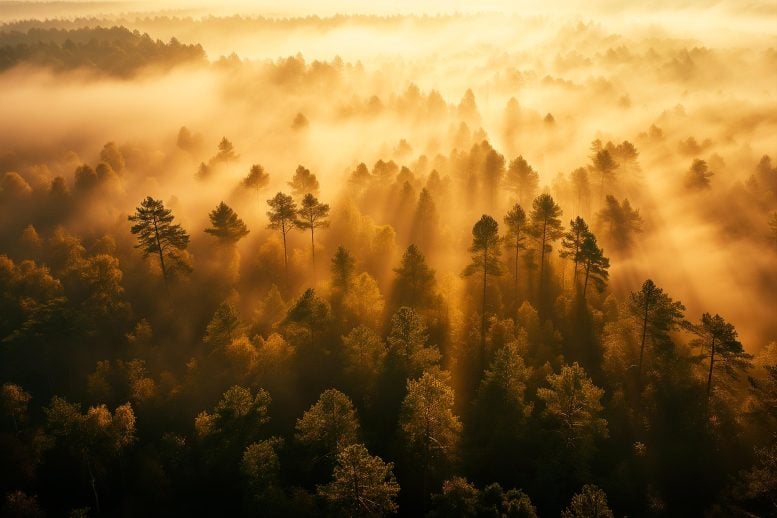
A brand new learn about displays that local weather exchange is disproportionately affecting U.S. forests, in particular within the West, the place opposed results like lowered tree enlargement are outstanding. This pattern demanding situations the forests’ position as carbon sinks and highlights the pressing want for greenhouse fuel emission discounts and woodland conservation. Credit score: SciTechDaily.comClimate exchange is impacting U.S. forests, particularly within the Western areas, resulting in reduced tree enlargement and difficult their talent to behave as carbon sinks.Local weather exchange is reshaping forests otherwise throughout america, in step with a brand new research of U.S. Woodland Carrier information. With emerging temperatures, escalating droughts, wildfires, and illness outbreaks taking a toll on bushes, researchers warn that forests around the American West are bearing the brunt of the results.Find out about Finds Regional Disparities in Woodland HealthThe learn about, led by way of UF Biology researchers J. Aaron Hogan and Jeremy W. Lichstein was once printed within the Court cases of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences. The learn about unearths a pronounced regional imbalance in woodland productiveness, a key barometer of woodland well being that gauges tree enlargement and biomass accumulation. Over the last twenty years, the Western U.S., grappling with extra critical local weather exchange affects, has exhibited a notable slowdown in productiveness, whilst the Japanese U.S., experiencing milder local weather results, has observed fairly speeded up enlargement.Forests as Carbon Sinks and Local weather RegulatorsForests play a important position in regulating the Earth’s local weather, performing as carbon sinks that sequester roughly 25% of human carbon emissions every year. Then again, their talent to retailer carbon hinges at the subtle stability between the certain and unwanted effects of local weather exchange. The learn about, the usage of national-scale woodland stock information, fashions developments from 1999 to 2020, inspecting 113,806 measurements in non-plantation forests.“We’re witnessing adjustments in woodland functioning as woodland ecosystems reply to world exchange drivers, corresponding to carbon dioxide fertilization and local weather exchange,” stated Hogan. “It’s the long run stability of those drivers which is able to decide the functioning of forests within the coming years to many years.”Carbon-Dioxide Fertilization and Tree GrowthSome drivers, corresponding to droughts and woodland pathogens, have unwanted effects on productiveness, however different drivers, corresponding to carbon dioxide fertilization, are predicted to have certain results. This phenomenon means that larger carbon dioxide ranges give a boost to plant enlargement by way of expanding photosynthesis, which galvanized the researchers to take a deeper have a look at its have an effect on.“The U.S. Woodland Carrier has been tracking the expansion and survival of over one million bushes around the U.S. for a couple of many years,” stated Lichstein. “We have been to look if their information equipped proof for larger charges of tree enlargement, as predicted by way of the carbon-dioxide fertilization speculation.”Difficult Assumptions About Carbon StorageWhile tree enlargement within the Japanese U.S. aligns with expectancies, the Western area displays excessive local weather results overshadowing any certain enlargement developments, difficult the present assumption that forests’ carbon-storing talent will proceed to extend.“Our learn about means that long run projections of local weather and sea-level upward push is also too constructive as a result of, in fact, ecosystems are prone to retailer much less carbon someday,” stated Lichstein. “Much less ecosystem carbon garage method extra carbon within the environment and due to this fact extra warming and accelerating local weather exchange.”Regional Permutations and Local weather ThresholdsThe findings additionally remove darkness from the truth that local weather exchange isn’t a uniform pressure however moderately a dynamic agent with region-specific influences. The learn about illustrates how the stage of local weather exchange can push forests previous a tipping level. Some forests are already coming near or surpassing local weather thresholds which shift them to change into assets of carbon, moderately than sinks that take away carbon from the ambience.