We analyzed CSF samples from 609 people that have been decided on from the Alzheimer Middle Amsterdam connected studies15,16,17,18 (for medical main points, see Strategies and Supplementary Desk 1). Of this pattern, 419 people had AD as outlined by means of an unusual amyloid biomarker and integrated all medical levels (this is, 107 with standard cognition, 103 with delicate cognitive impairment (MCI) and 209 with dementia). The 187 controls have been required to have standard cognition and standard amyloid and tau biomarkers. CSF proteins from each and every pattern have been enzymatically digested and the peptides have been categorized with tandem mass tags (TMTs), fractionated and analyzed by means of liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) (Strategies). A complete of three,863 proteins was once recognized, of which 1,309 proteins (outlined by means of 28,408 peptides) have been seen throughout all people. We then examined which proteins had other ranges in people with AD in comparison to controls, and repeated the ones analyses stratified on tau ranges or illness level as a result of protein ranges can exchange in a nonlinear method with those variables12,19. This ended in the number of 1,058 AD-related proteins for cluster analyses (Supplementary Desk 2; it additionally contains knowledge on the peptide degree). We then clustered people with AD on AD-related proteins with nonnegative matrix factorization20, which is a twin clustering method (Supplementary Fig. 1). A specific power of the set of rules is that persons are according to definition allotted to at least one subtype, which turns out to be useful for analysis or affected person stratification for trials.5 AD subtypes that vary on medical characteristicsThe sufferers’ proteomic profiles clustered into 5 subtypes (Fig. 1a and Supplementary Desk 3 for the are compatible and balance statistics): subtypes 1, 2 and 5 recapitulated our in the past detected subtypes with neuronal hyperplasticity (subtype 1), innate immune activation (subtype 2) and blood–mind barrier disorder (subtype 5); two further subtypes emerged: one with RNA dysregulation (subtype 3) and one with choroid plexus disorder (subtype 4). We examined the robustness of the subtypes by means of clustering the weighted protein coexpression community once more with the Louvain set of rules (Strategies), which additionally led to 5 protein clusters that have been very similar to the NMF protein clusters (93.5% overlap of cluster-specific proteins (Supplementary Desk 4, column X). The following sections speak about each and every subtype intimately in step with molecular, genetic and medical traits. We in brief summarize the subtype variations. Subgroups have been in comparison to controls and each and every different, with estimated marginal approach from linear fashions for steady results, that have been two-tailed assessments, and proportions have been examined with chi-squared assessments and repeated for each and every pairwise team aggregate (Desk 1, please observe those comparisons are uncorrected for more than one trying out as a result of it is a descriptive desk). In comparison to controls, subtypes 1, 2 and three had greater CSF t-tau and p-tau ranges, whilst subtypes 4 and 5 had most commonly standard tau ranges (see Desk 1 and Supplementary Desk 5for further analyses stratified in step with cognitive state and altered for intercourse and age). Subtypes differed in step with medical level, intercourse and age; all next analyses took those traits into consideration. In comparison to controls, subtypes differed within the charges of development from MCI to dementia, with subtypes 2 and 5 having the perfect chance, and subtype 4 the bottom (Fig. second), even if variations between subtypes didn’t succeed in statistical importance (Supplementary Desk 6a). Subtype 3 people with dementia had the shortest moderate survival time of five.6 years, which was once shorter than subtype 1 with the longest moderate survival time of 8.9 years (P = 0.04; Fig. 2 and Supplementary Desk 6b), and steeper decline on Mini Psychological State Exam (MMSE), language and reminiscence assessments (Prolonged Knowledge Figs. 1 and a couple of and Supplementary Desk 7). Those effects means that other underlying molecular processes would possibly provide an explanation for part of between-patient variability in decline. Research of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans in people with dementia (n = 159) indicated that subtypes differed within the stage and anatomical location of cortical atrophy (Fig. 2 and Supplementary Desk 8). All subtypes had a better occurrence of the APOE e4 genotype than controls, and a better AD PRS, supporting their underlying AD genetic chance structure. On the other hand, subtypes had distinct AD genetic chance profiles (mentioned intimately under).Desk 1 Comparability of subtypes in step with medical characteristicsWe subsequent tested the molecular processes related to the AD subtypes. For each and every subtype, we when put next the degrees of two,878 proteins towards the keep watch over team (Fig. 1b and Supplementary Desk 4). Proteins with other ranges between a subtype and the keep watch over team have been integrated within the enrichment analyses to review related organic processes and transcription elements. To assist comparison with the gene expression literature, we record gene names for proteins (see Supplementary Desk 4 for the UniProt codes). Stratification in step with medical level led to equivalent variations to controls (correlations of results ranging between 0.85 and zero.98; Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 4), additional supporting that AD subtypes replicate particular illness traits8,13.Fig. 1: Organic description of AD subtypes.