A small, apparently unremarkable fern that handiest grows on a faraway Pacific island used to be on Friday topped the Guinness Global Document holder for having the biggest genome of any organism on Earth.
The New Caledonian fern, Tmesipteris oblanceolata, has greater than 50 occasions extra DNA packed into the nucleus of its cells than people do.
If the DNA from probably the most fern’s cells – which can be only a fraction of a millimetre huge – had been unravelled, it might stretch out to 106 metres (350 ft), scientists stated in a brand new learn about.
Stood upright, the DNA could be taller that than the tower that holds London’s well-known Giant Ben bell.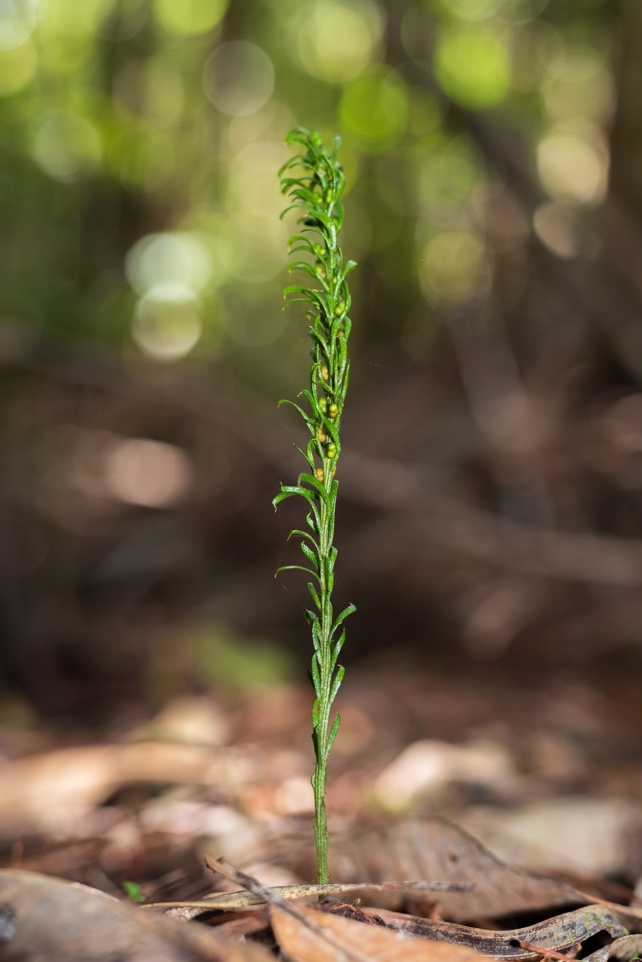 T. oblanceolata. (Pol Fernandez)The fern’s genome weighed in at a whopping 160 gigabase pairs (Gbp), the dimension for DNA period.
T. oblanceolata. (Pol Fernandez)The fern’s genome weighed in at a whopping 160 gigabase pairs (Gbp), the dimension for DNA period.
This is seven p.c greater than the former document holder, the Eastern flowering plant Paris japonica.
The human genome is a moderately puny 3.1 Gbp.
If our DNA had been unravelled, it might be round two metres lengthy.
Learn about co-author Ilia Leitch, a researcher at the United Kingdom’s Royal Botanic Gardens Kew, advised AFP that the workforce used to be “actually shocked to seek out one thing even larger than Paris japonica”.
“We idea we would already reached the organic restrict. We are actually pushing on the extremes of biology,” she stated.
The fern, which grows 5 to ten centimetres tall, is handiest present in New Caledonia, a French Pacific territory which has not too long ago observed unrest.
Two participants of the analysis workforce travelled to the primary island, Grand Terre, in 2023 and labored with native scientists for the learn about, which used to be printed within the magazine iScience.
Guinness Global Information awarded the fern its coveted “biggest genome identify”.
The win via “this innocuous-looking” fern demonstrates that “document holders are not at all times the showiest at the out of doors”, Guinness Global Information managing editor Adam Millward stated.
What is a genome once more?People are estimated to have greater than 30 trillion cells in our our bodies.
Inside of each and every of the ones cells is a nucleus which accommodates DNA, which is sort of a “ebook of directions that tells an organism like ourselves tips on how to are living and live to tell the tale”, Leitch defined.
All of an organism’s DNA is known as its genome.
Up to now, scientists have estimated the genome measurement of round 20,000 organisms, only a fraction of lifestyles on Earth.
Amongst animals, the marbled lungfish has the biggest, with 130 Gbp.
Whilst vegetation have the largest genomes, they may be able to even have extremely small ones. The carnivorous Genlisea aurea’s genome is simply 0.06 Gbp.
However we people needn’t really feel insufficient when evaluating ourselves to the mighty T. oblanceolata.
The entire proof means that having an enormous genome is a drawback, Leitch stated.
The extra DNA you’ve, the bigger your cells want to be to squeeze all of it in.
For vegetation, larger cells imply such things as the pores of leaves should be greater, which may make them develop extra slowly.
It is usually trickier to make new copies of all that DNA, restricting their reproductive talents.
This implies probably the most huge genomes are observed in slow-growing, perennial vegetation which can’t simply adapt to adversity or deal with pageant.
Genome measurement can subsequently impact how vegetation reply to local weather alternate, converting land use and different environmental demanding situations led to via people, Leitch stated.
What is all that DNA for?There may just nonetheless be larger genomes someplace in the market however Leitch thinks this fern will have to be close to the restrict.
“I will not know how an organism with all this DNA actually purposes,” she stated.
Scientists have no idea what lots of the DNA does in such large genomes, she admitted.
Some say maximum of it’s “junk DNA”.
“However that is most probably our personal lack of know-how. Perhaps it does have a serve as, and we have now but to seek out it,” Leitch stated.
Jonathan Wendel, a botanist at Iowa State College no longer concerned within the analysis, agreed it used to be “astonishing” how a lot DNA the fern is packing.
However this handiest “represents step one”, he advised AFP.
“An ideal thriller is the which means of all of this modification – how do genomes develop and shrink, and what are the evolutionary reasons and penalties of those phenomena?”© Agence France-Presse
Biggest Genome on Earth Published, And It's a Giant Marvel