![]()
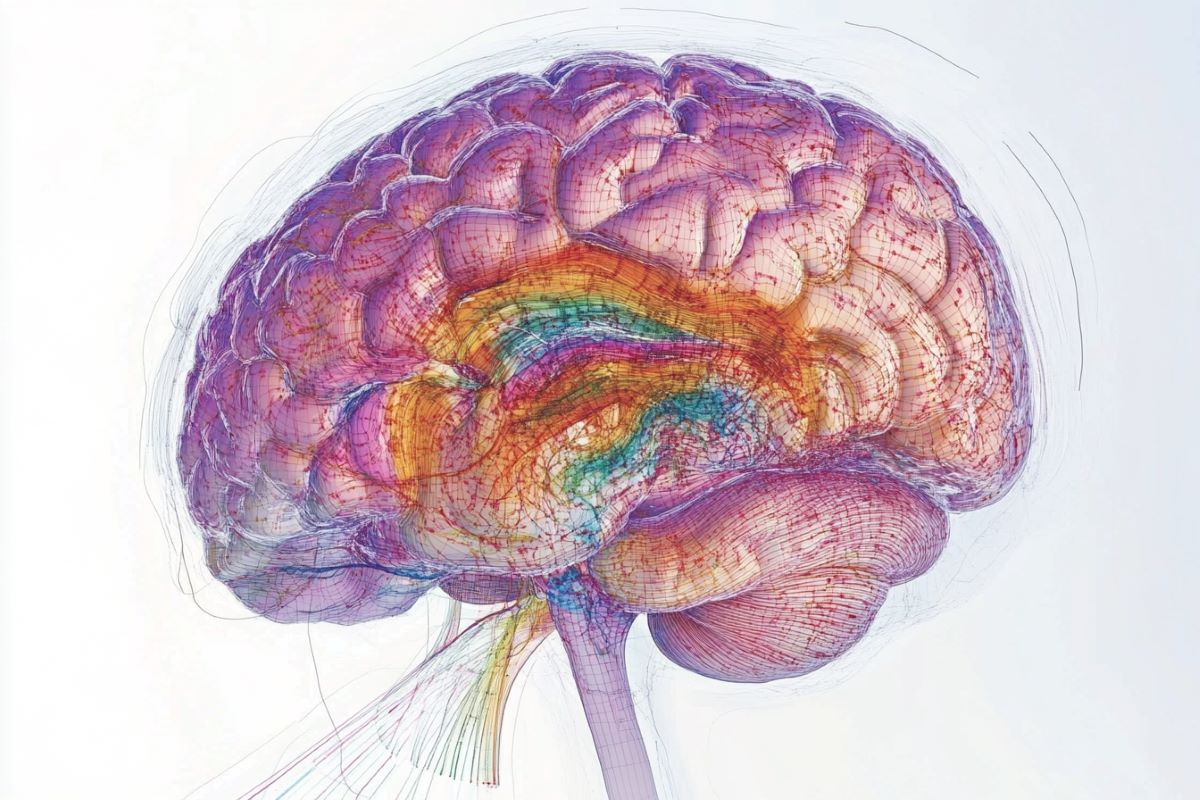
![]() A contemporary find out about has discovered that caffeine may exacerbate the uncomfortable side effects of continual sleep restriction at the mind’s gray subject. The researchers came upon that individuals who ate up caffeine throughout a duration of sleep restriction confirmed extra vital discounts in gray subject quantity when put next to those that didn’t devour caffeine. The findings had been not too long ago printed in Medical Studies.Caffeine is probably the most broadly used psychoactive substance globally, famend for its skill to toughen alertness and alleviate cognitive impairments brought about via loss of sleep. Then again, each acute sleep loss and day-to-day caffeine consumption had been related to discounts in grey subject quantity, a key element of the mind thinking about processing data and regulating more than a few cognitive purposes.Through analyzing the interplay between continual sleep restriction and day-to-day caffeine consumption, the researchers aimed to discover whether or not caffeine intake throughout classes of sleep deprivation would result in additional discounts in grey subject quantity. Moreover, the find out about sought to discover the function of the adenosine machine, specifically the provision of adenosine A1 receptors, in mediating the mind’s reaction to caffeine and sleep loss.Adenosine A1 receptors are a kind of receptor within the mind that performs a a very powerful function in regulating neural process and selling sleep. They’re a part of the adenosine machine, which is helping to stability power intake and deal with homeostasis. Caffeine acts as an antagonist to those receptors, blockading their motion and thereby improving alertness and counteracting sleepiness.The analysis used to be carried out, partly, via first creator Yu-Shiuan Lin of the College Psychiatric Clinics Basel in Switzerland and senior creator David Elmenhorst of the Institute of Neuroscience and Drugs at Forschungszentrum Jülich in Germany.“The conception of this paintings used to be impressed via the findings in Dr. Yu-Shiuan Lin’s earlier find out about on the Centre for Chronobiology. There we seen a caffeine concentration-dependent lower in grey subject after a managed 10-day caffeine consumption, which used to be unbiased of the caffeine-induced vasoconstriction and used to be most effective partly mitigated after 36 hours,” the 2 researchers informed PsyPost in a joint commentary.“This impact of caffeine on grey subject plasticity added as much as the plentiful animal proof that demonstrates the involvement of adenosine receptors, the principle belongings caffeine binds to and exerts results via, in modulating the synaptic plasticity in central frightened methods. To grasp a possible function of adenosine in grey subject plasticity, Yu-Shiuan reached out to Professor David Elmenhorst on the Forschungszentrum Jülich for this collaborative undertaking.”“On the time David, used to be accomplishing a PET-MRI find out about along side the German Aerospace Heart to research the consequences of continual sleep restriction and day-to-day caffeine consumption on adenosine A1 receptor (A1R) availability. But even so the A1R size in vivo, this find out about used to be exhilarating as it would probably supply insights to the adenosinergic modulation in mind plasticity during the interference with sleep.”“The metabolism and signaling of adenosine play a a very powerful function within the homeostatic mechanism of sleep,” Lin and Elmenhorst defined. “Disrupted sleep can in flip modify adenosine signaling and has been regularly discovered to impair mind constructions in each animal fashions and people. Inadequate sleep additionally consolidates the caffeine consumption behaviors, and each are, steadily at the same time as, prevalent within the fashionable society.