Earth isn’t any stranger to sun storms. Simply this 12 months we have now been bombarded with storms, some so robust they have got caused jaw-dropping auroras deep into mid-latitudes.Trendy generation guarantees that little or no is going overlooked. A fleet of satellites continuously displays area climate, whilst scientists analyze information and learn about its results on Earth. In the meantime, skywatchers flip their gaze and cameras skyward to seize the captivating auroras ignited via geomagnetic storms. However what about sun storms that happened previous to the introduction of recent generation? If a sun typhoon of exceptional magnitude took place hundreds of years in the past how would we all know?Fortunate for us historical timber act as time pills, silently recording Earth’s historical past. A analysis workforce from the College of Arizona led via Irina Panyushkina and Timothy Jull is unlocking those arboreal secrets and techniques via moderately inspecting tree rings to expose proof of colossal sun storms referred to as Miyake Occasions. Those area climate occasions are so uncommon that simplest 6 had been detected up to now 14,500 years, the newest of which took place simply between 664 and 663 BCE.We are fortunate this most up-to-date Miyake tournament came about goodbye in the past, the researchers say. “In the event that they came about these days, they’d have cataclysmic results on verbal exchange generation,” Panyushkina stated in a observation.Miyake occasions constitute an excessive form of sun process first recognized in 2012 via Eastern physicist Fusa Miyake. Miyake, a collaborator with Panyushkina’s workforce, revealed analysis revealing the unique signature of those occasions: sharp will increase in radioactive carbon isotopes, in particular carbon-14, present in tree expansion rings, consistent with the observation.Carbon-14 is a naturally happening radioactive variant of carbon, it paperwork within the setting when cosmic radiation interacts with nitrogen. Sooner or later, this carbon-14 reacts with oxygen to shape carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide then enters the timber by the use of photosynthesis.”After a couple of months, carbon-14 may have traveled from the stratosphere to the decrease setting, the place it’s taken up via timber and turns into a part of the picket as they develop,” Panyushkina stated within the observation.Breaking area information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!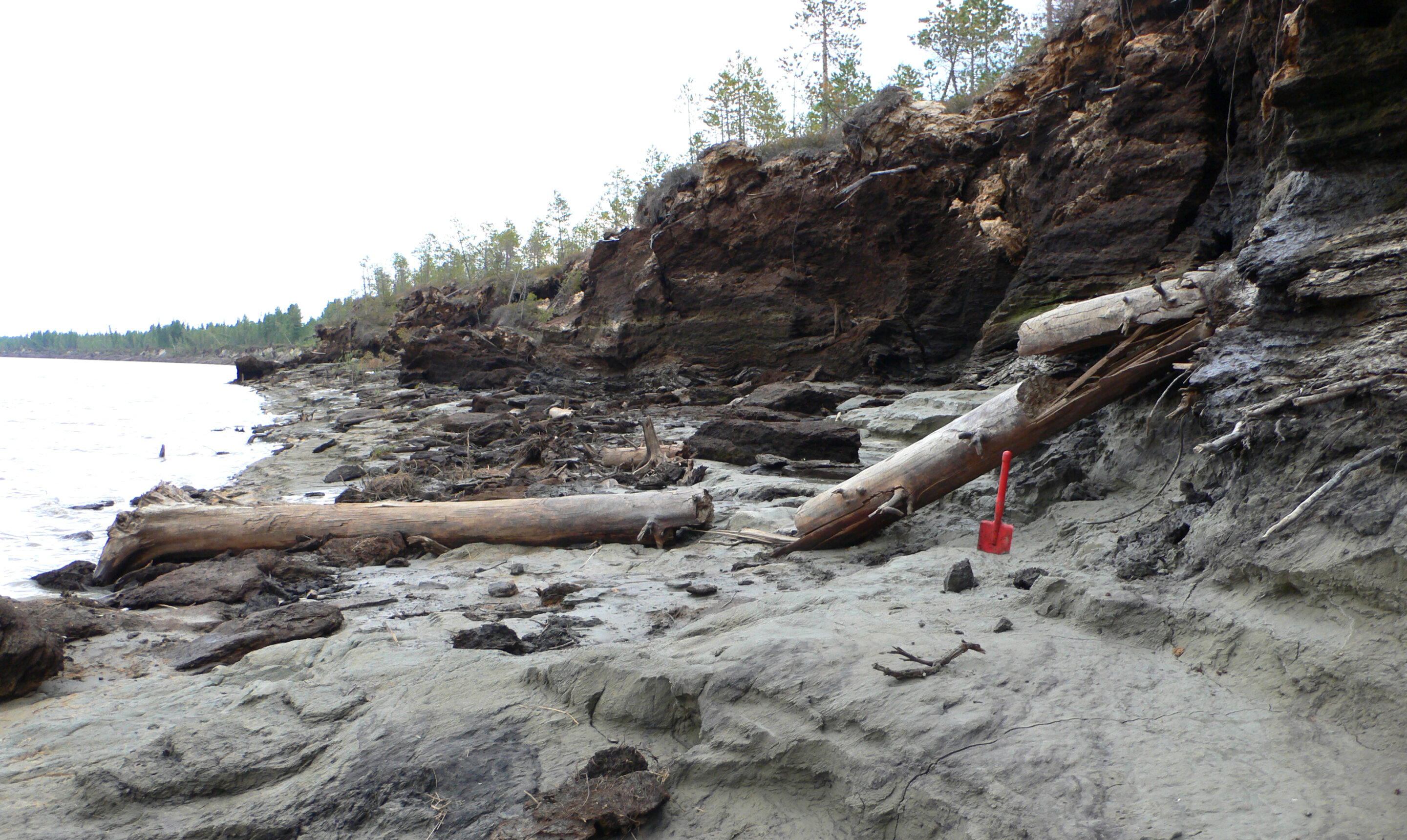 The trunk of an historical larch tree lies uncovered at the muddy banks of the river Ob in Siberia. Samples from such timber that lived a very long time in the past allowed the researchers to seek for spikes in radiocarbon documenting excessive sun storms within the far-off previous. (Symbol credit score: Irina Panyushkina)Panyushkina and her workforce on the College of Arizona moderately dissected person tree rings