 Artist’s impact of a microlensing tournament brought about via a black hollow seen from Earth towards the Huge Magellanic Cloud. The sunshine of a background superstar situated within the LMC is bent via a putative primordial black hollow (lens) within the Galactic halo and magnified when seen from the Earth. Microlensing reasons very feature variation of brightness of the background superstar, enabling the decision of the lens’s mass and distance. Credit score: J. Skowron / OGLE. Background symbol of the Huge Magellanic Cloud: generated with bsrender written via Kevin Loch, the usage of the ESA/Gaia database. Credit score: J. Skowron / OGLE. Background symbol of the Huge Magellanic Cloud: generated with bsrender written via Kevin Loch, the usage of the ESA/Gaia databaseA inhabitants of huge black holes whose starting place is likely one of the largest mysteries in trendy astronomy has been detected via the LIGO and Virgo gravitational wave detectors.In step with one speculation, those items could have shaped within the very early Universe and would possibly compose darkish subject, a mysterious substance filling the Universe. A staff of scientists has introduced the result of just about 20-year-long observations indicating that such large black holes would possibly contain at maximum a couple of % of darkish subject. Subsequently, every other rationalization is wanted for gravitational wave assets.The result of the learn about have been revealed in two articles, in Nature and the Astrophysical Magazine Complement Collection. The analysis was once performed via scientists from the OGLE (Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment) survey from the Astronomical Observatory of the College of Warsaw.
Artist’s impact of a microlensing tournament brought about via a black hollow seen from Earth towards the Huge Magellanic Cloud. The sunshine of a background superstar situated within the LMC is bent via a putative primordial black hollow (lens) within the Galactic halo and magnified when seen from the Earth. Microlensing reasons very feature variation of brightness of the background superstar, enabling the decision of the lens’s mass and distance. Credit score: J. Skowron / OGLE. Background symbol of the Huge Magellanic Cloud: generated with bsrender written via Kevin Loch, the usage of the ESA/Gaia database. Credit score: J. Skowron / OGLE. Background symbol of the Huge Magellanic Cloud: generated with bsrender written via Kevin Loch, the usage of the ESA/Gaia databaseA inhabitants of huge black holes whose starting place is likely one of the largest mysteries in trendy astronomy has been detected via the LIGO and Virgo gravitational wave detectors.In step with one speculation, those items could have shaped within the very early Universe and would possibly compose darkish subject, a mysterious substance filling the Universe. A staff of scientists has introduced the result of just about 20-year-long observations indicating that such large black holes would possibly contain at maximum a couple of % of darkish subject. Subsequently, every other rationalization is wanted for gravitational wave assets.The result of the learn about have been revealed in two articles, in Nature and the Astrophysical Magazine Complement Collection. The analysis was once performed via scientists from the OGLE (Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment) survey from the Astronomical Observatory of the College of Warsaw.
