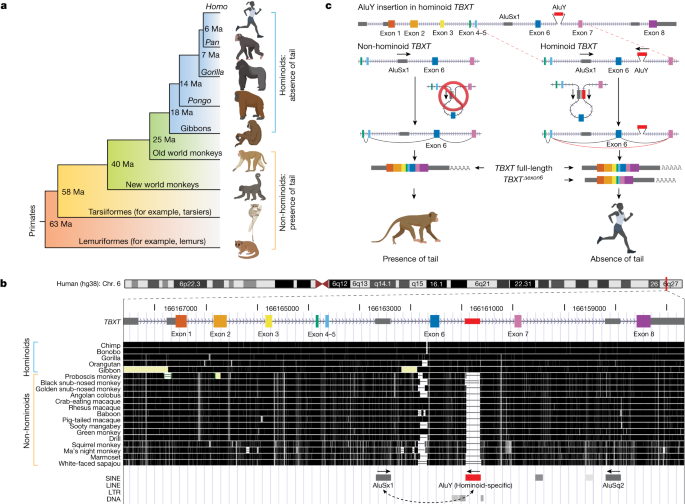
Comparative genomics analyses of tail-development-related genesHominoid evolution represents a longer level in primate evolution that concerned many phenotypic adjustments and popular genomic collection adjustments. Due to this fact, querying for hominoid-specific mutations around the genome leads to tens of tens of millions of applicants, with maximum of them disposed in non-coding areas. We used the next standards to outline {that a} candidate variant might give a contribution to the tail-loss evolution in hominoids: (1) must be hominoid-specific, because of this that the variant collection or amino acid is exclusive to hominoid species and can’t be shared through every other species that experience tails; (2) the serve as of the related genes pertains to tail advancement. Tail-development-related genes in vertebrates have been gathered from the MGI phenotype database and extra literature no longer lined through the MGI database. The preliminary analyses basically lined genes extracted from the MGI time period MP0003456 for ‘absent tail’ phenotype ( to a complete of 31 genes. Further analyses integrated genes from MP0002632 for ‘vestigial tail’ ( and MP0003456 for ‘quick tail’ ( In combination, the general checklist of genes associated with vertebrate tail advancement integrated 140 genes (as of MGI updates in February 2023) and the mutations of which might be reported to be associated with tail-reduction phenotypes (Supplementary Information 1).Gene construction annotations of the 140 genes have been downloaded from BioMart of Ensembl 109 ( The longest transcript with essentially the most exons have been decided on for each and every gene. Multiz30way alignments of genomic sequences throughout 27 primate species have been downloaded from the UCSC Genome Browser. We decided on all six hominoid species (hg38, gorGor5, panTro5, panPan2, ponAbe2 and nomLeu3) to calculate a hominoid-consensus collection, and used two non-hominoid species (pig-tailed macaque, macNem1, and marmoset, calJac3) because the outgroups. The homologous areas of the 140 genes, at the side of 10,000 bp each upstream and downstream sequences, within the 8 species have been extracted from Multiz30way alignment the use of bedtools (v.2.30.0)52. Hominoid-specific variants have been known the use of the next parameters: SNVs or substitutions shared through six hominoid species however other in any of the 2 outgroup monkey species have been known as putative hominoid-specific SNVs (Supplementary Information 2); DNA sequences found in all six hominoid species however absent in both of the 2 outgroup monkey species have been known as hominoid-specific insertions (Supplementary Information 3); and DNA sequences absent from all six hominoid species however found in either one of the 2 outgroup monkey species have been known as hominoid-specific deletions (Supplementary Information 4). Significantly, our standards for analysing hominoid-specific variants might come with a small percentage of false-positive hits which might be outgroup-specific variants.We used the Ensembl variant impact predictor (built-in in Ensembl 109)53 to deduce the possible useful affect of the detected hominoid-specific SNVs, insertions and deletions. Owing to the loss of an ancestral genome because the reference collection, variant impact predictor predictions have been carried out inversely the use of the human/hominoid genomic collection because the reference allele, and the outgroup collection served as the other allele. SNVs annotated as both ‘deleterious’ (<0.05) within the SIFT ranking or ‘harmful’ (>0.446) within the PolyPhen ranking (53 cases), and insertions (6 cases) or deletions (2 cases) that impact protein sequences have been gathered for additional handbook inspection comparability throughout species. This extra inspection used to be carried out around the Cactus Alignment of the genomes throughout 241 species within the UCSC Genome Browser Comparative Genomics module51. This inspection discovered that lots of the annotated variants that can impact host gene serve as fell into 3 classes: (1) outgroup-specific variants; (2) false-positive annotation of the variant serve as in a minor transcript; and (3) missense variants in hominoid species however sharing the similar amino acid in a minimum of one different tailed species. Those variants weren’t