“Therefore, we took the chance and repurposed the PET and T1-weighted MR photographs along with the information of Arterial Spin Labeling to account for the caffeine results on mind perfusion, and tested the grey subject plasticity after continual sleep restriction with and with out combining use of caffeine, in addition to the prospective mediation of A1R in those grey subject responses.”The find out about used to be carried out on the German Aerospace Heart’s analysis facility in Cologne with 36 wholesome grownup contributors, together with 15 women folk and 21 men, elderly round 29 years. Those contributors had been decided on in line with their low routine caffeine consumption (lower than 450 mg in keeping with day) and non-smoking standing. The contributors had been divided into two teams: one workforce gained caffeine-containing espresso (the CAFF workforce), whilst the opposite gained decaffeinated espresso (the DECAF workforce).The experiment spanned 9 days in a managed laboratory environment. It began with an adaptation day, adopted via two baseline days the place contributors had 8 hours of sleep in keeping with night time. This used to be adopted via 5 days of continual sleep restriction, with contributors restricted to five hours of sleep in keeping with night time, and concluded with a restoration day of 8 hours of sleep. Right through the continual sleep restriction section, the CAFF workforce gained 200 mg of caffeine within the morning and 100 mg within the afternoon, whilst the DECAF workforce gained an identical volumes of decaffeinated espresso.To measure the consequences on grey subject quantity, contributors underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans and positron emission tomography (PET) scans at 3 issues: after the baseline days, after the continual sleep restriction section, and after the restoration day. Saliva samples had been accrued ceaselessly to observe caffeine ranges, making sure correct monitoring of caffeine consumption and its physiological results.The result of the find out about indicated that continual sleep restriction ended in adjustments in grey subject quantity, that have been considerably influenced via caffeine consumption. Individuals who didn’t devour caffeine (DECAF workforce) throughout the sleep restriction section confirmed an build up in grey subject quantity in numerous mind areas, together with the prefrontal cortex, temporal-occipital cortex, and thalamus. Those areas are related to more than a few cognitive and sensory purposes, indicating a possible compensatory reaction to sleep loss.“It used to be reasonably sudden to us to watch an build up, as an alternative of a lower in grey subject within the contributors with out caffeine (DECAF workforce) after continual sleep restriction,” Lin and Elmenhorst informed PsyPost. “Then again, an previous find out about (Dai et al. (2018)) make clear a possible rationalization to this discovering. This find out about tested the adjustments in grey subject alongside the route between 20 and 36 hours of wakefulness, they usually discovered that more than one mind areas in truth began from appearing an build up within the early level (20h) and grew to become to be a discount later (36h).”