Figuring out the Universe’s Darkish Topic CompositionVarious astronomical observations point out that bizarre subject, which we will see or contact, incorporates best 5% of the overall mass and effort finances of the Universe. Within the Milky Method, for each pound of bizarre subject in stars, there are 15 kilos of “darkish subject,” which doesn’t emit any mild and interacts best thru its gravitational pull.“The character of darkish subject stays a thriller. Maximum scientists assume it’s composed of unknown basic debris,” says Dr. Przemek Mróz from the Astronomical Observatory, College of Warsaw, the lead writer of each articles. “Sadly, in spite of many years of efforts, no experiment (together with experiments performed with the Huge Hadron Collider) has discovered new debris that may be answerable for darkish subject.”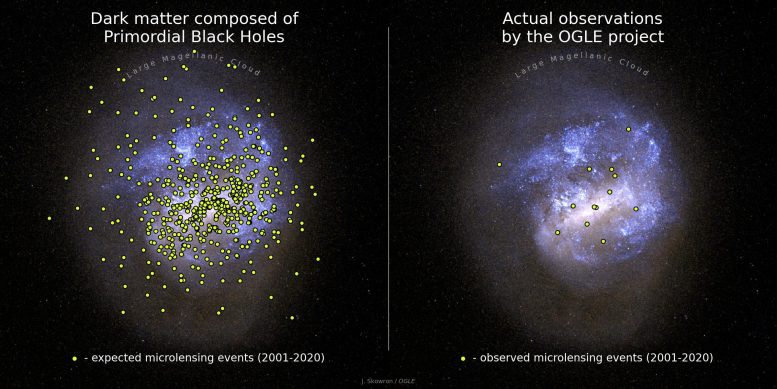 Anticipated vs. seen microlensing occasions via large items towards the Huge Magellanic Cloud as observed throughout the Milky Method halo. If the darkish subject within the Universe consisted of putative primordial black holes, over 500 microlensing occasions could be detected all the way through the OGLE survey within the years 2001-2020. In fact, the OGLE challenge registered best 13 detections of microlensing occasions, possibly brought about via common stars. Credit score: J. Skowron / OGLE. Background symbol of the Huge Magellanic Cloud: generated with bsrender written via Kevin Loch, the usage of the ESA/Gaia database. Credit score: J. Skowron / OGLE. Background symbol of the Huge Magellanic Cloud: generated with bsrender written via Kevin Loch, the usage of the ESA/Gaia databaseThe Thriller and Doable of Primordial Black HolesSince the primary detection of gravitational waves from a merging pair of black holes in 2015, the LIGO and Virgo experiments have detected greater than 90 such occasions. Astronomers spotted that black holes detected via LIGO and Virgo are most often considerably extra large (20–100 sun plenty) than the ones recognized prior to now within the Milky Method (5–20 sun plenty).“Explaining why those two populations of black holes are so other is likely one of the largest mysteries of recent astronomy,” says Dr. Mróz.One conceivable rationalization postulates that LIGO and Virgo detectors have exposed a inhabitants of primordial black holes that can have shaped within the very early Universe. Their lifestyles was once first proposed over 50 years in the past via the well-known British theoretical physicist Stephen Hawking and, independently, via the Soviet physicist Yakov Zeldovich.“We all know that the early Universe was once now not preferably homogeneous – small density fluctuations gave upward push to present galaxies and galaxy clusters,” says Dr. Mróz. “Equivalent density fluctuations, in the event that they exceed a important density distinction, would possibly cave in and shape black holes.”Because the first detection of gravitational waves, increasingly more scientists were speculating that such primordial black holes would possibly contain an important fraction, if now not all, of darkish subject.
Anticipated vs. seen microlensing occasions via large items towards the Huge Magellanic Cloud as observed throughout the Milky Method halo. If the darkish subject within the Universe consisted of putative primordial black holes, over 500 microlensing occasions could be detected all the way through the OGLE survey within the years 2001-2020. In fact, the OGLE challenge registered best 13 detections of microlensing occasions, possibly brought about via common stars. Credit score: J. Skowron / OGLE. Background symbol of the Huge Magellanic Cloud: generated with bsrender written via Kevin Loch, the usage of the ESA/Gaia database. Credit score: J. Skowron / OGLE. Background symbol of the Huge Magellanic Cloud: generated with bsrender written via Kevin Loch, the usage of the ESA/Gaia databaseThe Thriller and Doable of Primordial Black HolesSince the primary detection of gravitational waves from a merging pair of black holes in 2015, the LIGO and Virgo experiments have detected greater than 90 such occasions. Astronomers spotted that black holes detected via LIGO and Virgo are most often considerably extra large (20–100 sun plenty) than the ones recognized prior to now within the Milky Method (5–20 sun plenty).