Via C Raina MacIntyre, Ashley Quigley, Haley Stone, Matthew Scotch, and Rebecca Dawson April 8, 2024 The CDC issued a well being alert after a cow-to-human transmission of H5N1 chicken flu in Texas, marking a regarding building within the unfold of this extremely pathogenic virus, which has been affecting more than a few species globally and posing doable pandemic dangers.A Texas farm employee gotten smaller H5N1 from dairy farm animals, indicating a brand new direction of transmission for the virus, which has a prime mortality charge and various signs in people.America’ Facilities for Illness Keep watch over and Prevention (CDC) has issued a well being alert after the primary case of H5N1 avian influenza, or chicken flu, apparently unfold from a cow to a human.A farm employee in Texas gotten smaller the virus amid a plague in dairy farm animals. That is the second one human case in america; a poultry employee examined sure in Colorado in 2022.The virus pressure recognized within the Texan farm employee isn’t readily transmissible between people and subsequently now not an epidemic risk. But it surely’s an important building nevertheless.An individual examined sure for avian influenza after being uncovered to cows regarded as inflamed with the virus. It is the second one time a human has been inflamed with H5N1 within the U.S. Medical American (@sciam) April 4, 2024Some Background on Fowl FluThere are two sorts of avian influenza: extremely pathogenic or low pathogenic, in accordance with the extent of illness the stress reasons in birds. H5N1 is a extremely pathogenic avian influenza.H5N1 first emerged in 1997 in Hong Kong after which China in 2003, spreading via wild chicken migration and poultry buying and selling. It has brought about periodic epidemics in poultry farms, with occasional human instances.Influenza A viruses equivalent to H5N1 are additional divided into variants, known as clades. The original variant inflicting the present epidemic is H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b, which emerged in overdue 2020 and is now well-liked globally, particularly within the Americas.Prior to now, outbreaks may well be managed by way of culling of inflamed birds, and H5N1 would die down for some time. However this has turn into an increasing number of tricky because of escalating outbreaks since 2021.Wild Animals Are Now within the MixWaterfowl (geese, swans, and ducks) are the principle world spreaders of avian flu, as they migrate internationally by way of particular routes that bypass Australia. The primary hub for waterfowl emigrate world wide is Quinghai lake in China.However there’s been more and more inflamed non-waterfowl birds, equivalent to true thrushes and raptors, which use other flyways. Worryingly, the an infection has unfold to Antarctica too, this means that Australia is now in peril from other chicken species that fly right here.H5N1 has escalated in an exceptional model since 2021, and more and more mammals together with sea lions, goats, purple foxes, coyotes, or even home canine and cats have turn into inflamed world wide.Wild animals like purple foxes which are living in peri-urban spaces are a conceivable new direction of unfold to farms, home pets, and people.Dairy cows and goats have now turn into inflamed with H5N1 in a minimum of 17 farms throughout seven US states.What Are the Signs?Globally, there were 14 instances of H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b virus in people, and 889 H5N1 human instances general since 2003.Earlier human instances have introduced with a serious respiration sickness, however H5N1 2.3.4.4b is inflicting sickness affecting different organs too, just like the mind, eyes, and liver.As an example, more moderen instances have evolved neurological headaches together with seizures, organ failure, and stroke. It’s been estimated that round part of folks inflamed with H5N1 will die.The case within the Texan farm employee seems to be delicate. This individual introduced with conjunctivitis, which is bizarre.Meals SafetyContact with unwell poultry is a key chance issue for human an infection. Likewise, the farm employee in Texas used to be most probably in shut touch with the inflamed farm animals.The CDC advises that pasteurized milk and well-cooked eggs are secure. On the other hand, dealing with of inflamed meat or eggs within the strategy of cooking, or ingesting unpasteurized milk, might pose a chance.Even if there’s no H5N1 in Australian poultry or farm animals, hygienic meals practices are all the time a good suggestion, as uncooked milk or poorly cooked meat, eggs or poultry may also be infected with microbes equivalent to salmonella and E. coli.If It’s No longer a Pandemic, Why Are We Frightened?Scientists have feared avian influenza might motive an epidemic since about 2005. Avian flu viruses don’t simply unfold in people. But when an avian virus mutates to unfold in people, it might motive an epidemic.One fear is that if birds had been to contaminate an animal like a pig, this acts as a genetic blending vessel. In spaces the place people and farm animals exist in shut proximity, for instance, farms, markets and even in houses with yard poultry, the chance of chicken and human flu traces blending and mutating to motive a brand new pandemic pressure is upper.