“Even if the have an effect on of a complete sleep deprivation may now not be generalized to continual sleep restriction, we speculated that the grey subject responses to an expanding length and/or depth of sleep loss won’t observe a linear trajectory. Extra research are undoubtedly warranted to systematically read about the grey subject adjustments in several patterns of sleep restrictions.”By contrast, contributors who ate up caffeine (CAFF workforce) throughout the sleep restriction section exhibited a lower in grey subject quantity in those similar areas. This means that caffeine may inhibit the mind’s compensatory mechanisms throughout classes of inadequate sleep, probably exacerbating the damaging have an effect on of sleep loss on mind construction.The researchers additionally discovered that particular variations in adenosine receptor availability performed an important function within the extent of grey subject adjustments. The contributors with decrease baseline availability of subcortical adenosine receptors skilled larger discounts in grey subject quantity once they ate up caffeine throughout sleep restriction. This discovering highlights the significance of adenosine receptor process in mediating the consequences of sleep deprivation and caffeine on mind construction.“Individuals who have a better A1R availability appear to have extra resistance to the impact of caffeine on grey subject,” the researchers defined. “After a restoration sleep and round 30-hour caffeine withdrawal, lots of the adjustments in grey subject have recovered, apart from the larger dorsolateral prefrontal cortex related to continual sleep restriction and the diminished thalamus related caffeine consumption,”“It’s often identified that caffeine consumption combats sleepiness. Our information additional point out that caffeine consumption additionally interferes with the mind plasticity caused via sleep loss. Then again, caffeine does now not merely suppress or normalize the grey subject exchange but additionally affects grey subject in an other way. It’s unclear how the impact of this mind plasticity manifests at the cognitive behavioral ranges; what we all know is that it’s most likely demonstrating the adenosine modulation in neural homeostasis.”Regardless of its rigorous method, the find out about has some obstacles to believe. The pattern measurement used to be somewhat small, and contributors had been decided on in line with explicit genetic profiles associated with caffeine metabolism, which may restrict how smartly the findings observe to the wider inhabitants.Moreover, whilst MRI scans confirmed adjustments in gray subject, they are able to’t let us know precisely what brought about those adjustments. It can be a achieve or lack of neurons, adjustments in synapse density, or diversifications within the selection of enhance cells like microglia. To pinpoint those explicit adjustments, long term research may use PET scans with particular markers to measure synapses, mitochondria, or microglia, the researchers defined.“The synaptic homeostasis speculation (SHY) states that ‘sleep is the fee we pay for mind plasticity,’” the researchers stated. “A decade has handed since SHY used to be printed, and this attention-grabbing speculation remains to be but to be examined in people in vivo. David due to this fact has been devoted to learning the molecular mechanism of sleep-wake laws the usage of biomedical imaging. Alternatively, Yu-Shiuan continues that specialize in pharmacological PET-MR imaging to research the adenosinergic modulation and its function within the results of caffeine. We hope that long term results alongside those traces will supply insights to the findings on this present paintings.”The find out about, “Repeated caffeine consumption suppresses cerebral gray subject responses to continual sleep restriction in an A1 adenosine receptor-dependent approach: a double-blind randomized managed find out about with PET-MRI,” used to be authored via Yu-Shiuan Lin, Denise Lange, Diego Manuel Baur, Anna Foerges, Congying Chu, Changhong Li, Eva-Maria Elmenhorst, Bernd Neumaier, Andreas Bauer, Daniel Aeschbach, Hans-Peter Landolt, and David Elmenhorst.
