Boeing’s afflicted Starliner spacecraft — now not relied on via NASA to soundly deliver its workforce house from the Global Area Station — undocked Friday for an unpiloted go back to Earth to near out a disappointing take a look at flight marred via helium leaks and thruster issues.Leaving Starliner commander Barry “Butch” Wilmore and pilot Sunita Williams in the back of, the Boeing spacecraft undocked from the station’s ahead port at 6:04 p.m. EDT.Looping up over the station to some degree neatly above and in the back of the lab advanced, the Starliner’s braking rockets had been anticipated to fireside at 11:17 p.m. to drop the send out of orbit, putting in a fiery re-entry plunge to touchdown at White Sands, New Mexico, simply after nighttime Jap Time.
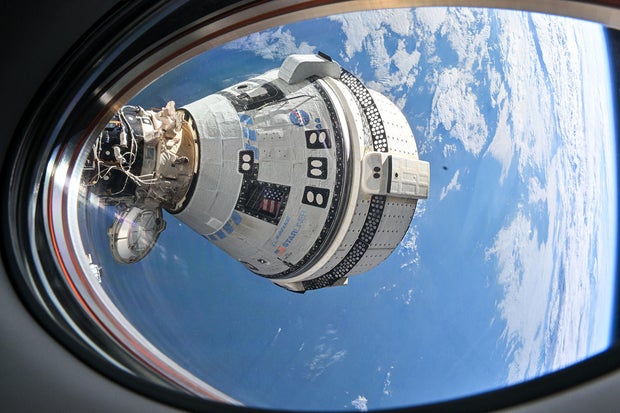
Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft backs clear of the Global Area Station to start out an unpiloted six-hour go back to Earth, concentrated on an in a single day touchdown at White Sands, New Mexico. Sept. 6, 2024.
NASA
In a while prior to undocking, Williams radioed flight controllers in Houston to thank the staff for its enhance. Relating to the Starliner via its casual identify, she mentioned “you guys, it’s time to deliver Calypso house. You’ve got this. We now have your backs, and you have this. Carry her again to Earth. Just right success.”
“We have now loved each and every coaching tournament and each and every assembly, we take into account each and every setback and each and every revelation with you,” the flight director answered. “The groups at the floor have labored numerous hours over the previous couple of weeks, months and, for a bunch people, years to deliver Calypso again, and we are in a position to try this lately.”
The Starliner docked to the distance station’s ahead port the day after release on Jun 5 and is observed right here via a window in a SpaceX Group Dragon docked 90 levels away on the Unity module’s space-facing port.
NASA
Wilmore then chimed in, pronouncing “we agree. A few years of serious enjoyment, simming (working simulations) in combination, enjoying in combination and being taken with each and every different’s lives. It is been particular. Carry it house.”
Regardless of take a look at information that satisfied Boeing engineers and bosses the Starliner may safely deliver its workforce house in spite of its previous issues, NASA managers concluded sufficient uncertainty remained to justify holding Wilmore and Williams on board the station and to deliver their send down via faraway regulate.
Boeing Starliner departs area station to go back to Earth with out a workforce
11:09
Astronauts to stay in area till FebruaryThe two astronauts will stay at the area station till overdue February, hitching a trip house aboard a SpaceX Group Dragon spacecraft being readied for release Sept. 24 to ferry the following long-duration workforce to the lab.The Group Dragon usually launches with 4 workforce participants, however two NASA astronauts had been bumped from the impending Group 9 flight to liberate seats for Wilmore and Williams. They are going to sign up for Group 9 commander Nick Hague and Russian cosmonaut Alexander Gorbunov for a traditional six-month excursion of accountability.By the point they go back to Earth round Feb. 22, Wilmore and Williams, who at first anticipated to spend about 8 days in orbit, can have logged greater than eight-and-a-half months in area.