The CDC issued a well being alert after a cow-to-human transmission of H5N1 chicken flu in Texas, marking a regarding building within the unfold of this extremely pathogenic virus, which has been affecting more than a few species globally and posing doable pandemic dangers.A Texas farm employee gotten smaller H5N1 from dairy farm animals, indicating a brand new direction of transmission for the virus, which has a prime mortality charge and various signs in people.America’ Facilities for Illness Keep watch over and Prevention (CDC) has issued a well being alert after the primary case of H5N1 avian influenza, or chicken flu, apparently unfold from a cow to a human.A farm employee in Texas gotten smaller the virus amid a plague in dairy farm animals. That is the second one human case in america; a poultry employee examined sure in Colorado in 2022.The virus pressure recognized within the Texan farm employee isn’t readily transmissible between people and subsequently now not an epidemic risk. But it surely’s an important building nevertheless.An individual examined sure for avian influenza after being uncovered to cows regarded as inflamed with the virus. It is the second one time a human has been inflamed with H5N1 within the U.S. Medical American (@sciam) April 4, 2024Some Background on Fowl FluThere are two sorts of avian influenza: extremely pathogenic or low pathogenic, in accordance with the extent of illness the stress reasons in birds. H5N1 is a extremely pathogenic avian influenza.H5N1 first emerged in 1997 in Hong Kong after which China in 2003, spreading via wild chicken migration and poultry buying and selling. It has brought about periodic epidemics in poultry farms, with occasional human instances.Influenza A viruses equivalent to H5N1 are additional divided into variants, known as clades. The original variant inflicting the present epidemic is H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b, which emerged in overdue 2020 and is now well-liked globally, particularly within the Americas.Prior to now, outbreaks may well be managed by way of culling of inflamed birds, and H5N1 would die down for some time. However this has turn into an increasing number of tricky because of escalating outbreaks since 2021.Wild Animals Are Now within the MixWaterfowl (geese, swans, and ducks) are the principle world spreaders of avian flu, as they migrate internationally by way of particular routes that bypass Australia. The primary hub for waterfowl emigrate world wide is Quinghai lake in China.However there’s been more and more inflamed non-waterfowl birds, equivalent to true thrushes and raptors, which use other flyways. Worryingly, the an infection has unfold to Antarctica too, this means that Australia is now in peril from other chicken species that fly right here.H5N1 has escalated in an exceptional model since 2021, and more and more mammals together with sea lions, goats, purple foxes, coyotes, or even home canine and cats have turn into inflamed world wide.Wild animals like purple foxes which are living in peri-urban spaces are a conceivable new direction of unfold to farms, home pets, and people.Dairy cows and goats have now turn into inflamed with H5N1 in a minimum of 17 farms throughout seven US states.What Are the Signs?Globally, there were 14 instances of H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b virus in people, and 889 H5N1 human instances general since 2003.Earlier human instances have introduced with a serious respiration sickness, however H5N1 2.3.4.4b is inflicting sickness affecting different organs too, just like the mind, eyes, and liver.As an example, more moderen instances have evolved neurological headaches together with seizures, organ failure, and stroke. It’s been estimated that round part of folks inflamed with H5N1 will die.The case within the Texan farm employee seems to be delicate. This individual introduced with conjunctivitis, which