from historical picket samples gathered from lifeless timber buried in riverbanks in addition to timbers excavated all over archaeological digs. The principle element of the picket, the cellulose, is then burned to decide the radiocarbon content material.When a radiocarbon spike is detected, the researchers then examine the tree-ring information to spikes in several isotopes similar to beryllium-10 which has been locked away in ice cores retrieved from glaciers and ice sheets, every other nice herbal time tablet. Identical to carbon-14, beryllium-10 paperwork within the setting on account of a bombardment of sun debris, precipitation similar to rain or snow captures the isotope and locks it into an ice sheet.”If ice cores from each the North Pole and South Pole display a spike within the isotope beryllium-10 for a selected 12 months comparable to higher radiocarbon in tree-rings, we all know there used to be a sun typhoon,” Panyushkina stated within the observation.Each tree ring and ice information pinpointed the date of the intense Miyake sun typhoon whose timing had lengthy eluded researchers to between 664 and 663 BCE.The learn about is revealed within the magazine Communications Earth & Atmosphere.
The trunk of an historical larch tree lies uncovered at the muddy banks of the river Ob in Siberia. Samples from such timber that lived a very long time in the past allowed the researchers to seek for spikes in radiocarbon documenting excessive sun storms within the far-off previous. (Symbol credit score: Irina Panyushkina)Panyushkina and her workforce on the College of Arizona moderately dissected person tree rings from historical picket samples gathered from lifeless timber buried in riverbanks in addition to timbers excavated all over archaeological digs. The principle element of the picket, the cellulose, is then burned to decide the radiocarbon content material.When a radiocarbon spike is detected, the researchers then examine the tree-ring information to spikes in several isotopes similar to beryllium-10 which has been locked away in ice cores retrieved from glaciers and ice sheets, every other nice herbal time tablet. Identical to carbon-14, beryllium-10 paperwork within the setting on account of a bombardment of sun debris, precipitation similar to rain or snow captures the isotope and locks it into an ice sheet.”If ice cores from each the North Pole and South Pole display a spike within the isotope beryllium-10 for a selected 12 months comparable to higher radiocarbon in tree-rings, we all know there used to be a sun typhoon,” Panyushkina stated within the observation.Each tree ring and ice information pinpointed the date of the intense Miyake sun typhoon whose timing had lengthy eluded researchers to between 664 and 663 BCE.The learn about is revealed within the magazine Communications Earth & Atmosphere.
‘Cataclysmic’ sun typhoon hit Earth round 2687 years in the past, historical tree rings disclose