rotation and provides upward thrust to diversifications within the differential rotation profiles.A statistical way for figuring out rotational profileThomas Hackman, docent of astronomy, who participated within the analysis, explains that the Solar has been the one celebrity for which finding out the rotational profile has been imaginable.“Stellar differential rotation is an overly a very powerful issue that has an impact at the magnetic exercise of stars. The process we now have evolved opens a brand new window into the interior workings of alternative stars.”The astronomers at Helsinki College’s Division of Particle Physics and Astrophysics have decided the rotational profile of 2 within reach younger stars through making use of a brand new statistical modeling to long-baseline brightness observations. They modeled the periodic diversifications within the observations through accounting for the variations within the obvious spot motion at other latitudes. The spot motion then enabled estimating the rotational profile of the celebs.The second one one of the crucial goal stars, LQ Hydrae within the constellation of Hydra, was once discovered to be rotating just like a inflexible frame — the rotation gave the impression unchanged from the equator to the poles, which signifies that the variations are very small.Observations From the Fairborn ObservatoryThe researchers base their effects at the observations of the objective stars from the Fairborn observatory. The brightnesses of the celebs were monitored with robot telescopes for round 30 years, which supplies insights into the conduct of the celebs over a protracted time frame.Tuomi appreciates the paintings of senior astronomer Gregory Henry, of Tennessee College, United States, who leads the Fairborne observational marketing campaign.“For a few years, Greg’s mission has been extraordinarily treasured in figuring out the conduct of within reach stars. Whether or not the inducement is to review the rotation and houses of younger, lively stars or to grasp the character of stars with planets, the observations from Fairborn Observatory were completely a very powerful. It’s superb that even within the generation of serious space-based observatories we will be able to download elementary knowledge at the stellar astrophysics with small 40cm ground-based telescopes.”The objective stars V889 Herculis and LQ Hydrae are each kind of 50 million-year-old stars that during many respects resemble the younger Solar. They each rotate very swiftly, with rotation classes of most effective about one and a part days. Because of this, the long-baseline brightness observations include many rotational cycles. The celebrities had been decided on as objectives as a result of they have got been noticed for many years and since they have got each been studied actively on the College of Helsinki.Reference: “Characterising the stellar differential rotation in line with largest-spot statistics from ground-based photometry” through Mikko Tuomi, J. Jyri Lehtinen, W. Gregory Henry and Thomas Hackman, 26 July 2024, Astronomy & Astrophysics.
A close-by celebrity V889 Herculis rotates the quickest at a latitude of about 40 levels. This unconventional rotational profile demanding situations established stellar fashions. Credit score: Jani Närhi, College of HelsinkiResearchers on the College of Helsinki have found out that the celebrity V889 Herculis rotates in some way this is in contrast to our Solar.Whilst the Solar spins quickest at its equator, V889 Herculis rotates quickest at a latitude of about 40 levels. This distinctive discovering is helping scientists higher perceive the complexities of ways stars just like the Solar function, in particular when it comes to floor exercise like sunspots and sun eruptions.Ordinary Stellar Rotation Seen in V889 HerculisThe Solar rotates the quickest on the equator and the rotation fee slows down at upper latitudes, changing into the slowest within the polar areas. However a close-by Solar-like celebrity V889 Herculis, some 115 light-years away within the constellation of Hercules, rotates the quickest at a latitude of about 40 levels, whilst each the equator and polar areas rotate extra slowly.A identical rotational profile has now not been noticed for another celebrity. The result’s surprising as a result of stellar rotation has been thought to be a well-understood elementary bodily parameter however any such rotational profile has now not been predicted even in pc simulations.“We implemented a newly evolved statistical strategy to the knowledge of a well-known celebrity that has been studied within the College of Helsinki for years. We didn’t be expecting to look such anomalies in stellar rotation. The anomalies within the rotational profile of V889 Herculis point out that our figuring out of stellar dynamics and magnetic dynamos is inadequate,” explains researcher Mikko Tuomi who coordinated the researchDynamics of a ball of plasmaThe goal celebrity V889 Herculis is just like a tender Solar, telling a tale in regards to the historical past and evolution of the Solar. Tuomi emphasizes that it is important to grasp stellar astrophysics with a view to, for example, expect activity-induced phenomena at the Sun floor, similar to spots and eruptions.Stars are round buildings the place subject is within the state of plasma, consisting of charged debris. They’re dynamic gadgets that dangle in a stability between the drive generated in nuclear reactions of their cores and their very own gravity. They’ve no cast surfaces, in contrast to many planets.The stellar rotation isn’t consistent for all latitudes – an impact referred to as differential rotation. It’s led to through the truth that scorching plasma rises to the celebrity’s floor by way of a phenomenon referred to as convection, which in flip has an impact at the native rotation fee. It is because angular momentum will have to be conserved and the convection happens perpendicular to the rotational axis close to the equator while it’s parallel to the axis close to the poles.On the other hand, many elements similar to stellar mass, age, chemical composition, rotation duration, and magnetic box have an affect on the rotation and provides upward thrust to diversifications within the differential rotation profiles.A statistical way for figuring out rotational profileThomas Hackman, docent of astronomy, who participated within the analysis, explains that the Solar has been the one celebrity for which finding out the rotational profile has been imaginable.“Stellar differential rotation is an overly a very powerful issue that has an impact at the magnetic exercise of stars. The process we now have evolved opens a brand new window into the interior workings of alternative stars.”The astronomers at Helsinki College’s Division of Particle Physics and Astrophysics have decided the rotational profile of 2 within reach younger stars through making use of a brand new statistical modeling to long-baseline brightness observations. They modeled the periodic diversifications within the observations through accounting for the variations within the obvious spot motion at other latitudes. The spot motion then enabled estimating the rotational profile of the celebs.The second one one of the crucial goal stars, LQ Hydrae within the constellation of Hydra, was once discovered to be rotating just like a inflexible frame — the rotation gave the impression unchanged from the equator to the poles, which signifies that the variations are very small.Observations From the Fairborn ObservatoryThe researchers base their effects at the observations of the objective stars from the Fairborn observatory. The brightnesses of the celebs were monitored with robot telescopes for round 30 years, which supplies insights into the conduct of the celebs over a protracted time frame.Tuomi appreciates the paintings of senior astronomer Gregory Henry, of Tennessee College, United States, who leads the Fairborne observational marketing campaign.“For a few years, Greg’s mission has been extraordinarily treasured in figuring out the conduct of within reach stars. Whether or not the inducement is to review the rotation and houses of younger, lively stars or to grasp the character of stars with planets, the observations from Fairborn Observatory were completely a very powerful. It’s superb that even within the generation of serious space-based observatories we will be able to download elementary knowledge at the stellar astrophysics with small 40cm ground-based telescopes.”The objective stars V889 Herculis and LQ Hydrae are each kind of 50 million-year-old stars that during many respects resemble the younger Solar. They each rotate very swiftly, with rotation classes of most effective about one and a part days. Because of this, the long-baseline brightness observations include many rotational cycles. The celebrities had been decided on as objectives as a result of they have got been noticed for many years and since they have got each been studied actively on the College of Helsinki.Reference: “Characterising the stellar differential rotation in line with largest-spot statistics from ground-based photometry” through Mikko Tuomi, J. Jyri Lehtinen, W. Gregory Henry and Thomas Hackman, 26 July 2024, Astronomy & Astrophysics.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202449861
Astronomers Shocked through Extraordinary Superstar: V889 Herculis Breaks Identified Regulations of Stellar Rotation