is bizarre.Meals SafetyContact with unwell poultry is a key chance issue for human an infection. Likewise, the farm employee in Texas used to be most probably in shut touch with the inflamed farm animals.The CDC advises that pasteurized milk and well-cooked eggs are secure. On the other hand, dealing with of inflamed meat or eggs within the strategy of cooking, or ingesting unpasteurized milk, might pose a chance.Even if there’s no H5N1 in Australian poultry or farm animals, hygienic meals practices are all the time a good suggestion, as uncooked milk or poorly cooked meat, eggs or poultry may also be infected with microbes equivalent to salmonella and E. coli.If It’s No longer a Pandemic, Why Are We Frightened?Scientists have feared avian influenza might motive an epidemic since about 2005. Avian flu viruses don’t simply unfold in people. But when an avian virus mutates to unfold in people, it might motive an epidemic.One fear is that if birds had been to contaminate an animal like a pig, this acts as a genetic blending vessel. In spaces the place people and farm animals exist in shut proximity, for instance, farms, markets and even in houses with yard poultry, the chance of chicken and human flu traces blending and mutating to motive a brand new pandemic pressure is upper.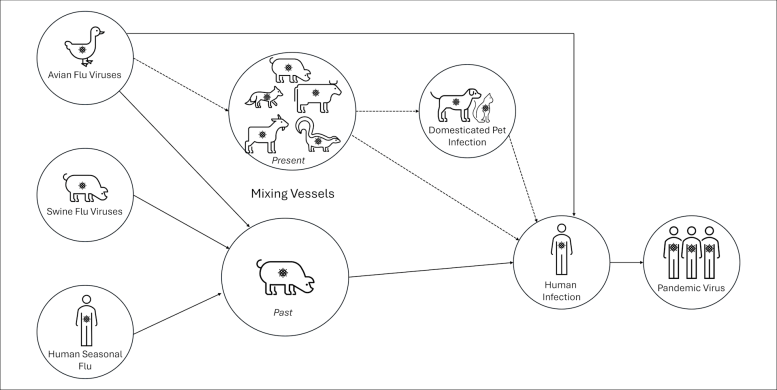 There are a selection of doable pathways to an epidemic brought about by way of influenza. Credit score: Creator providedThe cows inflamed in Texas had been examined as a result of farmers spotted they had been generating much less milk. If red meat farm animals are in a similar fashion affected, it might not be as simply recognized, and the commercial loss to farmers could also be a disincentive to check or file infections.How Can We Save you a Pandemic?For now there’s no unfold of H5N1 between people, so there’s no rapid chance of an epidemic.On the other hand, we have now exceptional and protracted an infection with H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b in farms, wild animals and a much broader vary of untamed birds than ever sooner than, growing extra probabilities for H5N1 to mutate and motive an epidemic.Not like the former epidemiology of avian flu, the place sizzling spots had been in Asia, the brand new sizzling spots (and most probably websites of emergence of an epidemic) are within the Americas, Europe or in Africa.Pandemics develop exponentially, so early warnings for animal and human outbreaks are a very powerful. We will track infections the usage of surveillance equipment equivalent to our EPIWATCH platform.
There are a selection of doable pathways to an epidemic brought about by way of influenza. Credit score: Creator providedThe cows inflamed in Texas had been examined as a result of farmers spotted they had been generating much less milk. If red meat farm animals are in a similar fashion affected, it might not be as simply recognized, and the commercial loss to farmers could also be a disincentive to check or file infections.How Can We Save you a Pandemic?For now there’s no unfold of H5N1 between people, so there’s no rapid chance of an epidemic.On the other hand, we have now exceptional and protracted an infection with H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b in farms, wild animals and a much broader vary of untamed birds than ever sooner than, growing extra probabilities for H5N1 to mutate and motive an epidemic.Not like the former epidemiology of avian flu, the place sizzling spots had been in Asia, the brand new sizzling spots (and most probably websites of emergence of an epidemic) are within the Americas, Europe or in Africa.Pandemics develop exponentially, so early warnings for animal and human outbreaks are a very powerful. We will track infections the usage of surveillance equipment equivalent to our EPIWATCH platform.