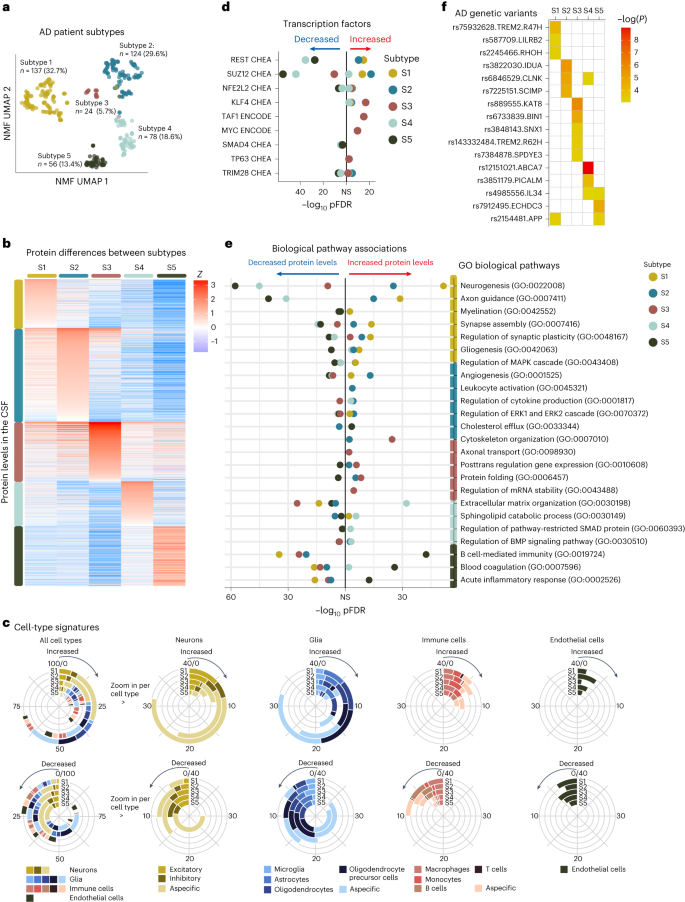 a, Affected person subtypes projected to the uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) area. b, CSF protein ranges (rows) averaged throughout people inside subtypes (columns). c, Mobile-type-specificity signatures for proteins related to the AD subtypes for proteins with greater (best row) and reduced (backside row) degree. The left circle diagram presentations all cellular varieties related to a subtype mixed. Proteins that would now not be assigned to a selected cellular form weren’t plotted (no color to 100% within the left circle diagrams). The circle diagrams to the correct zoom into the subcategories of particular cellular varieties (neurons, glia, immune cells and endothelial cells). Mobile-type specificity was once made up our minds in step with the Human Protein Atlas. d, Best transcription elements related to subtypes from the CHEA and ENCODE databases. e, Gene Ontology (GO) organic pathways related to subtypes (see Supplementary Desk 9 for all pathways). f, AD genetic chance elements related to particular subtypes; white signifies now not statistically vital. Variations between subtypes and controls have been made up our minds from linear regression fashions with estimated marginal approach, offering a two-tailed take a look at for team comparisons, uncorrected for more than one trying out as a result of it is a submit hoc comparability. Supplementary Tables 4 and 9–11 record all of the proteins, pathways, and transcription and genetic elements examined with the statistical metrics. NS, now not statistically vital; S1, subtype 1 (hyperplasticity); S2, subtype 2 (innate immune activation); S3, subtype 3 (RNA dysregulation); S4, subtype 4 (choroid plexus disorder); S5, subtype 5 (blood–mind barrier disorder).Beneath, we spotlight subtype-specific associations with organic processes, cellular varieties, AD genetic chance variants and atrophy patterns (see Supplementary Tables 4–11 for detailed effects).Subtype 1 hyperplasticitySubtype 1 people (n = 137, 32.7%) had 827 proteins with greater CSF ranges and 408 proteins with reduced ranges in comparison to controls. Of all of the subtypes, subtype 1 had the perfect share of proteins particular for neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and oligodendrocyte precursor cells (Fig. 1c). Proteins with greater ranges have been related to neuronal plasticity processes, together with synapse meeting, axon steerage, neurogenesis and gliogenesis (Fig. 1e; see Supplementary Desk 9 for all organic processes enriched). As well as, this neuronal hyperplasticity subtype had prime BACE1, amyloid-β1–40 and tau CSF ranges (Desk 1), as we in the past seen within the hyperplasticity subtype8. Whilst prime tau ranges have been in the past idea to replicate neuronal loss because of tangle formation, extra research are indicating that this may additionally replicate different processes21,22. As an example, neurons with greater job secrete extra amyloid and tau23,24,25,26,27; such hyperactive neurons were seen close to plaques28. Fragments of amyloid and tau would possibly in flip pressure hyperplasticity thru enhanced gene transcription29. Certainly, proteins greater in subtype 1 have been enriched for the transcription elements REST (Padjusted = 0.018 × 10−13; Fig. 1d and Supplementary Desk 7) and SUZ12 (Padjusted = 0.016 × 10−12), which control plasticity-related processes thru repression of neuronal differentiation genes30,31. Earlier research pointed against REST de-repression and will increase of tau and plasticity-related processes in AD mind tissue7,32, triggered pluripotent stem cellular (iPSC) neurons33,34 and tau tangle-bearing neurons35. Evaluating subtype 1 greater proteins with the ones research, we discovered an overlap 5 of six from Lu et al.32, 65 of 173 from Meyer et al.33 and 46 of 127 from Otero-Gracia35 (Supplementary Desk 4, columns AZ-BB). Additionally, with the upper choice of proteins that we measured in comparison to our earlier find out about, we discovered further mechanisms that can give a contribution to the plasticity reaction seen on this subtype. As an example, subtype 1 had the perfect CSF ranges of the lysosomal protein PLD3. Prime PLD3 ranges were reported in dystrophic neurites related to ‘amyloid axonal spheroids’36. Such spheroids cause axonal transforming and native hyperactivity36. Dystrophic neurites additionally gather BACE1, which is related to greater APP metabolism37, and would possibly provide an explanation for the increased BACE1 and amyloid-β ranges on this subtype.Subsequent, we