thought to be as applicants that can have affected tail-loss evolution in hominoids. Apart from those variants, we known 9 variants as true hominoid-specific coding area mutations, together with seven SNVs and two insertions and deletions (Supplementary Information 1). Following identity of best applicants, protein collection alignments throughout consultant vertebrate species have been downloaded from the NCBI database and analysed the use of the MUSCLE set of rules with MEGA X tool and default settings54.RNA secondary construction predictionRNA secondary construction prediction of the human TBXT exon 5–intron 5–exon 6–intron 6–exon 7 collection used to be carried out the use of RNAfold (v.2.6.0) throughout the ViennaRNA Internet Server ( The set of rules calculates the folding chance the use of a minimal unfastened power matrix with default parameters. As well as, the calculation integrated the partition serve as and base pairing chance matrix. Significantly, human TBXT transcripts have been annotated to have a 5′ untranslated area exon, making its exon numbers range from maximum of alternative species, together with mouse. To simplify, we referred to the primary coding exon of human TBXT as exon 1 and thus the other spliced exon as exon 6, in line with mouse Tbxt. RNA secondary construction prediction used the DNA collection from exon 5 to exon 7 following this order.Human ES mobile tradition and differentiationHuman ES cells (WA01, also referred to as H1, from WiCell Analysis Institute) have been authenticated through the distributor WiCell the use of quick tandem repeat profiling to authenticate the mobile strains. Human ES cells have been cultured in feeder-free stipulations on tissue-culture-grade plates covered with human ES cell-qualified Geltrex (Gibco, A1413302). Geltrex used to be 1:100 diluted in DMEM/F-12 (Gibco, 11320033) supplemented with 1× Glutamax (100X, Gibco, 35050061) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin (Gibco, 15070063). Prior to seeding human ES cells, the plate used to be handled with Geltrex running resolution in a tissue tradition incubator (37 °C and 5% CO2) for a minimum of 1 h.StemFlex medium (Gibco, A3349401) used to be used for human ES mobile repairs and culturing in a feeder-free situation in keeping with the producer’s protocol. In short, StemFlex whole medium used to be made through combining StemFlex basal medium (450 ml) with 50 ml of StemFlex complement (10×) plus 1% penicillin–streptomycin. Each and every Geltrex-coated properly on a 6-well plate used to be seeded with 200,000 cells to procure about 80% confluence in 3–4 days. Human ES cells have been cryopreserved in PSC Cryomedium (Gibco, A2644601). The tradition medium used to be supplemented with 1× RevitaCell (100×, Gibco, A2644501, which may be integrated within the PSC Cryomedium equipment) when cells had long gone thru stressed out stipulations, corresponding to freezing-and-thawing or nucleofection. RevitaCell supplemented medium used to be changed with common StemFlex whole medium on the second one day. Human ES cells grown underneath the RevitaCell situation may turn out to be stretched however would recuperate after returning to the standard StemFlex whole medium. All human ES mobile strains examined adverse all over our regimen quantitative PCR-based mycoplasma checks.The human ES mobile differentiation assay to urge a gene expression development of the primitive streak state used to be tailored from a in the past printed method36. On day −1, freshly cultured human ES mobile colonies have been dissociated into clumps (2–5 cells) the use of Versene buffer (with EDTA, Gibco, 15040066). The dissociated cells have been seeded on Geltrex-coated 6-well tissue tradition plates at 25,000 cells in line with cm2 (0.25 M in line with properly within the 6-well plates) in StemFlex whole medium. Differentiation to the primitive streak state used to be initiated on tomorrow (day 0) through switching StemFlex whole medium to basal differentiation medium. Basal differentiation medium (50 ml) used to be made the use of 48.5 ml DMEM/F-12, 1% Glutamax (500 µl), 1% ITS-G (500 µl, Gibco, 41400045) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin (500 µl), and supplemented with 3 µM GSK3 inhibitor CHIR99021 (10 µl of 15 mM inventory resolution in DMSO; Tocris, 4423). The cells have been gathered at differentiation day 1 to three