A contemporary find out about has discovered that caffeine may exacerbate the uncomfortable side effects of continual sleep restriction at the mind’s gray subject. The researchers came upon that individuals who ate up caffeine throughout a duration of sleep restriction confirmed extra vital discounts in gray subject quantity when put next to those that didn’t devour caffeine. The findings had been not too long ago printed in Medical Studies.Caffeine is probably the most broadly used psychoactive substance globally, famend for its skill to toughen alertness and alleviate cognitive impairments brought about via loss of sleep. Then again, each acute sleep loss and day-to-day caffeine consumption had been related to discounts in grey subject quantity, a key element of the mind thinking about processing data and regulating more than a few cognitive purposes.Through analyzing the interplay between continual sleep restriction and day-to-day caffeine consumption, the researchers aimed to discover whether or not caffeine intake throughout classes of sleep deprivation would result in additional discounts in grey subject quantity. Moreover, the find out about sought to discover the function of the adenosine machine, specifically the provision of adenosine A1 receptors, in mediating the mind’s reaction to caffeine and sleep loss.Adenosine A1 receptors are a kind of receptor within the mind that performs a a very powerful function in regulating neural process and selling sleep. They’re a part of the adenosine machine, which is helping to stability power intake and deal with homeostasis. Caffeine acts as an antagonist to those receptors, blockading their motion and thereby improving alertness and counteracting sleepiness.The analysis used to be carried out, partly, via first creator Yu-Shiuan Lin of the College Psychiatric Clinics Basel in Switzerland and senior creator David Elmenhorst of the Institute of Neuroscience and Drugs at Forschungszentrum Jülich in Germany.“The conception of this paintings used to be impressed via the findings in Dr. Yu-Shiuan Lin’s earlier find out about on the Centre for Chronobiology. There we seen a caffeine concentration-dependent lower in grey subject after a managed 10-day caffeine consumption, which used to be unbiased of the caffeine-induced vasoconstriction and used to be most effective partly mitigated after 36 hours,” the 2 researchers informed PsyPost in a joint commentary.“This impact of caffeine on grey subject plasticity added as much as the plentiful animal proof that demonstrates the involvement of adenosine receptors, the principle belongings caffeine binds to and exerts results via, in modulating the synaptic plasticity in central frightened methods. To grasp a possible function of adenosine in grey subject plasticity, Yu-Shiuan reached out to Professor David Elmenhorst on the Forschungszentrum Jülich for this collaborative undertaking.”“On the time David, used to be accomplishing a PET-MRI find out about along side the German Aerospace Heart to research the consequences of continual sleep restriction and day-to-day caffeine consumption on adenosine A1 receptor (A1R) availability. But even so the A1R size in vivo, this find out about used to be exhilarating as it would probably supply insights to the adenosinergic modulation in mind plasticity during the interference with sleep.”“The metabolism and signaling of adenosine play a a very powerful function within the homeostatic mechanism of sleep,” Lin and Elmenhorst defined. “Disrupted sleep can in flip modify adenosine signaling and has been regularly discovered to impair mind constructions in each animal fashions and people. Inadequate sleep additionally consolidates the caffeine consumption behaviors, and each are, steadily at the same time as, prevalent within the fashionable society.“Therefore, we took the chance and repurposed the PET and T1-weighted MR photographs along with the information of Arterial Spin Labeling to account for the caffeine results on mind perfusion, and tested the grey subject plasticity after continual sleep restriction with and with out combining use of caffeine, in addition to the prospective mediation of A1R in those grey subject responses.”The find out about used to be carried out on the German Aerospace Heart’s analysis facility in Cologne with 36 wholesome grownup contributors, together with 15 women folk and 21 men, elderly round 29 years. Those contributors had been decided on in line with their low routine caffeine consumption (lower than 450 mg in keeping with day) and non-smoking standing. The contributors had been divided into two teams: one workforce gained caffeine-containing espresso (the CAFF workforce), whilst the opposite gained decaffeinated espresso (the DECAF workforce).The experiment spanned 9 days in a managed laboratory environment. It began with an adaptation day, adopted via two baseline days the place contributors had 8 hours of sleep in keeping with night time. This used to be adopted via 5 days of continual sleep restriction, with contributors restricted to five hours of sleep in keeping with night time, and concluded with a restoration day of 8 hours of sleep. Right through the continual sleep restriction section, the CAFF workforce gained 200 mg of caffeine within the morning and 100 mg within the afternoon, whilst the DECAF workforce gained an identical volumes of decaffeinated espresso.To measure the consequences on grey subject quantity, contributors underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans and positron emission tomography (PET) scans at 3 issues: after the baseline days, after the continual sleep restriction section, and after the restoration day. Saliva samples had been accrued ceaselessly to observe caffeine ranges, making sure correct monitoring of caffeine consumption and its physiological results.The result of the find out about indicated that continual sleep restriction ended in adjustments in grey subject quantity, that have been considerably influenced via caffeine consumption. Individuals who didn’t devour caffeine (DECAF workforce) throughout the sleep restriction section confirmed an build up in grey subject quantity in numerous mind areas, together with the prefrontal cortex, temporal-occipital cortex, and thalamus. Those areas are related to more than a few cognitive and sensory purposes, indicating a possible compensatory reaction to sleep loss.