examined which AD genetic chance variants4 have been overrepresented on this subtype in comparison to controls. We discovered enrichment for TREM2R47H and variants in LILRB2, RHOH and APP (Fig. 1f and Supplementary Desk 11a). This subtype additionally integrated 3 of the 4 PSEN1 carriers and 3 of the 4 NCK2 carriers (Supplementary Desk 11b). TREM2 is a transmembrane protein that may turn on microglia when ligands, together with amyloid fibrils, bind to its extracellular part14. The R47H variant alters the extracellular phase, lowering its skill to bind ligands, leading to dampened microglia activation38,39. LILRB2 mediates TREM2 signaling and has additionally been related to dampened immune activation40,41. RHOH and NCK2 encode signaling molecules downstream from TREM2 that affect cytoskeleton rearrangement of microglia, which permits migration towards pathogens and amyloid plaques42. Usually, activated microglia shape a decent barrier round plaques, which decreases plaque floor and minimizes plaque touch with neurites14,38,43. When microglial activation is dampened, as seen in carriers of TREM2 variants, amyloid plaques are much less compact, with poisonous oligomers protruding that would harm close by neurites44 and would possibly result in axonal dystrophy44, most likely triggering a plasticity reaction as an try to restore. TREM2 has additionally been implicated in impaired microglial synaptic pruning, which might additional give a contribution to the hyperplasticity signature seen on this subtype45,46,47. Such an far more than synapses was once in the past related to milder atrophy in TREM2 mouse models45. MRI analyses in our knowledge indicated that this subtype had much less atrophy in comparison to the opposite subtypes (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 3 and Supplementary Desk 9), and was once limited to the temporal and parietal lobes.In combination, our effects supply additional enhance for a hyperplasticity subtype in AD, and supply further insights into the underlying mechanisms, comparable to that this subtype may well be associated with a dampened microglial reaction. Remedies boosting TREM2 activation are underneath development48. We argue that folks with this subtype may additionally reply to such therapies, even with out wearing the TREM2 R47H variant.Subtype 2 innate immune activationSubtype 2 people (n = 124, 29.6%) had, in comparison to controls, 986 proteins with greater CSF ranges and 506 with reduced ranges. A prime share of proteins greater in subtype 2 was once particular to microglia. Proteins with greater ranges have been related to innate immune activation, together with law of cytokine manufacturing. Those integrated proteins from the supplement advanced (C1QA, C1QB, C1QC, C1S and C1R), in addition to APOE and LPL, in step with our earlier findings. Moreover, we now seen that this subtype additionally had greater ranges of the microglial Tyro3, Axl and Mer (TAM) receptors AXL and MERTK, and GAS6 (a MERTK ligand), which is able to come across and engulf plaques49. We additional discovered greater PYCARD ranges in particular in subtype 2. PYCARD is sometimes called apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC), and is launched by means of microglia with NLRP3 inflammasome activation50,51. PYCARD can shape ASC specks, that are fibrils that irritate amyloid aggregation51 and induce tau phosphorylation52, offering a possible mechanism in which microglial activation would possibly irritate AD pathology. Certainly, subtype 2 people had upper p-tau ranges than observed in subtype 1 (Desk 1). Different subtype 2 greater proteins have been associated with neuron-microglia signaling, together with CSF1, CSF1R and CX3CL1. Neuroimmune signaling happens all through standard neuronal construction when microglia prune immature synapses53,54,55. In AD, activated microglia close to diffuse and neuritic plaques would possibly result in over the top synaptic pruning53. This is able to result in exacerbated atrophy as proven in mouse models56. In step with the ones fashions, subtype 2 was once one of the crucial two subtypes with essentially the most critical and common cortical atrophy on MRI in comparison to subtypes 1, 3 and 5 (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 2). Nonetheless, in spite of this critical atrophy, the degrees of proteins associated with neuroplasticity have been greater on this subtype and those proteins overlapped with subtype 1; they have been additionally enriched for the transcription elements REST and SUZ12. Perhaps, the rise of plasticity-related proteins would possibly replicate an try to restore synaptic contacts, which succumbs within the presence of activated microglia. On the other hand, greater protein ranges would possibly replicate neuronal loss.The AD genetic variants related to this subtype have been IDUA, CLNK and SCIMP, that are all excited by immune processes4,57.In combination, those effects give further detailed insights into the innate immune activation AD subtype and recommend that an overactive innate immune device worsens the illness.Subtype 3 RNA dysregulationSubtype 3 (n = 24, 5.7%) emerged as one of the crucial two