Over 400 million years in the past, an upwelling of scorching rock from Earth’s mantle wrenched aside the crust in Mongolia, developing an ocean that survived for 115 million years. The geological historical past of this ocean may lend a hand researchers perceive Wilson cycles, or the method in which supercontinents wreck aside and are available in combination. Those are sluggish, broad-scale processes that development through lower than an inch in keeping with 12 months, stated learn about co-author Daniel Pastor-Galán, a geoscientist on the Nationwide Spanish Analysis Council in Madrid. “It is telling us about processes within the earth that aren’t really easy to grasp and which can be additionally no longer really easy to look,” Pastor-Galán informed Reside Science. Geoscientists can relatively appropriately reconstruct the breakup of the remaining supercontinent, Pangea, 250 million years in the past. However previous to that, it is tricky to type precisely how the mantle and the crust interacted. In a brand new learn about, researchers have been intrigued through volcanic rocks in northwestern Mongolia from the Devonian length (419 million to 359 million years in the past). Comparable: Gravitational anomalies expose seamount thrice the peak of worldwide’s tallest buildingThe Devonian used to be the “Age of the Fishes,” when fish ruled the oceans and crops started to unfold on land. On the time, there have been two primary continents, Laurentia and Gondwana, in addition to a protracted stretch of microcontinents that will ultimately grow to be what’s now Asia. Those microcontinents regularly bumped up in opposition to each and every different and merged in a procedure referred to as accretion. Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!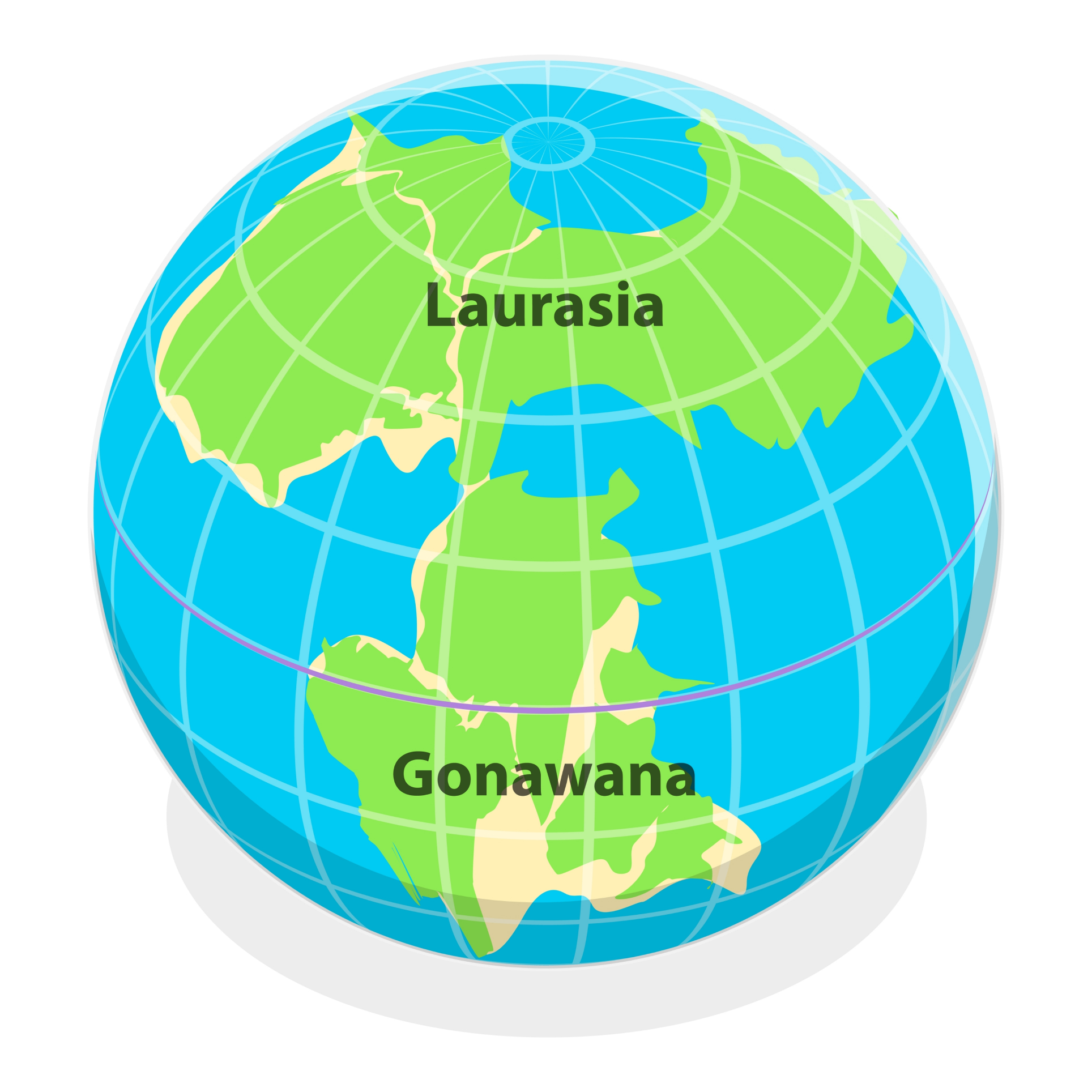 The sea existed when two primary continents, Gondwana and Laurasia existed on Earth. (Symbol credit score: TarikVision/Shutterstock)The researchers started doing fieldwork in northwest Mongolia the place rocks from those continent-building collisions are uncovered at the floor, in 2019, learning the ages and chemistry of the traditional rock layers. They discovered that between about 410 million and 415 million years in the past, an ocean referred to as the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean spread out within the area. The chemistry of the volcanic rocks that accompanied this rift printed the presence of a mantle plume — a circulate of in particular scorching, buoyant mantle rock.”Mantle plumes are in most cases concerned within the first level of the Wilson cycle: breakup of continents and opening of ocean, such because the Atlantic Ocean,” learn about lead writer Mingshuai Zhu, a professor of geology and geophysics on the Chinese language Academy of Sciences, informed Reside Science. In lots of circumstances, this occurs proper in the course of a forged chew of continent, tearing it aside. On this case, even though, the geology is especially advanced, for the reason that plume used to be tearing aside crust that had up to now come in combination thru accretion. Susceptible spots between the accreted microcontinents, mixed with the plume, most likely helped the sea to shape, Zhu stated. The researchers revealed their findings Would possibly 16 within the magazine Geophysical Analysis Letters. The sea closed in the similar spot that it opened, which is a not unusual development in ocean life-cycles, Pastor-Galán stated, however researchers handiest checked out a snapshot of the sea’s opening on this learn about. “A just right factor is {that a} hotspot is fairly strong so they preserve on, for lots of hundreds of thousands of years, in the similar position,” Pastor-Galán stated. As continents within the crust transfer over the mantle hotspot, the hotspot leaves in the back of volcanic rocks and a tell-tale chemistry; this is helping