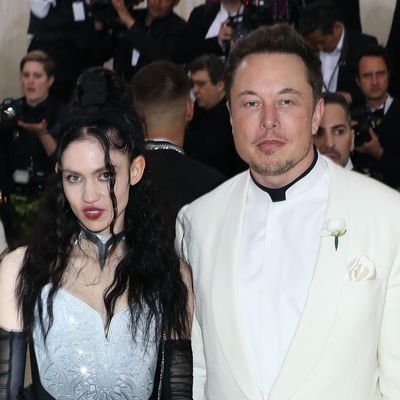
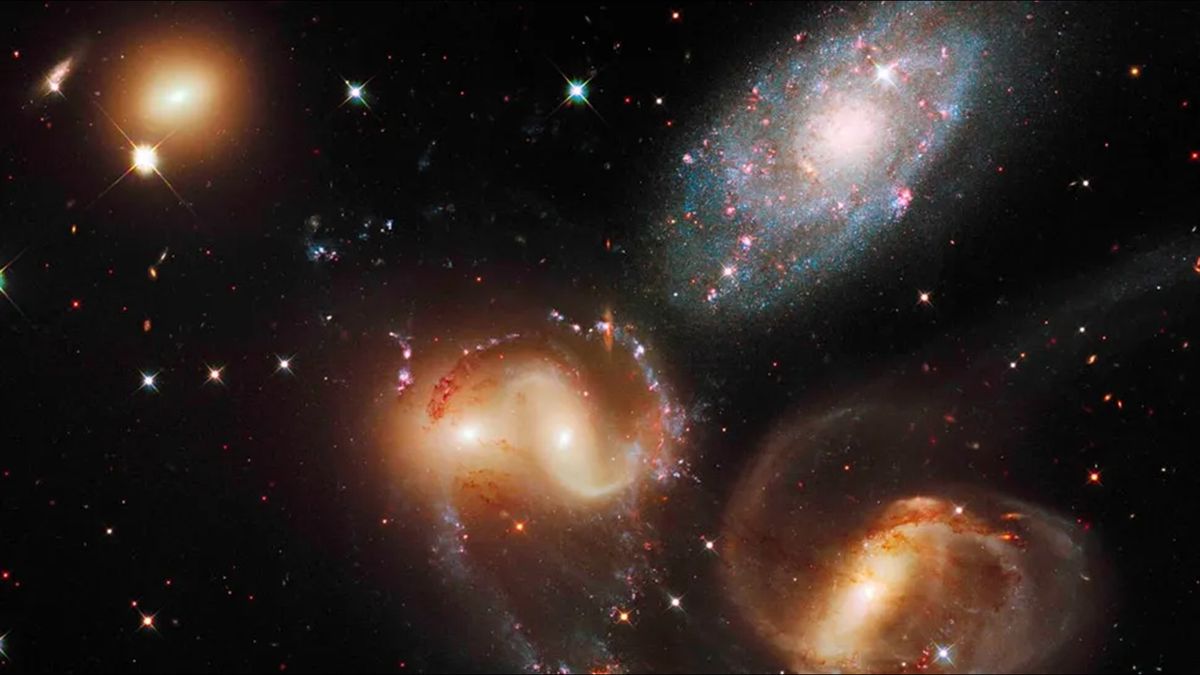
Astronomers have noticed some of the robust surprise waves ever observed, brought about by way of a galaxy slamming into 4 of its neighbors whilst touring at 2 million mph (3.2 million km/h).The cosmos-rattling tournament happened in Stephan’s Quintet, when one of the vital device’s 5 galaxies, known as NGC 7318b, smashed into the opposite 4.NGC 7318b’s access into the device created an immensely robust surprise entrance comparable to a “sonic increase from a jet fighter,” the researchers mentioned. They hope that by way of finding out it they may be able to perceive extra in regards to the violent and chaotic interactions between galaxies. They revealed their findings Nov. 22 within the magazine Per thirty days Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.”It is mainly an enormous intergalactic box of particles,” Marina Arnaudova, an astrophysicist on the College of Hertfordshire within the U.Ok., advised Reside Science. “The brand new intruder NGC7318b has smashed into the particles box, and compressed the plasma and gasoline in it. In doing so it has re-energised the plasma inflicting it to glow brightly at radio frequencies, and most likely brought about megastar formation within the procedure.”Named after French astronomer Édouard Stephan, who came upon it within the nineteenth century, Stephan’s Quintet is a gaggle of 5 galaxies which might be “locked in a cosmic dance of repeated shut encounters,” consistent with NASA.Comparable: James Webb Area Telescope discovers mysterious ‘pink monster’ galaxies so huge they mustn’t existThe quintet sits round 290 million light-years from Earth and was once the primary compact galaxy staff ever noticed. It’s been imaged by way of a lot of telescopes, together with the Hubble Area Telescope and the James Webb Area Telescope.Get the arena’s most attractive discoveries delivered instantly on your inbox.To research the quintet’s habits and cosmic historical past, the researchers at the back of the brand new learn about used the William Herschel Telescope Enhanced Space Speed Explorer (WEAVE), a spectrograph fixed to the William Herschel Telescope at the island of Los angeles Palma.By means of breaking mild from the device down into its constituent portions, the WEAVE spectrograph tracked the particles remnants, the births of latest stars and the paths of ionized gasoline left at the back of by way of the drive of the collision. All of those components had been stirred up by way of the surprise entrance, which rippled out at hypersonic speeds following NGC 7318b’s access into the device.Astronomers finding out Stephan’s Quintet may acquire precious insights into how collisions and mergers stretching again to the Large Bang formed the galaxies we see these days, and what the device might appear to be someday, the researchers mentioned.”This kind of galaxy collision in Stephan’s Quintet is an extraordinary likelihood to peer a posh set of galaxies stuck within the act of colliding,” Arnaudova mentioned. “As to how it’ll finally end up, smartly it is most likely that it’ll sooner or later merge with one of the vital staff participants, however now not for hundreds of thousands or billions of years for the reason that sizes and speeds of these items are so huge.”The observations are the primary to be made by way of WEAVE, however a long way from the remaining. The researchers say the spectrograph may also be used to check the reionization of the universe within the aftermath of the Large Bang; forged new mild on how stars shape and accrete through the years; and carry out numerous “galactic archaeology” experiments to search out how our personal Milky Method grew over cosmic time.




![Samsung launches cloud gaming for Galaxy gadgets, however it is not what you suppose [Gallery] Samsung launches cloud gaming for Galaxy gadgets, however it is not what you suppose [Gallery]](https://9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2024/11/samsung-gaming-hub-cloud-1.jpg?quality=82&strip=all&w=1600)