further subtypes. In comparison to controls, this subtype had greater CSF ranges for 516 proteins and reduced ranges for 757 proteins. Proteins with greater ranges have been related to cytoskeleton group, axonal shipping, and proteasome and protein folding (Supplementary Tables 4 and 9). This subtype had the perfect t-tau and NEFL CSF ranges. BACE1 ranges have been upper than in controls (Desk 1), however in contrast to subtypes 1 and a couple of, amyloid-β40 ranges have been very similar to controls, suggesting a distinct mechanism related to upper BACE1 ranges for this subtype. Proteins in particular greater in subtype 3 integrated heterogenous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) and different RNA-binding proteins, which would possibly level to RNA dysregulation. HnRNPs are concerned within the maturation of pre-mRNAs, mRNA stabilization all through shipping and native mRNA translation for plenty of RNAs, together with the ones vital for cytoskeleton organization58. Disruptions in hnRNPs and mRNA were related to tau tangles in earlier proteomic studies59. Mislocalized hnRNPs may just lead to dysfunctional proteins because of mis-splicing or cryptic splicing60. As an example, TDP43 mislocalization can result in cryptic splicing of STMN2 (ref. 61), leading to shorter proteins and reduced STMN2 ranges in tissue62. STMN2 was once detected in a subset (n = 84) of our pattern, and subtype 3 had reduced ranges of STMN2 in comparison to controls. Transcription elements related to subtype 3 greater proteins have been KLF4 (Padjusted = 0.02 × 10−15), which is related to axon regeneration63, and TAF1 (Padjusted = 0.008 × 10−13) and MYC (Padjusted = 0.02 × 10−10), that are interacting elements in cellular differentiation processes64,65. A prior gene expression find out about in mind tissue discovered a equivalent AD subtype with greater TAF1 and MYC signaling and aberrant synapse organization7.When trying out AD genetic chance elements, we discovered enrichment for BIN1, which is referred to as ‘Myc-box-dependent interplay protein’. Considered one of BIN1’s purposes is to bodily inhibit MYC66. BIN1 basically localizes in axons and has many isoforms coming up from splicing66. BIN1 mis-splicing has been related to de-inhibition of MYC and cytoskeleton disruption67. TREM2 R62H was once additionally related to this subtype. Different genetic chance variants related to subtype 3 integrated SPDYE3, concerned within the cellular cycle, SNX1, vital for endosome sorting, and KAT8, a lysine acetyltransferase4,57.Whilst RNA disorder has been basically seen in frontotemporal dementia68, those processes have additionally been seen in AD in tissue5 and tau tangle proteomic studies59; our effects means that this will also be detected within the CSF of a selected AD subtype.Subtype 4 choroid plexus dysfunctionSubtype 4 (n = 78, 18.6%) was once the opposite further subtype. In comparison to controls, this subtype had greater CSF ranges of 467 proteins and reduced ranges of 626 proteins. A prime share of proteins greater in subtype 4 have been particular to microglia and different immune cells. Additionally, a big subset of proteins with greater ranges (45%) was once related to prime expression within the lateral ventricle choroid plexus (Supplementary Desk 4), together with TTR, SPARC and extracellular matrix proteins comparable to DCN, LUM and COLA12. Organic processes related to subtype 4 integrated cellular adhesion, and BMP and SMAD pathways, that are excited by choroid plexus development69. The choroid plexus is situated alongside the ventricles, the place it produces CSF and is chargeable for nutrient, lipid and protein switch around the blood–CSF barrier69. It is composed of a extremely evolved extracellular matrix that connects a dense vasculature to its epithelial cells69. On MRI, subtype 4 had the biggest choroid plexus quantity (Fig. 2b). Larger choroid plexus quantity has been related to irritation and structural alterations in AD70,71. Even though this subtype maximum steadily had standard t-tau and p-tau ranges (Desk 1), it had worse atrophy than subtypes 1, 3 and 5, with particular involvement of anterior cingulate spaces (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 3). Moreover, proteins greater in subtype 4 have been enriched for fibroblasts (Supplementary Desk 4), which produce extracellular matrix proteins and supply structural enhance to the choroid plexus. Different proteins greater in subtype 4 integrated cytokines, comparable to CCL2, CCL21 and CCL15, which is able to draw in monocytes and T lymphocytes72. Of observe, proteins with reduced ranges in subtype 4 have been associated with axonal outgrowth and synaptic plasticity (for instance, BDNF), partly overlapping with proteins greater in subtypes 1 and a couple of, and have been additionally enriched for REST and SUZ12. This means that subtype 2 may be characterised by means of neuronal hypoplasticity.Fig. 2: AD subtype comparisons on MRI and medical results.