for downstream experiments, which proven the expression fluctuations of mesoderm genes (TBXT and MIXL1) in a 3-day differentiation period36 (Prolonged Information Fig. 3).Mouse ES mobile tradition and differentiationThe mouse ES mobile line (MK6) derived from the C57BL/6J mouse pressure used to be bought from the NYU Langone Well being Rodent Genetic Engineering Laboratory. The wild-type MK6 mouse ES mobile line used to be authenticated through its competence for contributing to embryos when cultured on feeder-cell-dependent stipulations adopted through blastomere injection. MK6 mouse ES cells used on this learn about have been cultured in each feeder-dependent and feeder-free tradition stipulations relying at the functions of the experiment. All mouse ES mobile strains examined adverse all over our regimen quantitative PCR-based mycoplasma checks. For feeder-dependent mouse ES mobile tradition stipulations, mouse ES cells have been plated on a pre-seeded monolayer of mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells (CellBiolabs, CBA-310). MEF-coated plates have been ready through seeding 50,000 cells in line with cm2 in tissue tradition plates handled with 0.1% gelatin resolution (EMD Millipore, ES-006-B). MEF culturing medium used to be constituted of DMEM (Gibco, 11965118) with 10% FBS (GeminiBio, 100–500), 0.1 mM MEM non-essential amino acids (Gibco, 11140050), 1× Glutamax (Gibco, 35050061) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin (Gibco, 15070063). Mouse ES mobile medium used to be constituted of Knockout DMEM (Gibco, 10829018) containing 15% (v/v) FBS (Hyclone, SH30070.03), 0.1 mM β-mercaptoethanol (Gibco, 31350010), 1× MEM non-essential amino acids (Gibco, 11140050), 1× Glutamax (Gibco, 35050061), 1× nucleosides (Millipore, ES-008-D) and 1,000 devices ml–1 LIF (EMD Millipore, ESG1107).For feeder-free mouse ES mobile tradition stipulations, cells have been grown on tissue-culture-grade plates that have been pre-coated with mouse ES cell-qualified 0.1% gelatin (EMD Millipore, ES-006-B) at room temperature for a minimum of 30 min. Prior to seeding mouse ES cells, feeder-free mouse ES mobile culturing medium used to be added to a gelatin-treated plate and warmed in a 37 °C and 5% CO2 incubator for a minimum of 30 min. Feeder-free mouse ES mobile culturing medium, also referred to as ‘80/20’ medium, contains 80% 2i medium and 20% of the above-mentioned mouse ES mobile medium through quantity. The 2i medium used to be constituted of a 1:1 mixture of Complicated DMEM/F-12 (Gibco, 12634010) and Neurobasal-A (Gibco, 10888022), adopted through including 1× N2 complement (Gibco, 17502048), 1× B-27 complement (Gibco, 17504044), 1× Glutamax (Gibco, 35050061), 0.1 mM β-mercaptoethanol (Gibco, 31350010), 1,000 devices ml–1 LIF (Millipore, ESG1107), 1 µM MEK1/2 inhibitor (Stemgent, PD0325901) and three µM GSK3 inhibitor CHIR99021 (Tocris, 4423).The mouse ES mobile differentiation protocol for inducing Tbxt gene expression used to be tailored from a in the past described way in a feeder cell-free condition37. Cells have been first plated in 80/20 medium for twenty-four h on a gelatin-coated 6-well plate, adopted through switching to N2/B27 medium with out LIF or 2i for every other 2 days of tradition. The N2/B27 medium (50 ml) used to be made with 18 ml Complicated DMEM/F-12, 18 ml Neurobasal-A, 9 ml Knockout DMEM, 2.5 ml Knockout Serum Alternative (Gibco, 10828028), 0.5 ml N2 complement, 1 ml B27 complement, 0.5 ml Glutamax (100×), 0.5 ml nucleosides (100×) and zero.1 mM β-mercaptoethanol. Then the N2/B27 medium used to be supplemented with 3 µM GSK3 inhibitor CHIR99021 to urge differentiation (day 0). The cells have been gathered at differentiation day–3 for downstream experiments, which confirmed constant result of Tbxt gene expression fluctuations in a 3-day differentiation length.CRISPR targetingAll information RNAs of the CRISPR experiments have been designed the use of the CRISPOR set of rules built-in within the UCSC Genome Browser55. Information RNAs have been cloned into the pX459V2.0-HypaCas9 plasmid (AddGene, plasmid 62988) or its customized by-product through changing the puromycin-resistance gene with the blasticidin-resistance gene. Information RNAs on this learn about have been designed in pairs to delete the intervening sequences. Insertion websites for the AluSx1 and AluY pair in mouse Tbxt (TbxtinsASAY) have