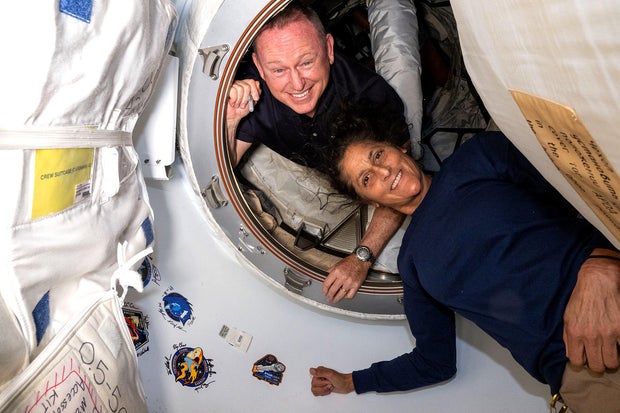
Starliner commander Barry “Butch” Wilmore and co-pilot Sunita Williams will stay in the back of aboard the Global Area Station after their Boeing-built ferry send departs for an unpiloted go back to Earth.
NASA
NASA astronaut Frank Rubio confronted a equivalent predicament in 2022 when his six-month keep aboard the station used to be prolonged to greater than a complete yr on account of issues of the Russian Soyuz spacecraft that carried him to orbit.
“I believe going from six months to twelve months is hard, however it is not as difficult as going from 8 days to 8 months,” Rubio mentioned in an interview with CBS Information. Requested how Wilmore and Williams took the inside track in their extension, he mentioned “they are doing nice.””Without a doubt, there is a little a part of you that is disillusioned,” he added. “It is ok to recognize that. However you can also’t mope round for all the time, proper? … You simply must more or less commit and rededicate your self to the challenge.”Sequence of setbacks for BoeingThe resolution to deliver the Starliner down with out its workforce used to be a morale-sapping blow to Boeing within the wake of previous issues that not on time the Starliner’s first piloted flight via just about 4 years, required a 2d unpiloted take a look at flight and value the corporate greater than $1.5 billion above and past its NASA fixed-price contract.The Starliner woes come on best of Boeing’s ongoing battle to revive public self belief within the wake of 2 737 Max 8 airliner crashes, a detailed name with an Alaska Airways 737 flight that suffered a door plug blowout previous this yr and newer issues of an upgraded model of the corporate’s long-haul 777 plane.It is not but identified what’s going to be had to proper the issues encountered on the most recent Starliner flight, whether or not every other pricey take a look at flight might be required or when the send may well be in a position for energetic carrier ferrying astronauts to and from the station.
Cameras aboard the Global Area Station captured impressive perspectives of the Starliner all the way through its ultimate strategy to docking on June 6.
NASA
The station workforce closed the Starliner’s hatch at 1:29 p.m. Thursday. The day prior to, as Williams labored throughout the Starliner serving to prepare go back pieces to make sure the appropriate stability and heart of gravity, she described the instant as “bittersweet.””Thank you for backing us up, thank you for taking a look over our shoulder and ensuring we now have were given the whole thing in the appropriate position,” she advised flight controllers. “We wish her to have a pleasing, comfortable touchdown within the wilderness.”
After a last take a look at of the elements on the New Mexico touchdown web site remained favorable, hooks within the Starliner’s docking mechanism disengaged, permitting springs at the station facet to push the uncrewed ferry send away.A sequence of thruster firings then had been performed to slowly push the spacecraft out in entrance of the lab advanced prior to looping up and excessive and departing to the rear. Seven mins after undocking, the Starliner used to be anticipated to go out a 1,300-foot-wide protection zone referred to as the “preserve out sphere.”Given the sooner thruster issues, NASA shortened the departure timeline to get the Starliner neatly clear of the station as briefly as conceivable. 16 mins after leaving the keep-out sphere, the spacecraft exited the bigger “manner ellipsoid,” every other protection zone across the ISS that measures 2.5 miles lengthy and 1.2 miles vast. The thrusters labored flawlessly during the early phases of the departure.The send’s flight computer systems had been programmed to lead the spacecraft towards an exact level in area the place braking rockets can fireplace to gradual the send, shedding it out of orbit and striking it on track for an in a single day touchdown at White Sands.To get out of orbit, 4 huge orbital maneuvering and perspective regulate rockets — OMACs — had been required to fireside for 59 seconds, slowing the send’s 17,100-mph speed via just about 300 mph. That is simply sufficient to drop the some distance facet of the orbit into the ambience for re-entry and descent to the New Mexico touchdown web site.Whilst the robust OMAC braking rockets are firing, smaller response regulate machine, or RCS, jets had been anticipated to fireside on pc command to preserve the Starliner strong and pointed in the appropriate path.As soon as the deorbit rocket firing is entire, the Starliner’s carrier module, housing the OMACs, 28 RCS jets, the helium tanks and different vital however no-longer-needed methods, might be jettisoned to fritter away at the environment.