researchers observe plate movement over millennia, he stated. Asia is not accreting new microcontinents, Pastor-Galán stated, however the formation of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean used to be most likely very similar to what’s noticed lately on the Crimson Sea, the place the crust is spreading through about 0.4 inches (1 centimeter) in keeping with 12 months. The Crimson Sea is a part of a bigger continental rift that might create a brand-new ocean in japanese Africa over tens of hundreds of thousands of years, even though geologists do not but know whether or not different continental forces will save you that ocean from totally opening, in step with Eos mag. Zhu and his colleagues now plan to make use of their information to make pc fashions to higher describe the sophisticated tectonics of the traditional Devonian ocean.
The sea existed when two primary continents, Gondwana and Laurasia existed on Earth. (Symbol credit score: TarikVision/Shutterstock)The researchers started doing fieldwork in northwest Mongolia the place rocks from those continent-building collisions are uncovered at the floor, in 2019, learning the ages and chemistry of the traditional rock layers. They discovered that between about 410 million and 415 million years in the past, an ocean referred to as the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean spread out within the area. The chemistry of the volcanic rocks that accompanied this rift printed the presence of a mantle plume — a circulate of in particular scorching, buoyant mantle rock.”Mantle plumes are in most cases concerned within the first level of the Wilson cycle: breakup of continents and opening of ocean, such because the Atlantic Ocean,” learn about lead writer Mingshuai Zhu, a professor of geology and geophysics on the Chinese language Academy of Sciences, informed Reside Science. In lots of circumstances, this occurs proper in the course of a forged chew of continent, tearing it aside. On this case, even though, the geology is especially advanced, for the reason that plume used to be tearing aside crust that had up to now come in combination thru accretion. Susceptible spots between the accreted microcontinents, mixed with the plume, most likely helped the sea to shape, Zhu stated. The researchers revealed their findings Would possibly 16 within the magazine Geophysical Analysis Letters. The sea closed in the similar spot that it opened, which is a not unusual development in ocean life-cycles, Pastor-Galán stated, however researchers handiest checked out a snapshot of the sea’s opening on this learn about. “A just right factor is {that a} hotspot is fairly strong so they preserve on, for lots of hundreds of thousands of years, in the similar position,” Pastor-Galán stated. As continents within the crust transfer over the mantle hotspot, the hotspot leaves in the back of volcanic rocks and a tell-tale chemistry; this is helping researchers observe plate movement over millennia, he stated. Asia is not accreting new microcontinents, Pastor-Galán stated, however the formation of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean used to be most likely very similar to what’s noticed lately on the Crimson Sea, the place the crust is spreading through about 0.4 inches (1 centimeter) in keeping with 12 months. The Crimson Sea is a part of a bigger continental rift that might create a brand-new ocean in japanese Africa over tens of hundreds of thousands of years, even though geologists do not but know whether or not different continental forces will save you that ocean from totally opening, in step with Eos mag. Zhu and his colleagues now plan to make use of their information to make pc fashions to higher describe the sophisticated tectonics of the traditional Devonian ocean.
Boiling rocks from Earth’s crust tore an ocean into Mongolia 410 million years in the past