been decided on through the information RNA high quality and the relative distance in comparison to the human TBXT gene construction. The insertion website online for the RCS component (TbxtinsRCS) used to be the similar as for insertion of the AluY component. The CRISPR-targeting websites and information RNA sequences are indexed in Supplementary Desk 2.All oligonucleotides (plus Golden-Gate meeting overhangs) have been synthesized through Built-in DNA Applied sciences (IDT) and ligated into an empty pX459V2.0 vector following the usual Golden Gate Meeting protocol the use of BbsI restriction enzyme (NEB, R3539). The built plasmids have been purified from 3 ml Escherichia coli cultures the use of a ZR Plasmid MiniPrep Purification equipment (Zymo Analysis, D4015) for collection verification. Plasmids for handing over into ES cells have been purified from 250 ml E. coli cultures the use of a PureLink HiPure Plasmid Midiprep equipment (Invitrogen, K210005). To facilitate DNA supply to ES cells thru nucleofection, the purified plasmids have been resolved in Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 7.5) to a focus of a minimum of 1 µg µl–1 in a sterile hood.DNA deliveryDNA supply into human or mouse ES cells for CRISPR–Cas9 concentrating on used to be carried out the use of a Nucleofector 2b tool (Lonza, BioAAB-1001). A Human Stem Mobile Nucleofector equipment 1 (VPH-5012) and a mouse ES mobile Nucleofector equipment (Lonza, VVPH-1001) have been used for handing over DNA into human and mouse ES cells, respectively. ES cells have been double-fed the day ahead of the nucleofection experiment to deal with a awesome situation.Prior to acting nucleofection on human ES cells, 6-cm tissue tradition plates have been handled with 0.5 µg cm–2 rLaminin-521 in a 37 °C and 5% CO2 incubator for a minimum of 2 h. rLaminin-521-treated plates give you the perfect viability when seeding human ES cells as unmarried cells. Cultured human ES cells have been washed with DPBS and dissociated into unmarried cells the use of TrypLE Make a selection Enzyme (no phenol pink; Gibco, 12563011). A million human ES mobile unmarried cells have been nucleofected the use of program A-023 in keeping with the producer’s directions for the Nucleofector 2b tool. Transfected cells have been transferred onto the rLaminin-521-treated 6-cm plates with pre-warmed StemFlex whole medium supplemented with 1× RevitaCell however no longer penicillin–streptomycin. Antibiotic variety used to be carried out 24 h after nucleofection with puromycin (ultimate focus of 0.8 μg ml–1; Gibco, A1113802).Mouse ES cells have been dissociated into unmarried cells the use of StemPro Accutase (Gibco, A1110501), and 5 million cells have been transfected the use of program A-023 in keeping with the producer’s directions. Exon 6 deletion in mouse ES cells used to be carried out the use of cells cultured within the feeder-free situation. Nucleofected cells have been plated on 0.1% gelatin-treated 10-cm plates, adopted through antibiotic variety 24 h after nucleofection with blasticidin (ultimate focus of seven.5 µg ml–1; Gibco, A1113903). The insertion of the AluSx1–AluY pair and insRCS engineering have been carried out the use of mouse ES cells cultured on a feeder-dependent situation. Mouse ES cells have been plated on a monolayer of MEF cells seeded on 0.1% gelatin-treated 10-cm plates, adopted through antibiotic variety 24 h after nucleofection.Along with the pX459V2.0-HypaCas9-gRNA plasmids for nucleofection, single-strand DNA oligonucleotides have been co-delivered for microhomology-induced deletion of the focused sequences56. Those ssDNA sequences have been synthesized through IDT thru its Ultramer DNA Oligo provider, together with 3 phosphorothioate bond adjustments on each and every finish. Detailed collection knowledge of those lengthy ssDNA oligonucleotides are indexed in Supplementary Desk 3.For TbxtinsASAY and TbxtinsRCS engineering, homology-based repairing template plasmids, together with a diffusion marker gene puro-ΔTK, (puromycin-resistance gene for high-quality variety and ΔTK, a truncated model of herpes simplex virus form 1 thymidine kinase, for adverse variety, as introduced in Prolonged Information Fig. 7), used to be transfected at the side of the pX459V2.0-HypaCas9-gRNA plasmids. Following nucleofection and antibiotic variety (0.8 μg ml–1 puromycin for three days