Earlier than the time of the dinosaurs, a unadorned, warm-blooded egg-layer referred to as a gorgonopsian sipped water from Pangea’s tropical floodplains amid herb-grazing reptiles off what is now Mallorca within the Mediterranean.
Its dying 270 million years in the past would possibly supply us with a important glimpse into our personal evolution. Paleontologists suspect it could be the oldest gorgonopsian specimen on file – as much as 15 million years older than any prior to now studied – making it the earliest recognized instance of a mammalian relative.
Even though the stays are incomplete, the number of bones stunned the paleontologists who discovered them. The fossils come with fragments of cranium, vertebrae, and ribs, in addition to a well-preserved femur, offering important main points at the diversification of what would turn out to be the primary true mammals.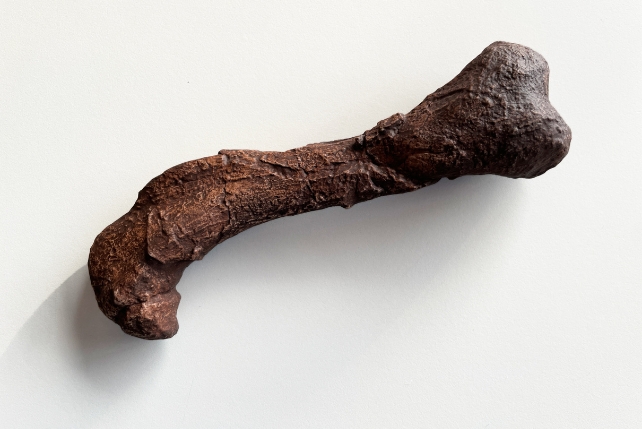 Reproduction of the left femur of the gorgonopsian from Mallorca. (Anna Solé/Institut Català de Paleontologia Miquel Crusafont/CC BY-ND)”Gorgonopsians are extra carefully associated with mammals than they’re to another residing animals,” says Ken Angielczy, a paleomammalogist from the Box Museum of Herbal Historical past in the United States. “They do not have any fashionable descendants, and whilst they are now not our direct ancestors, they are associated with species that had been our direct ancestors.”
Reproduction of the left femur of the gorgonopsian from Mallorca. (Anna Solé/Institut Català de Paleontologia Miquel Crusafont/CC BY-ND)”Gorgonopsians are extra carefully associated with mammals than they’re to another residing animals,” says Ken Angielczy, a paleomammalogist from the Box Museum of Herbal Historical past in the United States. “They do not have any fashionable descendants, and whilst they are now not our direct ancestors, they are associated with species that had been our direct ancestors.”
Whilst gorgonopsians lacked exterior ears, that they had a precursor characteristic of their jawbone that later advanced into our function mammalian ear bones. Their legs also are situated extra below their our bodies than the side-splayed reptilian legs of our older, non-mammalian ancestors.
“Should you noticed this animal strolling down the road, it could glance a little bit bit like a medium-sized canine, perhaps concerning the dimension of a husky, nevertheless it would not be slightly proper,” explains Angielczy. “It did not have any fur, and it do not need had dog-like ears.”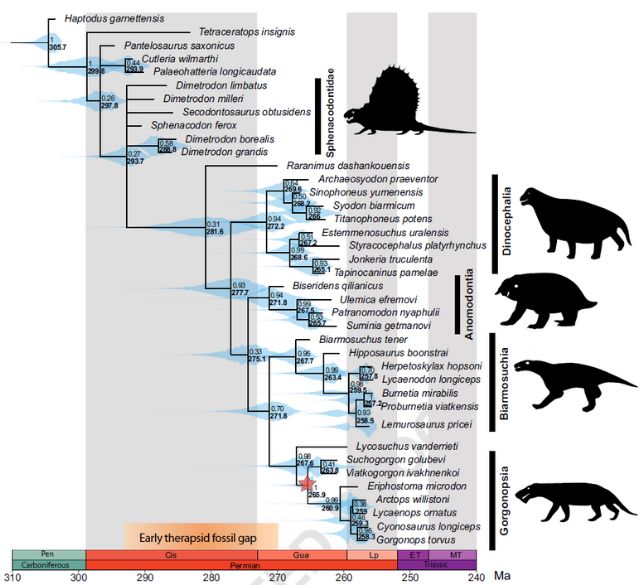 Gorgonopsia’s circle of relatives tree. (Matamales-Andreu et al, Nature Communications, 2024)Similar to mammals as of late, this this 1 meter (3 foot) lengthy gorgonopsian had jaw-muscle attachment holes at the aspects in their cranium.
Gorgonopsia’s circle of relatives tree. (Matamales-Andreu et al, Nature Communications, 2024)Similar to mammals as of late, this this 1 meter (3 foot) lengthy gorgonopsian had jaw-muscle attachment holes at the aspects in their cranium.