“Explaining why those two populations of black holes are so other is likely one of the largest mysteries of recent astronomy,” says Dr. Mróz.One conceivable rationalization postulates that LIGO and Virgo detectors have exposed a inhabitants of primordial black holes that can have shaped within the very early Universe. Their lifestyles was once first proposed over 50 years in the past via the well-known British theoretical physicist Stephen Hawking and, independently, via the Soviet physicist Yakov Zeldovich.“We all know that the early Universe was once now not preferably homogeneous – small density fluctuations gave upward push to present galaxies and galaxy clusters,” says Dr. Mróz. “Equivalent density fluctuations, in the event that they exceed a important density distinction, would possibly cave in and shape black holes.”Because the first detection of gravitational waves, increasingly more scientists were speculating that such primordial black holes would possibly contain an important fraction, if now not all, of darkish subject.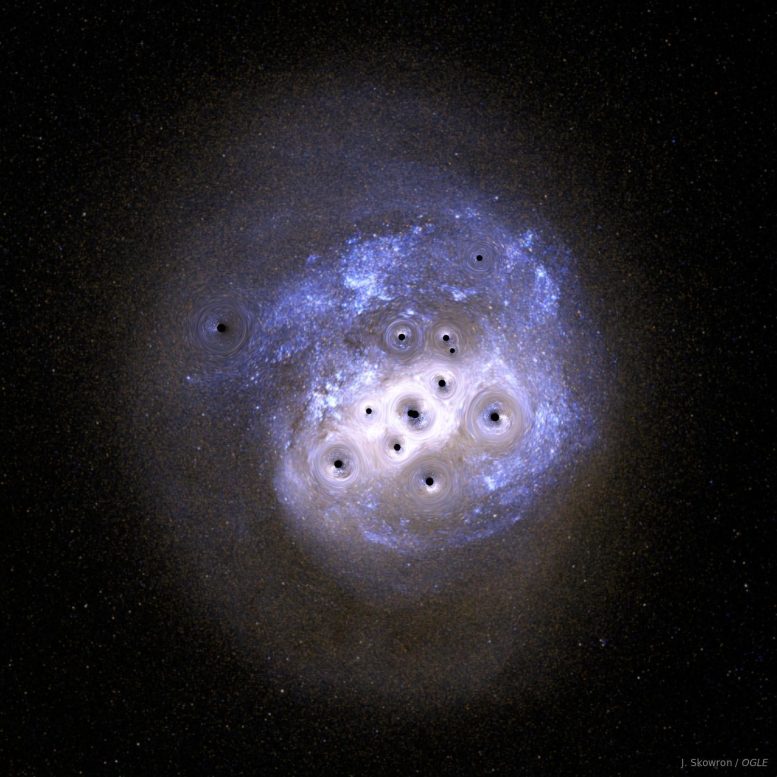 Artist’s impact of the Huge Magellanic Cloud being lensed via large items within the Milky Method halo. Credit score: J. Skowron / OGLEExploring Darkish Topic With Microlensing TechniquesFortunately, this speculation can also be verified with astronomical observations. We apply that copious quantities of darkish subject exist within the Milky Method. If it have been composed of black holes, we must have the ability to hit upon them in our cosmic group. Is that this conceivable, for the reason that black holes don’t emit any detectable mild?In step with Einstein’s idea of basic relativity, mild could also be bent and deflected within the gravitational box of huge items, a phenomenon known as gravitational microlensing.“Microlensing happens when 3 items – an observer on Earth, a supply of sunshine, and a lens – just about preferably align in area,” says Prof. Andrzej Udalski, the important investigator of the OGLE survey. “Throughout a microlensing tournament, the supply’s mild could also be deflected and magnified, and we apply a short lived brightening of the supply’s mild.”The period of the brightening will depend on the mass of the lensing object: the upper the mass, the longer the development. Microlensing occasions via sun mass items most often final a number of weeks, while the ones via black holes which might be 100 extra large than the Solar would final a couple of years.The speculation of the usage of gravitational microlensing to review darkish subject isn’t new. It was once first proposed within the Eighties via the well-known Polish astrophysicist Bohdan Paczyński. His thought impressed the beginning of 3 primary experiments: Polish OGLE, American MACHO, and French EROS. The primary effects from those experiments demonstrated that black holes much less large than one sun mass would possibly contain lower than 10 % of darkish subject. Those observations weren’t, on the other hand, delicate to extraordinarily long-timescale microlensing occasions and, subsequently, now not delicate to large black holes, very similar to the ones lately detected with gravitational-wave detectors.