ranging from the second one day of nucleofection), unmarried clones have been picked, adopted through PCR genotyping of CRISPR–Cas9-targeted loci (exon 6 deletion, placing AluY, placing AluSx1 or placing RCS). The genotyping PCR primers are indexed in Supplementary Desk 4.PCR genotyping-confirmed clones have been additional validated the use of Seize-seq (see beneath) to substantiate the genotype and to exclude the potential of any random integration of plasmid DNA. Therefore, Cre recombinase used to be transiently presented to take away the choice marker puro-ΔTK. Cells have been handled with 250 nM ganciclovir for counter-selecting ΔTK-negative cells as the choice marker gene-depleted cells. Following isolation of unmarried mouse ES mobile clones of TbxtinsASAY and TbxtinsRCS mouse ES cells with out the choice marker gene, those clones have been used for downstream experiments, together with in vitro differentiation assays and blastocyst injection for producing mouse fashions.Seize-seq genotypingCapture-seq, or focused sequencing of the loci of pastime, used to be carried out as in the past described39. Conceptually, Seize-seq makes use of customized biotinylated probes to pull-down the sequences at genomic loci of pastime from the usual whole-genome sequencing libraries, thereby enabling sequencing of the precise genomic loci in a far upper intensity whilst decreasing the fee.Genomic DNA used to be purified from mouse ES cells or from ear punches of mice of pastime the use of a Zymo Fast-DNA Miniprep Plus equipment (D4068) in keeping with the producer’s protocol. DNA sequencing libraries suitable for Illumina sequencers have been ready following the usual protocol. In short, 1 µg of gDNA used to be sheared to 500–900 base pairs in a 96-well microplate the use of a Covaris LE220 (450 W, 10% accountability issue, 200 cycles in line with burst and 90-s remedy time), adopted through purification with a DNA Blank and Pay attention-5 equipment (Zymo Analysis, D4013). Sheared and purified DNA have been then handled with finish restore enzyme combine (T4 DNA polymerase, Klenow DNA polymerase and T4 polynucleotide kinase, NEB, M0203, M0210 and M0201, respectively), and A-tailed the use of Klenow 3′−5′ exo-enzyme (NEB, M0212). Illumina sequencing library adapters have been therefore ligated to DNA ends adopted through PCR amplification with KAPA 2X Hello-Fi Hotstart Readymix (Roche, KR0370).Customized biotinylated probes have been ready as bait thru nick translation the use of BAC DNA and/or plasmids because the template. The probes have been ready to comprehensively duvet all of the locus. We used BAC strains RP24-88H3 and RP23-159G7, bought from BACPAC Genomics, to generate bait probes protecting the mouse Tbxt locus and about 200 kb flanking sequences in each upstream and downstream areas. The pooled whole-genome sequencing libraries have been hybridized with the biotinylated baits in resolution and purified the use of streptavidin-coated magnetic beads. Following pull-down, DNA sequencing libraries have been quantified the use of a Qubit 3.0 Fluorometer (Invitrogen, Q33216) with a dsDNA HS Assay equipment (Invitrogen, Q32851). The sequencing libraries have been therefore sequenced on an Illumina NextSeq 500 sequencer in paired-end mode.Sequencing effects have been demultiplexed the use of Illumina bcl2fastq (v.2.20), requiring a super fit to indexing BC sequences. Low-quality reads or bases and Illumina adapter sequences have been trimmed the use of Trimmomatic (v.0.39). Reads have been then mapped to the mouse genome (mm10) the use of bwa (v.0.7.17). The protection and mutations in and across the Tbxt locus have been checked thru visualization in a reflect model of the UCSC Genome Browser.Mouse experiments and producing Tbxt