a, Affected person subtypes projected to the uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) area. b, CSF protein ranges (rows) averaged throughout people inside subtypes (columns). c, Mobile-type-specificity signatures for proteins related to the AD subtypes for proteins with greater (best row) and reduced (backside row) degree. The left circle diagram presentations all cellular varieties related to a subtype mixed. Proteins that would now not be assigned to a selected cellular form weren’t plotted (no color to 100% within the left circle diagrams). The circle diagrams to the correct zoom into the subcategories of particular cellular varieties (neurons, glia, immune cells and endothelial cells). Mobile-type specificity was once made up our minds in step with the Human Protein Atlas. d, Best transcription elements related to subtypes from the CHEA and ENCODE databases. e, Gene Ontology (GO) organic pathways related to subtypes (see Supplementary Desk 9 for all pathways). f, AD genetic chance elements related to particular subtypes; white signifies now not statistically vital. Variations between subtypes and controls have been made up our minds from linear regression fashions with estimated marginal approach, offering a two-tailed take a look at for team comparisons, uncorrected for more than one trying out as a result of it is a submit hoc comparability. Supplementary Tables 4 and 9–11 record all of the proteins, pathways, and transcription and genetic elements examined with the statistical metrics. NS, now not statistically vital; S1, subtype 1 (hyperplasticity); S2, subtype 2 (innate immune activation); S3, subtype 3 (RNA dysregulation); S4, subtype 4 (choroid plexus disorder); S5, subtype 5 (blood–mind barrier disorder).Beneath, we spotlight subtype-specific associations with organic processes, cellular varieties, AD genetic chance variants and atrophy patterns (see Supplementary Tables 4–11 for detailed effects).Subtype 1 hyperplasticitySubtype 1 people (n = 137, 32.7%) had 827 proteins with greater CSF ranges and 408 proteins with reduced ranges in comparison to controls. Of all of the subtypes, subtype 1 had the perfect share of proteins particular for neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and oligodendrocyte precursor cells (Fig. 1c). Proteins with greater ranges have been related to neuronal plasticity processes, together with synapse meeting, axon steerage, neurogenesis and gliogenesis (Fig. 1e; see Supplementary Desk 9 for all organic processes enriched). As well as, this neuronal hyperplasticity subtype had prime BACE1, amyloid-β1–40 and tau CSF ranges (Desk 1), as we in the past seen within the hyperplasticity subtype8. Whilst prime tau ranges have been in the past idea to replicate neuronal loss because of tangle formation, extra research are indicating that this may additionally replicate different processes21,22. As an example, neurons with greater job secrete extra amyloid and tau23,24,25,26,27; such hyperactive neurons were seen close to plaques28. Fragments of amyloid and tau would possibly in flip pressure hyperplasticity thru enhanced gene transcription29. Certainly, proteins greater in subtype 1 have been enriched for the transcription elements REST (Padjusted = 0.018 × 10−13; Fig. 1d and Supplementary Desk 7) and SUZ12 (Padjusted = 0.016 × 10−12), which control plasticity-related processes thru repression of neuronal differentiation genes30,31. Earlier research pointed against REST de-repression and will increase of tau and plasticity-related processes in AD mind tissue7,32, triggered pluripotent stem cellular (iPSC) neurons33,34 and tau tangle-bearing neurons35. Evaluating subtype 1 greater proteins with the ones research, we discovered an overlap 5 of six from Lu et al.32, 65 of 173 from Meyer et al.33 and 46 of 127 from Otero-Gracia35 (Supplementary Desk 4, columns AZ-BB). Additionally, with the upper choice of proteins that we measured in comparison to our earlier find out about, we discovered further mechanisms that can give a contribution to the plasticity reaction seen on this subtype. As an example, subtype 1 had the perfect CSF ranges of the lysosomal protein PLD3. Prime PLD3 ranges were reported in dystrophic neurites related to ‘amyloid axonal spheroids’36. Such spheroids cause axonal transforming and native hyperactivity36. Dystrophic neurites additionally gather BACE1, which is related to greater APP metabolism37, and would possibly provide an explanation for the increased BACE1 and amyloid-β ranges on this subtype.Subsequent, we examined which AD genetic chance variants4 have been overrepresented on this subtype in comparison to controls. We discovered enrichment for TREM2R47H and variants in LILRB2, RHOH and APP (Fig. 1f and Supplementary Desk 11a). This subtype additionally integrated 3 of the 4 PSEN1 carriers and 3 of the 4 NCK2 carriers (Supplementary Desk 11b). TREM2 is a transmembrane protein that may turn on microglia when ligands, together with amyloid fibrils, bind to its extracellular part14. The R47H variant alters the extracellular phase, lowering its skill to bind ligands, leading to dampened microglia activation38,39. LILRB2 mediates TREM2 signaling and has additionally been related to dampened immune activation40,41. RHOH and NCK2 encode signaling molecules downstream from TREM2 that affect cytoskeleton rearrangement of microglia, which permits