Artist’s impact of the Huge Magellanic Cloud being lensed via large items within the Milky Method halo. Credit score: J. Skowron / OGLEExploring Darkish Topic With Microlensing TechniquesFortunately, this speculation can also be verified with astronomical observations. We apply that copious quantities of darkish subject exist within the Milky Method. If it have been composed of black holes, we must have the ability to hit upon them in our cosmic group. Is that this conceivable, for the reason that black holes don’t emit any detectable mild?In step with Einstein’s idea of basic relativity, mild could also be bent and deflected within the gravitational box of huge items, a phenomenon known as gravitational microlensing.“Microlensing happens when 3 items – an observer on Earth, a supply of sunshine, and a lens – just about preferably align in area,” says Prof. Andrzej Udalski, the important investigator of the OGLE survey. “Throughout a microlensing tournament, the supply’s mild could also be deflected and magnified, and we apply a short lived brightening of the supply’s mild.”The period of the brightening will depend on the mass of the lensing object: the upper the mass, the longer the development. Microlensing occasions via sun mass items most often final a number of weeks, while the ones via black holes which might be 100 extra large than the Solar would final a couple of years.The speculation of the usage of gravitational microlensing to review darkish subject isn’t new. It was once first proposed within the Eighties via the well-known Polish astrophysicist Bohdan Paczyński. His thought impressed the beginning of 3 primary experiments: Polish OGLE, American MACHO, and French EROS. The primary effects from those experiments demonstrated that black holes much less large than one sun mass would possibly contain lower than 10 % of darkish subject. Those observations weren’t, on the other hand, delicate to extraordinarily long-timescale microlensing occasions and, subsequently, now not delicate to large black holes, very similar to the ones lately detected with gravitational-wave detectors.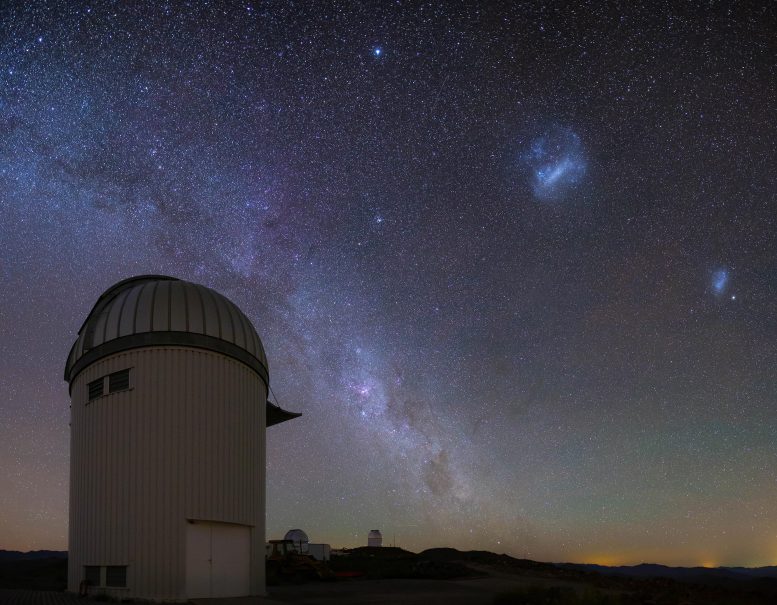 Evening over the Las Campanas Observatory in Chile (operated via the Carnegie Establishment for Science). The OGLE challenge gazing station and the Huge and Small Magellanic Clouds. Credit score: Krzysztof UlaczykLong-Time period Observational Research via OGLEIn the brand new article within the Astrophysical Magazine Complement Collection, OGLE astronomers provide the result of just about 20-year-long photometric tracking of just about 80 million stars situated in a close-by galaxy, known as the Huge Magellanic Cloud, and the searches for gravitational microlensing occasions. The analyzed information have been accrued all the way through the 3rd and fourth stages of the OGLE challenge from 2001 to 2020.“This knowledge set supplies the longest, greatest, and maximum correct photometric observations of stars within the Huge Magellanic Cloud within the historical past of recent astronomy,” says Prof. Udalski.Implications of Fresh Findings on Darkish MatterThe 2nd article, revealed in Nature, discusses the astrophysical penalties of the findings.“If all the darkish subject within the Milky Method was once composed of black holes of 10 sun plenty, we must have detected 258 microlensing occasions,” says Dr. Mróz. “For 100 sun mass black holes, we anticipated 99 microlensing occasions. For 1000 sun mass black holes – 27 microlensing occasions.”By contrast, the OGLE astronomers have discovered best 13 microlensing occasions. Their detailed research demonstrates that every one of them can also be defined via the recognized stellar populations within the Milky Method or the Huge Magellanic Cloud itself, now not via black holes.“That signifies that huge black holes can compose at maximum a couple of % of darkish subject,” says Dr. Mróz.The detailed calculations show that black holes of 10 sun plenty would possibly contain at maximum 1.2% of darkish subject, 100 sun mass black holes – 3.0% of darkish subject, and 1000 sun mass black holes – 11% of darkish subject.“Our observations point out that primordial black holes can not contain an important fraction of the darkish subject and, concurrently, provide an explanation for the seen black hollow merger charges measured via LIGO and Virgo,” says Prof. Udalski.Subsequently, different explanations are wanted for enormous black holes detected via LIGO and Virgo. In step with one speculation, they shaped as a manufactured from the evolution of huge, low-metallicity stars. Some other risk comes to mergers of much less large items in dense stellar environments, similar to globular clusters.“Our effects will stay in astronomy textbooks for many years to come back,” provides Prof. Udalski.Reference:“No large black holes within the Milky Method halo” via Przemek Mróz, Andrzej Udalski, Michał Okay. Szymański, Igor Soszyński, Łukasz Wyrzykowski, Paweł Pietrukowicz, Szymon Kozłowski, Radosław Poleski, Jan Skowron, Dorota Skowron, Krzysztof Ulaczyk, Mariusz Gromadzki, Krzysztof Rybicki, Patryk Iwanek, Marcin Wrona and Milena Ratajczak, 24 June 2024, Nature.
