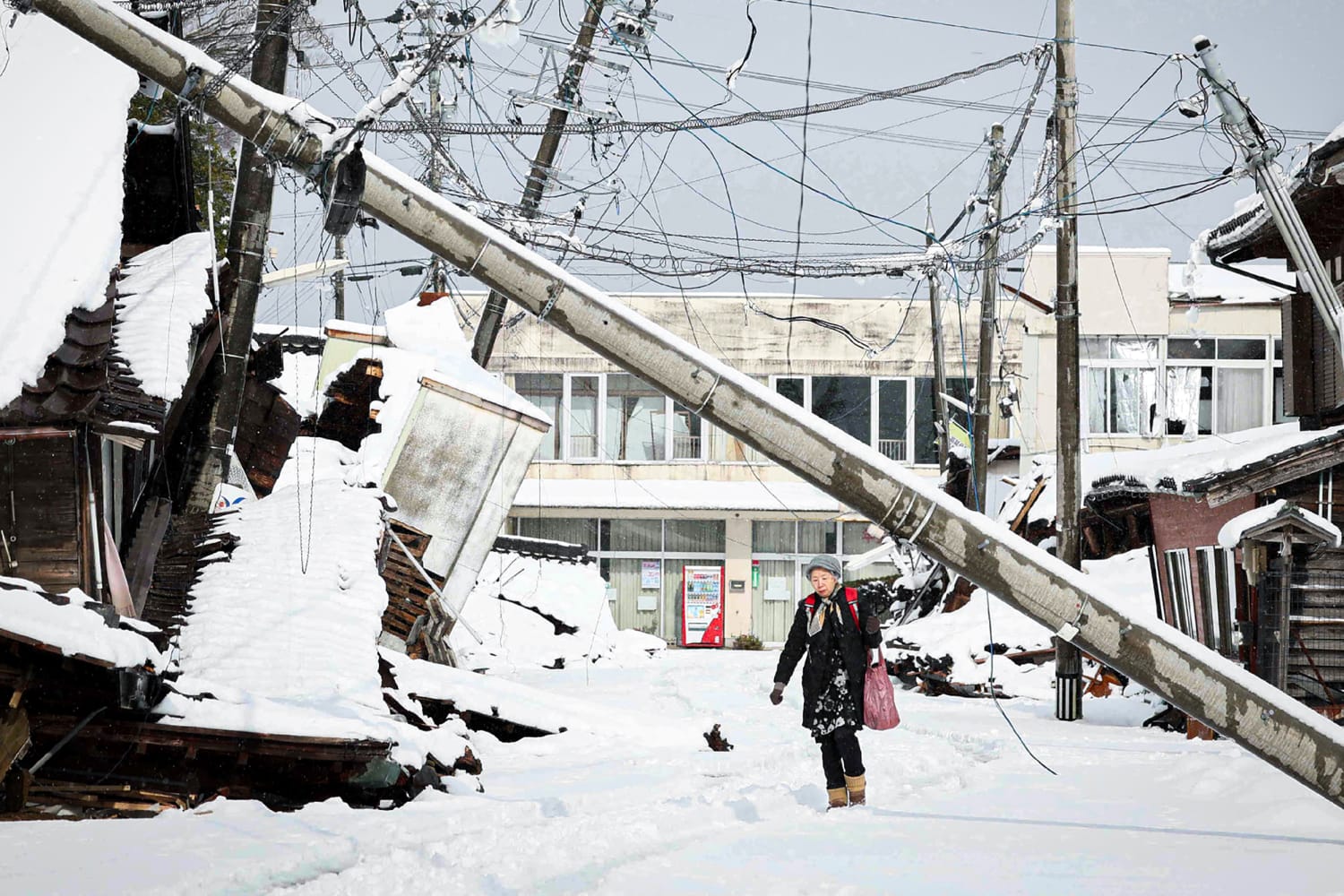
A brand new principle means that heavy snowstorm can be a think about triggering swarms of earthquakes — proof that what’s taking place on and above the Earth’s floor might play a task in occasions underground. That’s consistent with a find out about revealed Wednesday within the magazine Science Advances, which issues to a possible hyperlink between heavy snowstorm on Japan’s Noto Peninsula and 1000’s of quakes measured there since overdue 2020.It’s one of the most first research to hyperlink adjustments in climate or local weather to earthquake task. “The ones giant snowstorm occasions appear to correlate neatly with the beginning of those giant earthquake swarms,” mentioned William Frank, an writer of the find out about and an assistant professor of Earth, atmospheric and planetary sciences on the Massachusetts Institute of Era. “We shouldn’t put out of your mind the local weather itself too can play a task in converting the strain state at intensity the place earthquakes are taking place.” The find out about does no longer say that adjustments in local weather or climate are without delay inflicting earthquakes. As a substitute, it means that the velocity of earthquakes in a given house may build up or lower on account of adjustments in how water is shifting underneath the skin and what kind of force the burden of the snow exerts. David Shelly, a analysis geophysicist with america Geological Society, mentioned the find out about raises attention-grabbing questions, however extra analysis is had to validate its findings. “What they’re appearing is that seismicity turns out to start up and ramp up following those occasions of snowstorm. It’s an intriguing statement, I’m no longer positive it’s conclusive,” he mentioned. Nonetheless, Shelly expects different seismologists to be keenly within the analysis.“The collection is a topic of numerous hobby in the neighborhood. That is the primary paper that implies there could be an environmental component,” Shelly mentioned. An earthquake-affected space at the Noto Peninsula of Japan on Jan. 14.Akram Muthanna / Anadolu by means of Getty Pictures fileThe find out about evaluated 1000’s of earthquakes on Japan’s Noto Peninsula, which is situated about 190 miles northwest of Tokyo at the Sea of Japan. In 2021, after a heavy snow, the velocity of earthquakes within the house rose considerably — with loads recorded on a daily basis. “They have been seeing a factor-10 build up within the collection of earthquakes on this area in comparison to what used to be taking place in the past,” Frank mentioned. The largest within the swarm used to be a magnitude-7.5 earthquake on New Yr’s Day