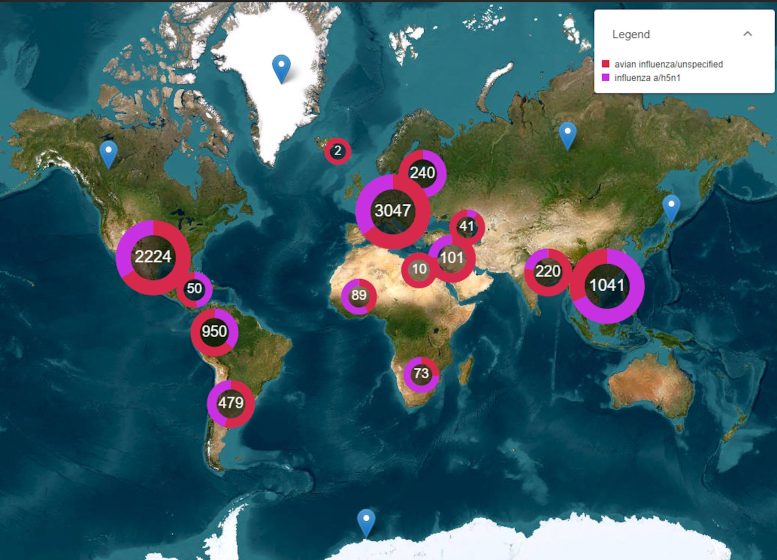 This map displays avian flu studies on EPIWATCH. Credit score: EPIWATCH/writer providedThe previous epidemics may also be detected, the simpler the risk of stamping them out and impulsively growing vaccines.Even if there’s a vaccine for birds, it’s been in large part have shyed away from till lately as it’s handiest in part efficient and will masks outbreaks. But it surely’s now not possible to keep watch over a plague by way of culling inflamed birds, so some nations like France started vaccinating poultry in 2023.For people, seasonal flu vaccines might supply a small quantity of cross-protection, however for the most efficient defense, vaccines wish to be matched precisely to the pandemic pressure, and this takes time. The 2009 flu pandemic began in Might in Australia, however the vaccines had been to be had in September, after the pandemic top.To scale back the danger of an epidemic, we should determine how H5N1 is spreading to such a lot of mammalian species, what new wild chicken pathways pose a chance, and track for early indicators of outbreaks and sickness in animals, birds, and people. Financial repayment for farmers could also be a very powerful to verify we come across all outbreaks and keep away from compromising the meals provide.Written by way of:C Raina MacIntyre – Professor of International Biosecurity, NHMRC L3 Analysis Fellow, Head, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute, UNSW SydneyAshley Quigley – Senior Analysis Affiliate, International Biosecurity, UNSW SydneyHaley Stone – PhD Candidate, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute, UNSW SydneyMatthew Scotch – Affiliate Dean of Analysis and Professor of Biomedical Informatics, School of Well being Answers, Arizona State UniversityRebecca Dawson – Analysis Affiliate, The Kirby Institute, UNSW SydneyAdapted from an editorial at the beginning printed in The Dialog.
This map displays avian flu studies on EPIWATCH. Credit score: EPIWATCH/writer providedThe previous epidemics may also be detected, the simpler the risk of stamping them out and impulsively growing vaccines.Even if there’s a vaccine for birds, it’s been in large part have shyed away from till lately as it’s handiest in part efficient and will masks outbreaks. But it surely’s now not possible to keep watch over a plague by way of culling inflamed birds, so some nations like France started vaccinating poultry in 2023.For people, seasonal flu vaccines might supply a small quantity of cross-protection, however for the most efficient defense, vaccines wish to be matched precisely to the pandemic pressure, and this takes time. The 2009 flu pandemic began in Might in Australia, however the vaccines had been to be had in September, after the pandemic top.To scale back the danger of an epidemic, we should determine how H5N1 is spreading to such a lot of mammalian species, what new wild chicken pathways pose a chance, and track for early indicators of outbreaks and sickness in animals, birds, and people. Financial repayment for farmers could also be a very powerful to verify we come across all outbreaks and keep away from compromising the meals provide.Written by way of:C Raina MacIntyre – Professor of International Biosecurity, NHMRC L3 Analysis Fellow, Head, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute, UNSW SydneyAshley Quigley – Senior Analysis Affiliate, International Biosecurity, UNSW SydneyHaley Stone – PhD Candidate, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute, UNSW SydneyMatthew Scotch – Affiliate Dean of Analysis and Professor of Biomedical Informatics, School of Well being Answers, Arizona State UniversityRebecca Dawson – Analysis Affiliate, The Kirby Institute, UNSW SydneyAdapted from an editorial at the beginning printed in The Dialog.![]()
CDC Warns of Cow-to-Human Transmission of H5N1 Fowl Flu in Texas











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-699097697-ae69508d0dbd402d8db8f46f05cc0b16.jpg)