Evening over the Las Campanas Observatory in Chile (operated via the Carnegie Establishment for Science). The OGLE challenge gazing station and the Huge and Small Magellanic Clouds. Credit score: Krzysztof UlaczykLong-Time period Observational Research via OGLEIn the brand new article within the Astrophysical Magazine Complement Collection, OGLE astronomers provide the result of just about 20-year-long photometric tracking of just about 80 million stars situated in a close-by galaxy, known as the Huge Magellanic Cloud, and the searches for gravitational microlensing occasions. The analyzed information have been accrued all the way through the 3rd and fourth stages of the OGLE challenge from 2001 to 2020.“This knowledge set supplies the longest, greatest, and maximum correct photometric observations of stars within the Huge Magellanic Cloud within the historical past of recent astronomy,” says Prof. Udalski.Implications of Fresh Findings on Darkish MatterThe 2nd article, revealed in Nature, discusses the astrophysical penalties of the findings.“If all the darkish subject within the Milky Method was once composed of black holes of 10 sun plenty, we must have detected 258 microlensing occasions,” says Dr. Mróz. “For 100 sun mass black holes, we anticipated 99 microlensing occasions. For 1000 sun mass black holes – 27 microlensing occasions.”By contrast, the OGLE astronomers have discovered best 13 microlensing occasions. Their detailed research demonstrates that every one of them can also be defined via the recognized stellar populations within the Milky Method or the Huge Magellanic Cloud itself, now not via black holes.“That signifies that huge black holes can compose at maximum a couple of % of darkish subject,” says Dr. Mróz.The detailed calculations show that black holes of 10 sun plenty would possibly contain at maximum 1.2% of darkish subject, 100 sun mass black holes – 3.0% of darkish subject, and 1000 sun mass black holes – 11% of darkish subject.“Our observations point out that primordial black holes can not contain an important fraction of the darkish subject and, concurrently, provide an explanation for the seen black hollow merger charges measured via LIGO and Virgo,” says Prof. Udalski.Subsequently, different explanations are wanted for enormous black holes detected via LIGO and Virgo. In step with one speculation, they shaped as a manufactured from the evolution of huge, low-metallicity stars. Some other risk comes to mergers of much less large items in dense stellar environments, similar to globular clusters.“Our effects will stay in astronomy textbooks for many years to come back,” provides Prof. Udalski.Reference:“No large black holes within the Milky Method halo” via Przemek Mróz, Andrzej Udalski, Michał Okay. Szymański, Igor Soszyński, Łukasz Wyrzykowski, Paweł Pietrukowicz, Szymon Kozłowski, Radosław Poleski, Jan Skowron, Dorota Skowron, Krzysztof Ulaczyk, Mariusz Gromadzki, Krzysztof Rybicki, Patryk Iwanek, Marcin Wrona and Milena Ratajczak, 24 June 2024, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07704-6Reference: “Microlensing Optical Intensity and Match Charge towards the Huge Magellanic Cloud In line with 20 12 months of OGLE Observations” via Przemek Mróz, Andrzej Udalski, Michał Okay. Szymański, Mateusz Kapusta, Igor Soszyński, Łukasz Wyrzykowski, Paweł Pietrukowicz, Szymon Kozłowski, Radosław Poleski, Jan Skowron, Dorota Skowron, Krzysztof Ulaczyk, Mariusz Gromadzki, Krzysztof Rybicki, Patryk Iwanek, Marcin Wrona and Milena Ratajczak, 24 June 2024, The Astrophysical Magazine Complement Collection.
DOI: 10.3847/1538-4365/ad452e
Black Holes and Darkish Revelations: Gravitational Waves Supply New Clues to the Composition of Darkish Topic







![Galaxy S25 ‘Slender’ is almost definitely thicker than ‘iPhone 17 Air’ as leak finds 6.4mm design [Gallery] Galaxy S25 ‘Slender’ is almost definitely thicker than ‘iPhone 17 Air’ as leak finds 6.4mm design [Gallery]](https://9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/01/galaxy-s25-slim-4.jpg?quality=82&strip=all&w=1600)







