Mysterious swirling patterns noticed at the moon’s floor could also be related to underground magma process, a brand new find out about suggests. The “lunar swirls” noticed at the moon show off a spiral development created by way of magnetized rocks that deflect or redirect sun wind debris that repeatedly bombard the moon. Moon rocks that fall throughout the lunar swirls stay mild coloured, whilst neighboring rocks that do not — and which have been subsequently impacted by way of charged debris from the solar — appear to go through a chemical response that reasons them to look darker, in keeping with a observation from Washington College in St. Louis. Then again, given the moon does not have a vintage magnetic box of its personal, researchers needed to search for some other supply that can have magnetized the lunar swirls, which, in some spaces, can prolong for masses of miles, in keeping with photographs from NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). “Affects may just motive a lot of these magnetic anomalies. However there are some swirls the place we are simply now not positive how an affect may just create that form and that measurement of factor,” Michael J. Krawczynski, co-author of the find out about and an affiliate professor of earth, environmental and planetary sciences at Washington College in St. Louis, mentioned within the observation. “Every other principle is that you’ve got lavas underground, cooling slowly in a magnetic box and developing the magnetic anomaly.” Similar: How the Moon Developed: A Picture Timeline “Affects may just motive a lot of these magnetic anomalies. However there are some swirls the place we are simply now not positive how an affect may just create that form and that measurement of factor,” Michael J. Krawczynski, co-author of the find out about and an affiliate professor of earth, environmental and planetary sciences at Washington College in St. Louis, mentioned within the observation. “Every other principle is that you’ve got lavas underground, cooling slowly in a magnetic box and developing the magnetic anomaly.” 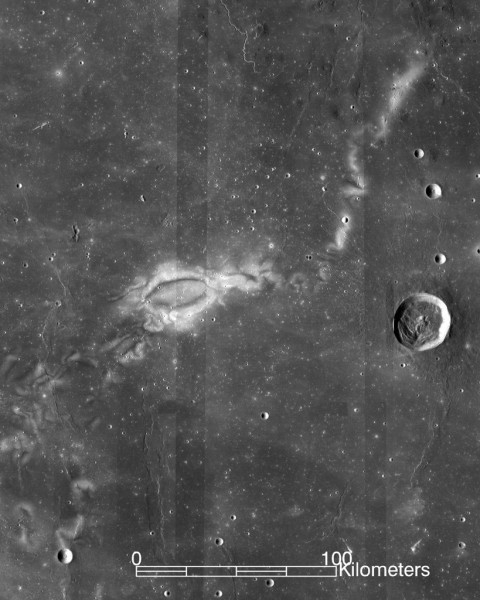 A mosaic of Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Digicam photographs displays a gentle lunar swirl. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Goddard House Flight Heart/Arizona State College.)The usage of a mineral referred to as ilmenite, which is considerable at the moon, the researchers aimed to duplicate the magnetizing impact. They studied the response between ilmenite and other mixtures of atmospheric chemistry and magmatic cooling charges to create debris of iron steel, which can also be magnetized.Breaking house information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!”Our analog experiments confirmed that at lunar stipulations, lets create the magnetizable subject matter that we wanted. So, it is believable that those swirls are led to by way of subsurface magma,” Krawczynski mentioned within the observation, noting that the underground magma must have prime titanium for the consequences to carry true. “Now we have noticed hints of this response developing iron steel in lunar meteorites and in lunar samples from Apollo. However all of the ones samples are floor lava flows, and our find out about displays cooling underground will have to considerably toughen those metal-forming reactions.”Figuring out the foundation of lunar swirls provides new clues at the processes that experience formed the lunar floor and the historical past of the moon’s magnetic box. NASA plans to ship a rover to a lunar swirl referred to as Reiner Gamma in 2025 as a part of the Lunar Vertex venture, which can permit researchers to research those floor options up shut. “If lets simply drill down, lets see if this response used to be going down,” Krawczynski mentioned within the observation. “That may be nice, but it surely’s now not imaginable but. At this time, we’re caught with the skin.”Their findings have been revealed Might 20 within the Magazine of Geophysical Analysis: Planets.
A mosaic of Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Digicam photographs displays a gentle lunar swirl. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Goddard House Flight Heart/Arizona State College.)The usage of a mineral referred to as ilmenite, which is considerable at the moon, the researchers aimed to duplicate the magnetizing impact. They studied the response between ilmenite and other mixtures of atmospheric chemistry and magmatic cooling charges to create debris of iron steel, which can also be magnetized.Breaking house information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!”Our analog experiments confirmed that at lunar stipulations, lets create the magnetizable subject matter that we wanted. So, it is believable that those swirls are led to by way of subsurface magma,” Krawczynski mentioned within the observation, noting that the underground magma must have prime titanium for the consequences to carry true. “Now we have noticed hints of this response developing iron steel in lunar meteorites and in lunar samples from Apollo. However all of the ones samples are floor lava flows, and our find out about displays cooling underground will have to considerably toughen those metal-forming reactions.”Figuring out the foundation of lunar swirls provides new clues at the processes that experience formed the lunar floor and the historical past of the moon’s magnetic box. NASA plans to ship a rover to a lunar swirl referred to as Reiner Gamma in 2025 as a part of the Lunar Vertex venture, which can permit researchers to research those floor options up shut. “If lets simply drill down, lets see if this response used to be going down,” Krawczynski mentioned within the observation. “That may be nice, but it surely’s now not imaginable but. At this time, we’re caught with the skin.”Their findings have been revealed Might 20 within the Magazine of Geophysical Analysis: Planets.
Below the moon’s floor, magnetized lava might create ‘lunar swirls’