migration towards pathogens and amyloid plaques42. Usually, activated microglia shape a decent barrier round plaques, which decreases plaque floor and minimizes plaque touch with neurites14,38,43. When microglial activation is dampened, as seen in carriers of TREM2 variants, amyloid plaques are much less compact, with poisonous oligomers protruding that would harm close by neurites44 and would possibly result in axonal dystrophy44, most likely triggering a plasticity reaction as an try to restore. TREM2 has additionally been implicated in impaired microglial synaptic pruning, which might additional give a contribution to the hyperplasticity signature seen on this subtype45,46,47. Such an far more than synapses was once in the past related to milder atrophy in TREM2 mouse models45. MRI analyses in our knowledge indicated that this subtype had much less atrophy in comparison to the opposite subtypes (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 3 and Supplementary Desk 9), and was once limited to the temporal and parietal lobes.In combination, our effects supply additional enhance for a hyperplasticity subtype in AD, and supply further insights into the underlying mechanisms, comparable to that this subtype may well be associated with a dampened microglial reaction. Remedies boosting TREM2 activation are underneath development48. We argue that folks with this subtype may additionally reply to such therapies, even with out wearing the TREM2 R47H variant.Subtype 2 innate immune activationSubtype 2 people (n = 124, 29.6%) had, in comparison to controls, 986 proteins with greater CSF ranges and 506 with reduced ranges. A prime share of proteins greater in subtype 2 was once particular to microglia. Proteins with greater ranges have been related to innate immune activation, together with law of cytokine manufacturing. Those integrated proteins from the supplement advanced (C1QA, C1QB, C1QC, C1S and C1R), in addition to APOE and LPL, in step with our earlier findings. Moreover, we now seen that this subtype additionally had greater ranges of the microglial Tyro3, Axl and Mer (TAM) receptors AXL and MERTK, and GAS6 (a MERTK ligand), which is able to come across and engulf plaques49. We additional discovered greater PYCARD ranges in particular in subtype 2. PYCARD is sometimes called apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC), and is launched by means of microglia with NLRP3 inflammasome activation50,51. PYCARD can shape ASC specks, that are fibrils that irritate amyloid aggregation51 and induce tau phosphorylation52, offering a possible mechanism in which microglial activation would possibly irritate AD pathology. Certainly, subtype 2 people had upper p-tau ranges than observed in subtype 1 (Desk 1). Different subtype 2 greater proteins have been associated with neuron-microglia signaling, together with CSF1, CSF1R and CX3CL1. Neuroimmune signaling happens all through standard neuronal construction when microglia prune immature synapses53,54,55. In AD, activated microglia close to diffuse and neuritic plaques would possibly result in over the top synaptic pruning53. This is able to result in exacerbated atrophy as proven in mouse models56. In step with the ones fashions, subtype 2 was once one of the crucial two subtypes with essentially the most critical and common cortical atrophy on MRI in comparison to subtypes 1, 3 and 5 (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 2). Nonetheless, in spite of this critical atrophy, the degrees of proteins associated with neuroplasticity have been greater on this subtype and those proteins overlapped with subtype 1; they have been additionally enriched for the transcription elements REST and SUZ12. Perhaps, the rise of plasticity-related proteins would possibly replicate an try to restore synaptic contacts, which succumbs within the presence of activated microglia. On the other hand, greater protein ranges would possibly replicate neuronal loss.The AD genetic variants related to this subtype have been IDUA, CLNK and SCIMP, that are all excited by immune processes4,57.In combination, those effects give further detailed insights into the innate immune activation AD subtype and recommend that an overactive innate immune device worsens the illness.Subtype 3 RNA dysregulationSubtype 3 (n = 24, 5.7%) emerged as one of the crucial two further subtypes. In comparison to controls, this subtype had greater CSF ranges for 516 proteins and reduced ranges for 757 proteins. Proteins with greater ranges have been related to cytoskeleton group, axonal shipping, and proteasome and protein folding (Supplementary Tables 4 and 9). This subtype had the perfect t-tau and NEFL CSF ranges. BACE1 ranges have been upper than in controls (Desk 1), however in contrast to subtypes 1 and a couple of, amyloid-β40 ranges have been very similar to controls, suggesting a distinct mechanism related to upper BACE1 ranges for this subtype. Proteins in particular greater in subtype 3 integrated heterogenous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) and different RNA-binding proteins, which would possibly level to RNA dysregulation. HnRNPs are concerned within the maturation of pre-mRNAs, mRNA