Δexon6/+ miceAll mouse experiments have been carried out following NYULH’s animal protocol tips and carried out on the NYU Langone Well being Rodent Genetic Engineering Laboratory. Mice have been housed within the NYU Langone Well being BSL1 barrier facility in a 12-h mild to 12-h darkish cycle, with ambient temperature and humidity stipulations. All experimental procedures have been licensed through the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at NYU Langone Well being. Wild-type C57BL/6J (pressure 000664) mice have been bought from The Jackson Laboratory.The TbxtΔexon6/+ heterozygous mouse type used to be generated thru zygotic microinjection of CRISPR reagents into wild-type C57BL/6J zygotes (Jackson Laboratory pressure 000664), adapting a in the past printed protocol57. In short, Cas9 mRNA (MilliporeSigma, CAS9MRNA), artificial information RNAs and single-stranded DNA oligonucleotide have been co-injected into 1-cell level zygotes following the described procedures57. Artificial information RNAs have been ordered from Synthego as their customized CRISPRevolution sgRNA EZ equipment, with the similar concentrating on websites as used within the CRISPR deletion experiment of mouse ES cells (AUUUCGGUUCUGCAGACCGG and CAAGAUGCUGGUUGAACCAG). The co-injected single-stranded DNA oligonucleotide is equal to described above. Injected embryos have been then in vitro cultured to the blastomeric level, adopted through embryo shifting to the pseudopregnant foster moms. Following zygotic microinjection and shifting, founder puppies have been screened according to their atypical tail phenotypes. DNA samples have been gathered thru ear punches at about day 21 for PCR genotyping and Seize-seq validation to exclude off-targeting on the Tbxt locus.After confirming the genotype, TbxtΔexon6/+ founder mice have been backcrossed with wild-type C57B/6J mice for producing heterozygous F1 mice. Owing to the assorted tail phenotypes, intercrossing between F1 heterozygotes have been carried out in two classes: form 1 intercrossing integrated a minimum of one mother or father having no tail or a brief tail, while form 2 intercrossing have been mated between two long-tailed F1 heterozygotes (Desk 1). As summarized in Desk 1, each forms of intercrossing produced heterogeneous tail phenotypes in F2 TbxtΔexon6/+ mice, thereby confirming the unfinished penetrance of tail phenotypes and the absence of homozygotes (TbxtΔexon6/Δexon6). Grownup mice (>12 weeks) have been anaesthetized for X-ray imaging of vertebra the use of a Bruker In-Vivo Xtreme IVIS imaging machine. To verify the embryonic phenotypes in homozygotes, embryos have been dissected at E11.5 gestation level from the timed pregnant mice the use of a typical protocol.Producing Tbxt
insASAY and Tbxt
insRCS2 miceThe engineered TbxtinsASAY and TbxtinsRCS mouse ES cells have been injected into both C57BL/6J-albino (Charles River Laboratories, pressure 493) blastocysts for chimeric F0 founder mice or injected into B6D2F1/J (a F1 hybrid between C57BL/6J feminine and DBA/2J male, Jackson Laboratory pressure 100006) tetraploid blastocysts for homozygote F0 founder mice manufacturing. The tetraploid complementation technique aimed to generate homozygous mice with the proposed genotype within the F0 generation58. Via a couple of trials of injection the use of each mouse ES mobile strains, we accomplished just one TbxtinsASAY/insASAY F0 founder mouse (male) however none for the TbxtinsRCS mouse. Alternatively, all over genotype screening for TbxtΔexon6/+ founder mice, we serendipitously known a male gray mouse that integrated a heterozygous insertion in intron 5. Genotype research published that the insertion used to be a 220 bp DNA collection from intron 6 of Tbxt (chromosome 17: 8439335–8439554, mm10), inserted in a opposite complementary situation into intron 5 at a designed CRISPR concentrating on website online (chromosome 17: 8438386, mm10). The inserted collection insRCS2 in intron 5 due to this fact bureaucracy a 220 bp inverted complementary collection pair with its unique collection in intron 6 (chromosome 17: 8439335–8439554, mm10), corresponding to the designed TbxtinsRCS and TbxtinsASAY gene constructions. This genotype used to be due to this fact referred to as TbxtinsRCS2. Seize-seq genotyping of this TbxtinsRCS2/+ mouse proven that the TbxtinsRCS2 allele is within the C57BL/6 background, while the wild-type Tbxt locus of the TbxtinsRCS2/+ founder mouse is from the DBA/2J background. This TbxtinsRCS2/+ mouse used to be due to this fact backcrossed to C57BL/6 wild-type mice and additional intercrossed between F1 heterozygotes to supply homozygotes (TbxtinsRCS2/insRCS2) within the F2 era. Seize-seq research of TbxtinsRCS2/insRCS2 mice proven their C57BL/6 background on the Tbxt locus (Prolonged Information Fig. 8). We additionally when put next the tail phenotypes in age-matched C57BL/6 and DBA/2J mice and located no distinction (information no longer proven), which steered that any genetic background