“Ecosystem carbon sequestration isn’t assured to be everlasting, and it may be reversed by way of local weather exchange,” stated Lichstein. “This reversal is already taking place within the Western U.S., and there are indicators that it will also be taking place in different drought-impacted areas of the sector, such because the Amazon.”It could be tempting to chalk the losses as much as excessive occasions. However, in step with the researchers, the decline in productiveness within the Western U.S. can’t be attributed to larger charges of tree mortality.Decline in Tree Expansion and Productiveness“We listen so much about wildfires within the Western U.S., which kill numerous bushes and liberate carbon to the ambience,” stated Lichstein. “However our learn about displays that further ecosystem carbon loss in Western forests is going on because of declining tree enlargement charges.”With bushes rising slower because of opposed local weather exchange results, together with reduced precipitation, the learn about means that, even with out the intensifying wildfires, the carbon sink in Western forests will proceed to weaken with out pressing motion to cut back human greenhouse fuel emissions.“We should have wholesome forests in reference to emissions aid to revive the worldwide carbon stability and restrict local weather exchange,” stated Hogan.Pressing Want for Woodland Conservation and Emissions ReductionThe transformations noticed in U.S. forests lift considerations about their long run resilience and sustainability. The researchers hope their findings spotlight the pressing want for governments and trade to paintings in combination to cut back greenhouse fuel emissions and reach net-zero emissions once imaginable.“Our effects spotlight the will for lowered world greenhouse fuel emissions,” stated Lichstein. “With out the emissions discounts that scientists were urging for many years, woodland carbon sinks will most likely weaken, which is able to boost up the tempo of local weather exchange.”Reference: “Local weather exchange determines the signal of productiveness developments in US forests” by way of J. Aaron Hogan, Grant M. Domke, Kai Zhu, Daniel J. Johnson and Jeremy W. Lichstein, 16 January 2024, Court cases of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
A brand new learn about displays that local weather exchange is disproportionately affecting U.S. forests, in particular within the West, the place opposed results like lowered tree enlargement are outstanding. This pattern demanding situations the forests’ position as carbon sinks and highlights the pressing want for greenhouse fuel emission discounts and woodland conservation. Credit score: SciTechDaily.comClimate exchange is impacting U.S. forests, particularly within the Western areas, resulting in reduced tree enlargement and difficult their talent to behave as carbon sinks.Local weather exchange is reshaping forests otherwise throughout america, in step with a brand new research of U.S. Woodland Carrier information. With emerging temperatures, escalating droughts, wildfires, and illness outbreaks taking a toll on bushes, researchers warn that forests around the American West are bearing the brunt of the results.Find out about Finds Regional Disparities in Woodland HealthThe learn about, led by way of UF Biology researchers J. Aaron Hogan and Jeremy W. Lichstein was once printed within the Court cases of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences. The learn about unearths a pronounced regional imbalance in woodland productiveness, a key barometer of woodland well being that gauges tree enlargement and biomass accumulation. Over the last twenty years, the Western U.S., grappling with extra critical local weather exchange affects, has exhibited a notable slowdown in productiveness, whilst the Japanese U.S., experiencing milder local weather results, has observed fairly speeded up enlargement.Forests as Carbon Sinks and Local weather RegulatorsForests play a important position in regulating the Earth’s local weather, performing as carbon sinks that sequester roughly 25% of human carbon emissions every year. Then again, their talent to retailer carbon hinges at the subtle stability between the certain and unwanted effects of local weather exchange. The learn about, the usage of national-scale woodland stock information, fashions developments from 1999 to 2020, inspecting 113,806 measurements in non-plantation forests.