of this 12 months. Greater than 240 deaths have been connected to this mainshock match, consistent with the Eastern Crimson Move Society. RecommendedThe timing of the swarm used to be additionally bizarre in comparison to a normal collection of aftershocks, consistent with Frank. “They have got this statistical signature of earthquakes being pushed by means of one thing else,” he mentioned. An earthquake-affected highway buried underneath snow on Japan’s Noto Peninsula in January.Akram Muthanna / Anadolu by means of Getty Pictures fileHe and the opposite find out about authors when compared the development of earthquakes within the Noto Peninsula with a style of force inside of pores underneath the Earth’s floor. The style accounts for above-ground elements that vary the force throughout the rock beneath — corresponding to seasonal sea-level adjustments, fluctuations in atmospheric force and heavy rain or snow occasions.The consequences indicated that the burden of the snowpack at the Noto Peninsula greater the force in the ones pores. Force adjustments from including and taking away weight as snow accumulates after which melts can destabilize pre-existing faults, the researchers suppose. “When you’ve got sufficient snow, you’ll in fact be pushing the earth down and if you’re taking the snow off, it’s going to leap again up,” Frank mentioned. Some earlier analysis has additionally prompt that environmental elements can play a task in beginning earthquakes. In a 2019 find out about, Shelly and his colleagues discovered that spring snowmelt flowing into cracks within the earth close to a caldera within the house round Mammoth Lakes, California, most probably caused a swarm of earthquakes. The snowmelt recharged groundwater swiftly, and the force adjustments perceived to cause task on fairly shallow faults. The researchers discovered that seismic task within the area used to be traditionally about 37 occasions much more likely right through rainy sessions than dry. Analysis like this has piqued scientists’ interest about whether or not local weather trade may have a small affect on earthquake conduct. “There are extra research that display a connection in some circumstances between the timing of earthquakes and those processes taking place at the floor,” Shelly mentioned. “What I perceive of local weather trade forecasts is that there’s extra excessive climate, extra sessions of extended drought and excessive rainy sessions. That would possibly make those results extra evident.” Evan BushEvan Bush is a science reporter for NBC Information. He may also be reached at Evan.Bush@nbcuni.com.
Can heavy snowstorm cause earthquakes? New find out about suggests a hyperlink.