Veteran army take a look at pilots and area station astronauts, Williams and Wilmore will spend the following a number of months operating as researchers within the lab advanced along the station’s different long-duration workforce participants.
NASA
The workforce module, secure via a warmth protect and provided with 12 RCS jets of its personal, then will start its re-entry at an altitude of about 400,000 toes, enduring temperatures as top as 3,000 levels Fahrenheit as plunges again into the discernible environment at just about 5 miles consistent with 2d.
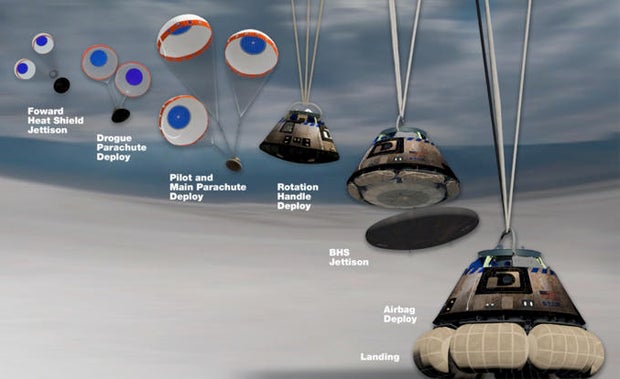
The southwest-to-northeast re-entry trajectory will raise the Starliner around the Baja Peninsula, the Gulf of California, northern Mexico and into New Mexico.At an altitude of about 24,500 toes, two small drogue parachutes will unfurl, slowing and stabilizing the Starliner. About one minute later, at an altitude of 8,000 toes, 3 pilot parachutes will pull out the send’s 3 104-foot-wide primary parachutes, slowing the first rate to about 18 mph.At an altitude of two,500 toes, airbags will inflate to cut back touchdown have an effect on forces to the an identical of strolling velocity. Landing is anticipated one minute after nighttime EDT (10:01 p.m. Friday native time).The deorbit burn and computer-orchestrated perspective regulate machine firings are an important to getting out of orbit at the exact trajectory crucial for a pinpoint touchdown. And all of the ones firings require pressurized helium to push propellants to wholesome thrusters.
A sequence of small pilot and drogue parachutes are designed to gradual and stabilize the Starliner prior to its 3 primary parachutes unfurl and inflate at an altitude of about 8.000 toes. After the no-longer-needed warmth protect is jettisoned, airbags will inflate to cut back the surprise of landing.
Boeing
All over the Starliner’s rendezvous with the distance station on June 6, the day after release, 5 RCS jets had been “deselected” via the flight pc on account of degraded thrust. As well as, 4 helium leaks within the propulsion pressurization machine had been detected, including to a small leak that used to be detected prior to release.After in depth checks and analyses, Boeing engineers concluded the helium leaks had been the results of rather degraded seals uncovered to poisonous propellants over a longer length. However even with the leaks, they mentioned the Starliner had 10 instances extra helium on board than had to get out of orbit.The thruster downside, checking out indicated, used to be led to via top temperatures that, in flip, led to inside Teflon seals to deform in poppet valves, limiting the waft of gas.
The top temperatures, the engineers concluded, had been in large part the results of guide flight regulate checks that led to the jets to fireside loads of instances in rapid-fire style whilst the craft used to be orientated so those self same jets had been in direct daylight for a longer length.In take a look at firings later within the challenge the jets looked to be operating usually, indicating the seals had shrunk again to, or close to, their authentic form.Boeing argued guide flight checks can be dominated out for a piloted go back to Earth, the craft can be orientated to attenuate sun heating at the suspect jets and less firings can be crucial within the absence of a rendezvous.Boeing attempted to persuade their opposite numbers at NASA that the Starliner had a number of margin and would deliver Wilmore and Williams safely again to Earth.However NASA managers didn’t settle for Boeing’s “flight rationale” and opted to deliver the Starliner down with out its workforce.”Spaceflight is tricky. The margins are skinny. The distance atmosphere isn’t forgiving,” mentioned Norm Knight, director of flight operations on the Johnson Area Middle. “And we should be proper.”
Extra
William Harwood
Invoice Harwood has been overlaying the U.S. area program full-time since 1984, first as Cape Canaveral bureau leader for United Press Global and now as a specialist for CBS Information.