“We’re witnessing adjustments in woodland functioning as woodland ecosystems reply to world exchange drivers, corresponding to carbon dioxide fertilization and local weather exchange,” stated Hogan. “It’s the long run stability of those drivers which is able to decide the functioning of forests within the coming years to many years.”Carbon-Dioxide Fertilization and Tree GrowthSome drivers, corresponding to droughts and woodland pathogens, have unwanted effects on productiveness, however different drivers, corresponding to carbon dioxide fertilization, are predicted to have certain results. This phenomenon means that larger carbon dioxide ranges give a boost to plant enlargement by way of expanding photosynthesis, which galvanized the researchers to take a deeper have a look at its have an effect on.“The U.S. Woodland Carrier has been tracking the expansion and survival of over one million bushes around the U.S. for a couple of many years,” stated Lichstein. “We have been to look if their information equipped proof for larger charges of tree enlargement, as predicted by way of the carbon-dioxide fertilization speculation.”Difficult Assumptions About Carbon StorageWhile tree enlargement within the Japanese U.S. aligns with expectancies, the Western area displays excessive local weather results overshadowing any certain enlargement developments, difficult the present assumption that forests’ carbon-storing talent will proceed to extend.“Our learn about means that long run projections of local weather and sea-level upward push is also too constructive as a result of, in fact, ecosystems are prone to retailer much less carbon someday,” stated Lichstein. “Much less ecosystem carbon garage method extra carbon within the environment and due to this fact extra warming and accelerating local weather exchange.”Regional Permutations and Local weather ThresholdsThe findings additionally remove darkness from the truth that local weather exchange isn’t a uniform pressure however moderately a dynamic agent with region-specific influences. The learn about illustrates how the stage of local weather exchange can push forests previous a tipping level. Some forests are already coming near or surpassing local weather thresholds which shift them to change into assets of carbon, moderately than sinks that take away carbon from the ambience.“Ecosystem carbon sequestration isn’t assured to be everlasting, and it may be reversed by way of local weather exchange,” stated Lichstein. “This reversal is already taking place within the Western U.S., and there are indicators that it will also be taking place in different drought-impacted areas of the sector, such because the Amazon.”It could be tempting to chalk the losses as much as excessive occasions. However, in step with the researchers, the decline in productiveness within the Western U.S. can’t be attributed to larger charges of tree mortality.Decline in Tree Expansion and Productiveness“We listen so much about wildfires within the Western U.S., which kill numerous bushes and liberate carbon to the ambience,” stated Lichstein. “However our learn about displays that further ecosystem carbon loss in Western forests is going on because of declining tree enlargement charges.”With bushes rising slower because of opposed local weather exchange results, together with reduced precipitation, the learn about means that, even with out the intensifying wildfires, the carbon sink in Western forests will proceed to weaken with out pressing motion to cut back human greenhouse fuel emissions.“We should have wholesome forests in reference to emissions aid to revive the worldwide carbon stability and restrict local weather exchange,” stated Hogan.Pressing Want for Woodland Conservation and Emissions ReductionThe transformations noticed in U.S. forests lift considerations about their long run resilience and sustainability. The researchers hope their findings spotlight the pressing want for governments and trade to paintings in combination to cut back greenhouse fuel emissions and reach net-zero emissions once imaginable.“Our effects spotlight the will for lowered world greenhouse fuel emissions,” stated Lichstein. “With out the emissions discounts that scientists were urging for many years, woodland carbon sinks will most likely weaken, which is able to boost up the tempo of local weather exchange.”Reference: “Local weather exchange determines the signal of productiveness developments in US forests” by way of J. Aaron Hogan, Grant M. Domke, Kai Zhu, Daniel J. Johnson and Jeremy W. Lichstein, 16 January 2024, Court cases of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2311132121This learn about was once evolved with Grant Domke from the U.S. Woodland Carrier Northern Analysis Station, Kai Zhu from the College of Michigan, and Dan Johnson from UF’s College of Woodland, Fisheries, and Geomatics Sciences.
Carbon Sinks in Disaster: Local weather Trade Threatens World Woodland CO2 Sequestration