The face of a car-size, millipede-like creature — the most important arthropod ever to are living — has after all been published thank you to 2 well-preserved fossils, a brand new learn about experiences.The arthropod, Arthropleura, lived in forests close to the equator between 346 million and 290 million years in the past, throughout the past due Paleozoic technology. Within the oxygen-rich setting at the moment, Arthropleura may develop to an enormous 8.5 ft (2.6 meters) lengthy and weigh over 100 kilos (45 kilograms).”Arthropleura … has been recognized for the reason that 18th century, over 100 years, and we hadn’t discovered an entire head,” learn about first writer Mickaël Lheritier, a paleontologist at Claude Bernard Lyon 1 College in France, informed Are living Science. “Now with the finished head, you’ll see the mandibles, the eyes, and those traits can [help us understand] the placement of this [creature] in evolution.”The large arthropod had confused paleontologists for many years. Arthropleura’s frame had traits like a millipede. However with out the top, scientists could not perceive the creature’s courting to fashionable arthropods like millipedes and centipedes. Whilst those two trendy creatures might glance equivalent, they in reality diverged about 440 million years in the past, approach earlier than Arthropleura came visiting. Paleontologists puzzled if Arthropleura used to be a member of the millipede crew or the centipede crew.Arthropleura’s family-tree controversy “options fierce debates about its affinities,” James Lamsdell, a paleontologist at West Virginia College who used to be now not concerned with the learn about, wrote in an accompanying point of view printed in the similar magazine. However with the invention of an intact head, “the thriller of Anthropleura now seems solved.”Similar: 7-foot-long arthropods commanded the ocean 470 million years in the past, ‘beautiful’ fossils showThe CT scans nearly exposed the fossilized head of 2 juvenile Arthropleura came upon inside rock within the Montceau-les-Mines Lagerstätte fossil website online in France. The CT scans published distinctive stalked eyes jutting from the facet of the top; gently curved antennae; and small, centipede-like mandibles. In combination, those characteristics made up a complicated amalgamation of centipede- and millipede-like traits.Get the arena’s most enticing discoveries delivered instantly on your inbox.