Those fossils paint an in depth photograph of what is additionally the earliest recognized saber-toothed animal. This enamel association suggests gorgonopsians had been the superpredators in their time, most probably devouring the herbivorous, historical lizard-like creature, Tramuntanasaurus tiai, whose bones had been discovered on the identical fossil web page.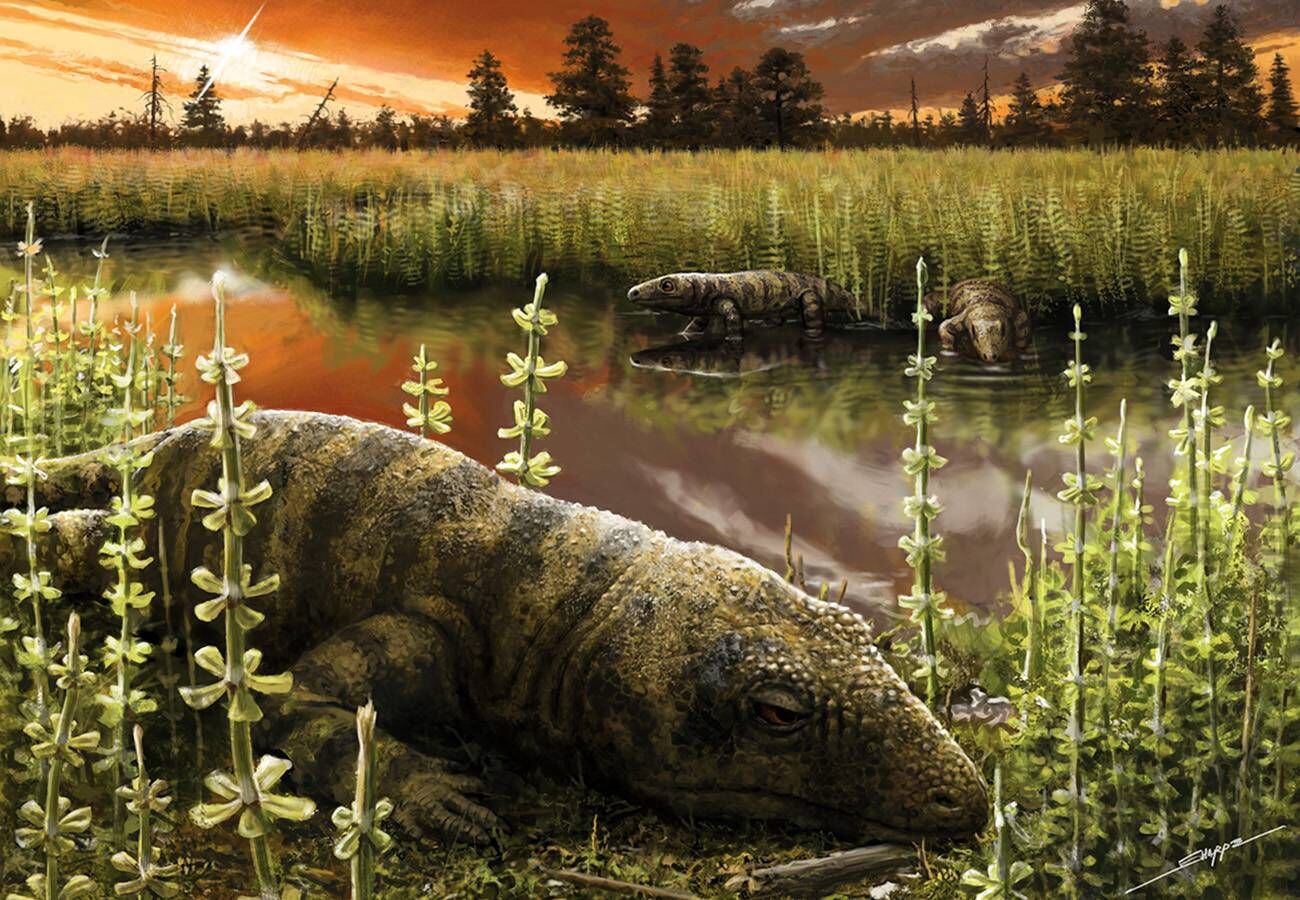 Historical 270-million-year-old reptile, Tramuntanasaurus tiai, present in the similar area. (ICP)”The saber tooth are a not unusual characteristic in massive predators of ecosystems, and what we now have discovered was once most probably one within the atmosphere during which it lived,” says ICP paleontologist Àngel Galobart. “We all know that it is a carnivorous animal, a function shared through all gorgonopsians international.”
Historical 270-million-year-old reptile, Tramuntanasaurus tiai, present in the similar area. (ICP)”The saber tooth are a not unusual characteristic in massive predators of ecosystems, and what we now have discovered was once most probably one within the atmosphere during which it lived,” says ICP paleontologist Àngel Galobart. “We all know that it is a carnivorous animal, a function shared through all gorgonopsians international.”
The workforce suspects the mass extinction match that passed off 273 million years in the past, Olson’s Extinction, will have equipped the ecological area for gorgonopsian and different mammalian ancestors to develop into and flourish, planting the seeds for our later evolution as soon as the dinosaurs had their flip. frameborder=”0″ permit=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>That this discovery was once abruptly present in what was once a tropical area suggests there is also extra clues at the origins of mammals in those areas too.
“Earlier than the time of dinosaurs, there was once an age of historical mammal relations. Maximum of the ones historical mammal relations appeared actually other from what we bring to mind mammals taking a look like as of late,” says Angielczyk.
“However they had been actually numerous and performed numerous other ecological roles. The invention of this new fossil is every other piece of the puzzle for the way mammals advanced.”This analysis was once printed in Nature Communications.
Canine-Like Predator’s Bones Belong to Oldest Identified Mammal Relative