distinction between the 2 traces does no longer impact tail duration. The TbxtinsRCS2 mice (each heterozygotes and homozygotes) have been due to this fact used for the research of tail phenotypes.The TbxtinsASAY and TbxtinsRCS2 founder mice, each male, have been one at a time backcrossed to wild-type C57B/6J mice for producing heterozygous F1 puppies, adopted through intercrossing between F1 heterozygotes to generate homozygotes in F2 era. With all genotypes to be had, mouse tail lengths have been measured per month throughout genotypes and intercourse teams. Moreover, two forms of breading pairs, TbxtinsRCS2/+ × TbxtΔexon6/+ and TbxtinsRCS2/insRCS2 × TbxtΔexon6/+, have been carried out throughout other founder strains of TbxtΔexon6/+ mice to analyse tail phenotypes of their offspring. Those effects are summarized and introduced in Desk 2.To analyse the isoform expression patterns of mouse Tbxt within the embryonic tailbud area, wild-type, heterozygote and homozygote embryos from intercrossing experiments (TbxtinsRCS2/+ × TbxtinsRCS2/+, TbxtinsASAY/+ × TbxtinsASAY/+) have been dissected on the E10.5 gestation level. The tailbud for each and every embryo used to be gathered for setting apart overall RNA, and at the side of embryonic tissue for gDNA for use for genotyping. Those effects are introduced in Fig. 4e.Splicing isoform detectionTotal RNA used to be gathered from undifferentiated and differentiated cells of each human and mouse ES cells, and from embryonic tailbud samples, the use of a typical column-based purification equipment (Qiagen RNeasy Package, 74004). DNase remedy used to be carried out all over RNA extraction to take away any doable DNA contamination. Following extraction, RNA high quality used to be assessed thru electrophoresis according to ribosomal RNA integrity. Opposite transcription used to be carried out the use of 1 µg of top of the range overall RNA for each and every pattern and a Prime-Capability RNA-to-cDNA equipment (Carried out Biosystems, 4387406). DNA oligonucleotides used for RT–PCR and/or quantitative RT–PCR are indexed in Supplementary Desk 1.Transcriptomics analyses in differentiated mouse ES cellsTotal RNA samples remoted from day-1 in vitro-differentiated mouse ES mobile strains throughout wild-type, TbxtinsASAY/insASAY, TbxtΔexon6/+ and TbxtΔexon6/Δexon6 genotypes have been used for bulk RNA sequencing research. RNA samples have been ready the use of a typical column-based purification equipment (Qiagen RNeasy equipment, 74004). Two organic replicates have been ready for each and every mouse ES mobile genotype, with the 2 TbxtΔexon6/Δexon6 mouse ES mobile samples coming from other clones. RNA sequencing libraries have been ready the use of a NEBNext Extremely II Directional RNA Library Prep equipment (NEB, E7765L) thru its polyA mRNA sequencing workflow through the use of the NEBNext Poly(A) mRNA Magnetic Isolation Module (NEB, E7490L).Uncooked sequencing reads have been mapped to the mouse genome (mm10) with STAR (v.2.7.2a) aligner59. The ensuing strand-specific learn counts of all samples have been built-in right into a matrix for downstream research. Differentially expressed genes have been detected the use of DESeq2 (v.1.40.2)60, the use of its default two-sided Wald verify with the cut-off of log2(fold expression exchange) > 0.5 and a couple of test-adjusted P price < 0.05. The highest 500 variable genes from DESeq2 throughout all samples have been used to accomplish essential part research. The Tbxt goal genes have been bought from a prior publication41, outlined through important Tbxt ChIP–seq top alerts detected in in vitro-differentiated mouse ES cells. The set of Tbxt goal genes used to be intersected with the numerous differentially expressed genes known in each and every mutant pattern when put next with the wild-type controls, and those have been aggregated to generate the entire set of differentially expressed Tbxt goal genes around the analysed mouse ES mobile strains. Those differentially expressed Tbxt goal genes have been visualized the use of a heatmap, with the log10-transformed normalized transcript matrix adopted through z ranking standardization throughout samples.Reporting summaryFurther knowledge on analysis design is to be had within the Nature Portfolio Reporting Abstract related to this text.
At the genetic foundation of tail-loss evolution in people and apes – Nature