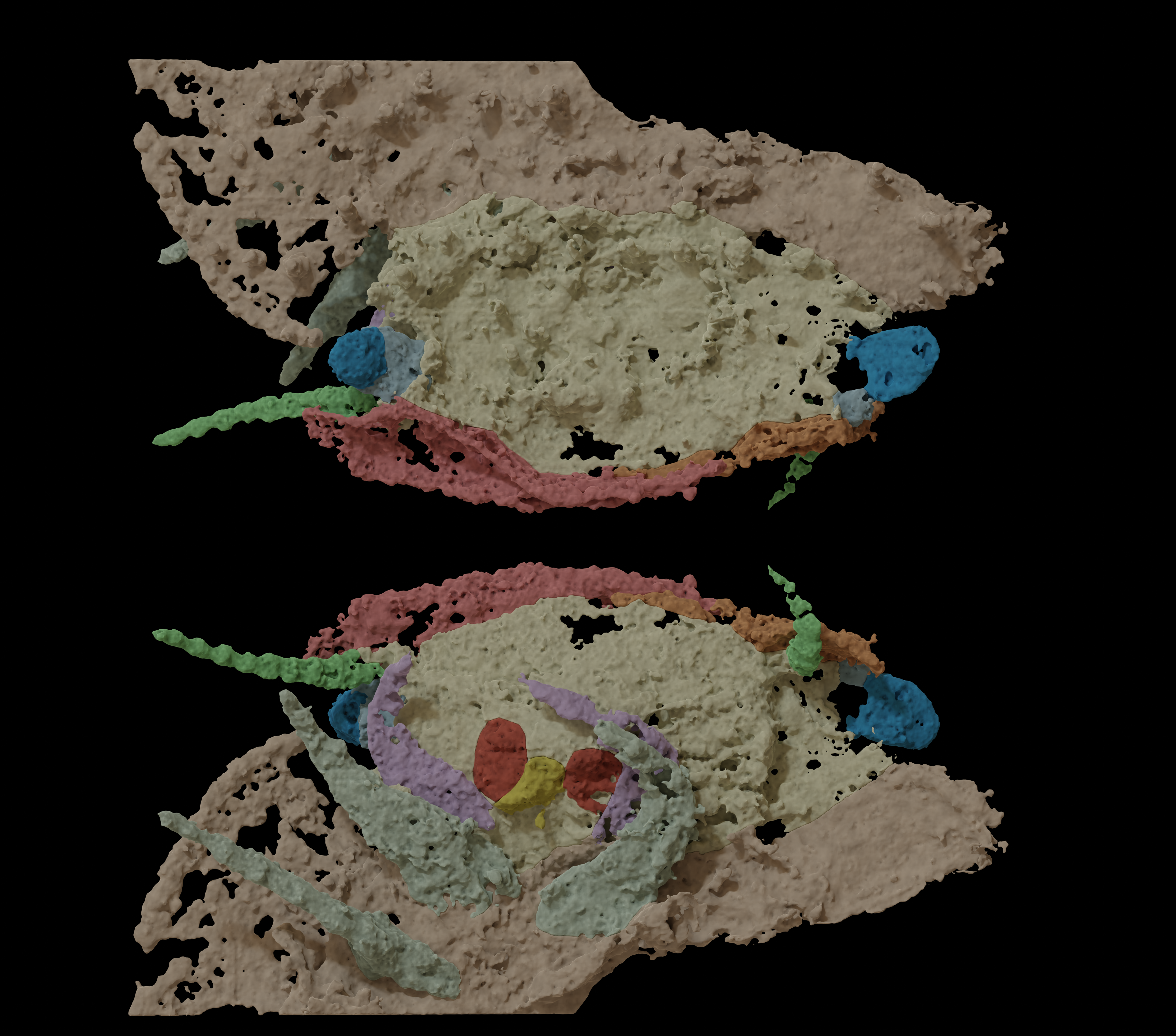 The stalked eyes of Arthropleura, in blue, might recommend that juveniles frolicked within the water earlier than changing into adults that lived on land. (Symbol credit score: Mickaël Lhéritier (LGL-TPE, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1) and Vincent Fernandez (ESRF))”Those main points, in combination, might seem to go away Arthropleura as a lot — if now not extra — a puzzle than earlier than,” Lamsdell stated. “However the apparently chimeric nature of Arthropleura is in reality necessary proof that can lend a hand resolution a basic query in regards to the [evolution of these species].”According to anatomical options, paleontologists in the end grouped Arthropleura as maximum carefully associated with the millipede kin. Then again, the stalked eyeballs have by no means been considered within the millipede or centipede households. Arthropleura has been broadly thought to be terrestrial, however eyestalks are most often present in semiaquatic or absolutely aquatic animals, like crustaceans.Since the head belongs to a juvenile, the rationale would possibly lie within the animal’s existence level, Lamsdell recommended. As juveniles, Arthropleura can have spent extra time within the water, earlier than dropping the stalked eyes in maturity. “The stalked eyes stay a large thriller, as a result of we do not in reality know the way to provide an explanation for this,” Lheritier stated.
The stalked eyes of Arthropleura, in blue, might recommend that juveniles frolicked within the water earlier than changing into adults that lived on land. (Symbol credit score: Mickaël Lhéritier (LGL-TPE, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1) and Vincent Fernandez (ESRF))”Those main points, in combination, might seem to go away Arthropleura as a lot — if now not extra — a puzzle than earlier than,” Lamsdell stated. “However the apparently chimeric nature of Arthropleura is in reality necessary proof that can lend a hand resolution a basic query in regards to the [evolution of these species].”According to anatomical options, paleontologists in the end grouped Arthropleura as maximum carefully associated with the millipede kin. Then again, the stalked eyeballs have by no means been considered within the millipede or centipede households. Arthropleura has been broadly thought to be terrestrial, however eyestalks are most often present in semiaquatic or absolutely aquatic animals, like crustaceans.Since the head belongs to a juvenile, the rationale would possibly lie within the animal’s existence level, Lamsdell recommended. As juveniles, Arthropleura can have spent extra time within the water, earlier than dropping the stalked eyes in maturity. “The stalked eyes stay a large thriller, as a result of we do not in reality know the way to provide an explanation for this,” Lheritier stated.