“It used to be reasonably sudden to us to watch an build up, as an alternative of a lower in grey subject within the contributors with out caffeine (DECAF workforce) after continual sleep restriction,” Lin and Elmenhorst informed PsyPost. “Then again, an previous find out about (Dai et al. (2018)) make clear a possible rationalization to this discovering. This find out about tested the adjustments in grey subject alongside the route between 20 and 36 hours of wakefulness, they usually discovered that more than one mind areas in truth began from appearing an build up within the early level (20h) and grew to become to be a discount later (36h).”“Even if the have an effect on of a complete sleep deprivation may now not be generalized to continual sleep restriction, we speculated that the grey subject responses to an expanding length and/or depth of sleep loss won’t observe a linear trajectory. Extra research are undoubtedly warranted to systematically read about the grey subject adjustments in several patterns of sleep restrictions.”By contrast, contributors who ate up caffeine (CAFF workforce) throughout the sleep restriction section exhibited a lower in grey subject quantity in those similar areas. This means that caffeine may inhibit the mind’s compensatory mechanisms throughout classes of inadequate sleep, probably exacerbating the damaging have an effect on of sleep loss on mind construction.The researchers additionally discovered that particular variations in adenosine receptor availability performed an important function within the extent of grey subject adjustments. The contributors with decrease baseline availability of subcortical adenosine receptors skilled larger discounts in grey subject quantity once they ate up caffeine throughout sleep restriction. This discovering highlights the significance of adenosine receptor process in mediating the consequences of sleep deprivation and caffeine on mind construction.“Individuals who have a better A1R availability appear to have extra resistance to the impact of caffeine on grey subject,” the researchers defined. “After a restoration sleep and round 30-hour caffeine withdrawal, lots of the adjustments in grey subject have recovered, apart from the larger dorsolateral prefrontal cortex related to continual sleep restriction and the diminished thalamus related caffeine consumption,”“It’s often identified that caffeine consumption combats sleepiness. Our information additional point out that caffeine consumption additionally interferes with the mind plasticity caused via sleep loss. Then again, caffeine does now not merely suppress or normalize the grey subject exchange but additionally affects grey subject in an other way. It’s unclear how the impact of this mind plasticity manifests at the cognitive behavioral ranges; what we all know is that it’s most likely demonstrating the adenosine modulation in neural homeostasis.”Regardless of its rigorous method, the find out about has some obstacles to believe. The pattern measurement used to be somewhat small, and contributors had been decided on in line with explicit genetic profiles associated with caffeine metabolism, which may restrict how smartly the findings observe to the wider inhabitants.Moreover, whilst MRI scans confirmed adjustments in gray subject, they are able to’t let us know precisely what brought about those adjustments. It can be a achieve or lack of neurons, adjustments in synapse density, or diversifications within the selection of enhance cells like microglia. To pinpoint those explicit adjustments, long term research may use PET scans with particular markers to measure synapses, mitochondria, or microglia, the researchers defined.“The synaptic homeostasis speculation (SHY) states that ‘sleep is the fee we pay for mind plasticity,’” the researchers stated. “A decade has handed since SHY used to be printed, and this attention-grabbing speculation remains to be but to be examined in people in vivo. David due to this fact has been devoted to learning the molecular mechanism of sleep-wake laws the usage of biomedical imaging. Alternatively, Yu-Shiuan continues that specialize in pharmacological PET-MR imaging to research the adenosinergic modulation and its function within the results of caffeine. We hope that long term results alongside those traces will supply insights to the findings on this present paintings.”The find out about, “Repeated caffeine consumption suppresses cerebral gray subject responses to continual sleep restriction in an A1 adenosine receptor-dependent approach: a double-blind randomized managed find out about with PET-MRI,” used to be authored via Yu-Shiuan Lin, Denise Lange, Diego Manuel Baur, Anna Foerges, Congying Chu, Changhong Li, Eva-Maria Elmenhorst, Bernd Neumaier, Andreas Bauer, Daniel Aeschbach, Hans-Peter Landolt, and David Elmenhorst.
Caffeine exacerbates mind adjustments brought about via sleep loss, find out about suggests









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-2188577068-c0ca50790729408fafd4969812cd4a5e.jpg)