stabilization all through shipping and native mRNA translation for plenty of RNAs, together with the ones vital for cytoskeleton organization58. Disruptions in hnRNPs and mRNA were related to tau tangles in earlier proteomic studies59. Mislocalized hnRNPs may just lead to dysfunctional proteins because of mis-splicing or cryptic splicing60. As an example, TDP43 mislocalization can result in cryptic splicing of STMN2 (ref. 61), leading to shorter proteins and reduced STMN2 ranges in tissue62. STMN2 was once detected in a subset (n = 84) of our pattern, and subtype 3 had reduced ranges of STMN2 in comparison to controls. Transcription elements related to subtype 3 greater proteins have been KLF4 (Padjusted = 0.02 × 10−15), which is related to axon regeneration63, and TAF1 (Padjusted = 0.008 × 10−13) and MYC (Padjusted = 0.02 × 10−10), that are interacting elements in cellular differentiation processes64,65. A prior gene expression find out about in mind tissue discovered a equivalent AD subtype with greater TAF1 and MYC signaling and aberrant synapse organization7.When trying out AD genetic chance elements, we discovered enrichment for BIN1, which is referred to as ‘Myc-box-dependent interplay protein’. Considered one of BIN1’s purposes is to bodily inhibit MYC66. BIN1 basically localizes in axons and has many isoforms coming up from splicing66. BIN1 mis-splicing has been related to de-inhibition of MYC and cytoskeleton disruption67. TREM2 R62H was once additionally related to this subtype. Different genetic chance variants related to subtype 3 integrated SPDYE3, concerned within the cellular cycle, SNX1, vital for endosome sorting, and KAT8, a lysine acetyltransferase4,57.Whilst RNA disorder has been basically seen in frontotemporal dementia68, those processes have additionally been seen in AD in tissue5 and tau tangle proteomic studies59; our effects means that this will also be detected within the CSF of a selected AD subtype.Subtype 4 choroid plexus dysfunctionSubtype 4 (n = 78, 18.6%) was once the opposite further subtype. In comparison to controls, this subtype had greater CSF ranges of 467 proteins and reduced ranges of 626 proteins. A prime share of proteins greater in subtype 4 have been particular to microglia and different immune cells. Additionally, a big subset of proteins with greater ranges (45%) was once related to prime expression within the lateral ventricle choroid plexus (Supplementary Desk 4), together with TTR, SPARC and extracellular matrix proteins comparable to DCN, LUM and COLA12. Organic processes related to subtype 4 integrated cellular adhesion, and BMP and SMAD pathways, that are excited by choroid plexus development69. The choroid plexus is situated alongside the ventricles, the place it produces CSF and is chargeable for nutrient, lipid and protein switch around the blood–CSF barrier69. It is composed of a extremely evolved extracellular matrix that connects a dense vasculature to its epithelial cells69. On MRI, subtype 4 had the biggest choroid plexus quantity (Fig. 2b). Larger choroid plexus quantity has been related to irritation and structural alterations in AD70,71. Even though this subtype maximum steadily had standard t-tau and p-tau ranges (Desk 1), it had worse atrophy than subtypes 1, 3 and 5, with particular involvement of anterior cingulate spaces (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 3). Moreover, proteins greater in subtype 4 have been enriched for fibroblasts (Supplementary Desk 4), which produce extracellular matrix proteins and supply structural enhance to the choroid plexus. Different proteins greater in subtype 4 integrated cytokines, comparable to CCL2, CCL21 and CCL15, which is able to draw in monocytes and T lymphocytes72. Of observe, proteins with reduced ranges in subtype 4 have been associated with axonal outgrowth and synaptic plasticity (for instance, BDNF), partly overlapping with proteins greater in subtypes 1 and a couple of, and have been additionally enriched for REST and SUZ12. This means that subtype 2 may be characterised by means of neuronal hypoplasticity.Fig. 2: AD subtype comparisons on MRI and medical results.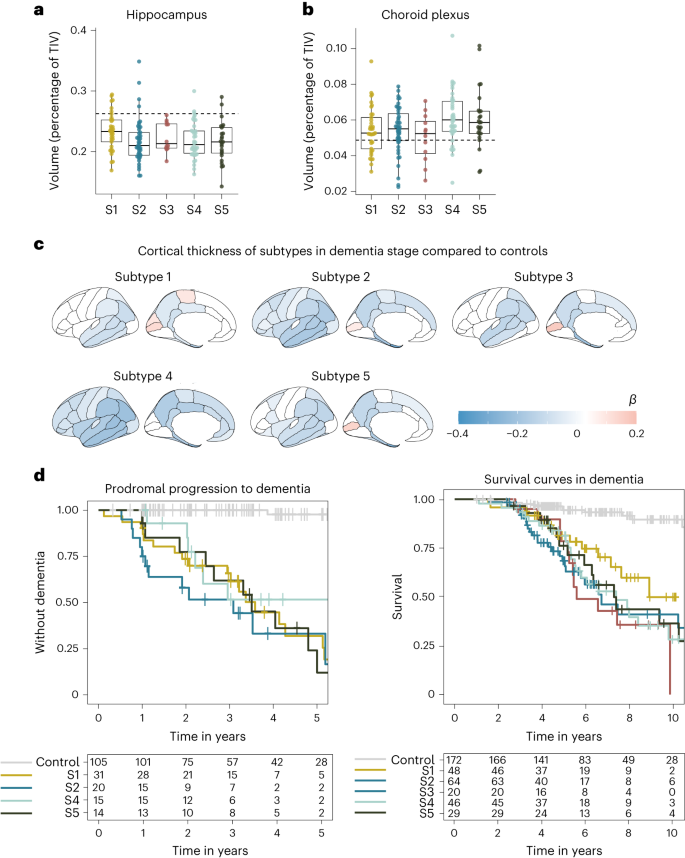 a, Median hippocampal quantity as the share of general intracranial quantity (TIV) in comparison to subtypes within the dementia level. b, Choroid plexus quantity as the share of TIV in comparison to subtypes within the dementia level. c, Cortical atrophy related to AD subtypes within the dementia level in comparison to controls (n = 160). β signifies imply cortical thickness in mm, averaged over the correct and left hemispheres and altered for age and intercourse. d, Medical development from MCI to dementia in step with subtype (left; except for subtype 3 because of n = 2) and time from dementia to dying in step with subtypes (proper). All atrophy measures are according to people with dementia most effective. a,b, The boxplots depict the median within the middle; the bounds point out the primary and 3rd quartiles, whilst the whiskers prolong up and down to one.5 occasions the interquartile vary (restricted to exact seen knowledge issues), and the issues point out person individual values (subtype 1, n = 37; subtype 2, n = 45; subtype 3, n = 12; subtype 4, n = 40; subtype 5, n = 25). See Supplementary Tables 6a,b and eight for the detailed statistical metrics.When trying out AD genetic chance variants, we discovered enrichment for ABCA7, PICALM, IL-34 and CLNK. Whilst ABCA7 and IL-34 are expressed within the choroid plexus73,74, PICALM is expressed within the blood–mind barrier75. Each ABCA7 and PICALM have a task in lipid metabolism76,77 and feature been related to amyloid clearance together with LRP1 (ref. 78). IL-34 has been related to impaired macrophage function79, which might intervene with the macrophage uptake of amyloid fibrils80. At the side of the reduced ranges of BACE1 and amyloid-β40 on this subtype in comparison to controls (Desk 1), suggesting reduced amyloid metabolism, those genetic elements means that impaired clearance mechanisms give a contribution to AD pathogenesis in subtype 4.Taken in combination, those effects recommend that choroid plexus disorder is every other contributor to AD, in a selected subgroup of sufferers.Subtype 5 blood–mind barrier dysfunctionSubtype 5 (n = 56, 13.4%) was once extremely very similar to our in the past recognized blood–mind barrier disorder subtype with greater ranges of 640 proteins that integrated blood proteins comparable to albumin, fibrinogens, plasminogen, prothrombin and lots of immunoglobulins, comparable to IgG1, all proteins that leak into the mind when the blood–mind barrier is compromised81. Pathways related to greater proteins integrated blood coagulation, B cell-mediated immunity and acute inflammatory reaction. No transcription issue enrichment was once seen for proteins with greater CSF ranges. On MRI, this subtype had extra microbleeds than controls (P = 0.01; Desk 1), in contrast to the opposite subtypes. Maximum proteins related to subtype 5 (1,013, 61%) had, then again, reduced CSF ranges in comparison to controls, and those have been related to neuroplasticity and converged at the transcription elements SUZ12 and REST. This means that the blood–mind barrier subtype additionally has hypoplasticity, just like the choroid plexus subtype. Neuronal plasticity processes will also be impaired by means of leakage of blood proteins, together with fibrin, that have been in particular greater on this subtype82. Moreover, in comparison to our earlier find out about, we discovered further proteins altered within the blood–mind barrier subtype, that have been related to pericytes, cells that usually quilt capillaries, and with explicit vascular cellular varieties, comparable to decrease ranges of PDGFRB, CDH2 (N-cadherin), MFGE8 (medin), HTRA1, LAMB1 (laminin), EDN1, LRP1 and JAM3, in addition to greater ranges of CDH5 (VE-cadherin), ANXA3, ICAM1, AMBP, VWF and PTPRB (Supplementary Desk 4, columns AV-AX). All of those were in the past related to deposition of blood proteins within the parenchyma75,83,84,85,86,87. The low PDGFRb ranges we seen would possibly replicate lack of pericytes, which is in step with mind tissue measures of PDGFRb in rodent fashions and postmortem AD83,88. A reduced choice of pericytes may additionally provide an explanation for the reduced ranges of LRP1 we seen on this subtype, which would possibly obstruct amyloid clearance around the blood–mind barrier78. On the other hand, the low concentrations we seen within the blood–mind barrier subtype may just replicate lack of different vascular cells, comparable to arterial easy muscle cells, which additionally specific PDGFRb86.When it comes to genetic chance, this subtype had the perfect share of APOE e4 carriers, even if the variation with different subtypes didn’t succeed in statistical importance (Desk 1). This subtype was once additional enriched for the IL-34, ECHDC3 and APP variants. IL-34 was once additionally related to the choroid plexus subtype, suggesting that it contributes to AD pathogenesis thru processes associated with the mind barrier. ECHDC3 has been related to lipid metabolism57. Some variants in APP were related to vascular disruption or greater prevalence of cerebral amyloid angiopathy, thru amyloid fragments which are tougher to clear89. The perception that this subtype has blood–mind barrier disorder, means that this commonplace APP variant would possibly give a contribution to AD chance thru vascular integrity.In combination, those knowledge supply further insights into the underlying pathophysiological processes related to the blood–mind barrier disorder AD subtype.Predicting AD subtypes in replication cohortsWe then studied if the subtypes may well be recognized in six impartial replication datasets with to be had CSF TMT MS. To this finish, we skilled random wooded area classifiers at the present dataset after which used those classifiers to expect subtype labels for people within the replication cohorts, together with sufferers from over 9 other nations in Europe and america (Strategies). All 5 subtypes have been seen in maximum replication cohorts with prime subtype-specific possibilities and similar frequencies as within the discovery cohort: on moderate 27.9% had subtype 1, 35.5% subtype 2, 5.8% subtype 3, 17.1% subtype 4 and 16.6% subtype 5 (Fig. 3a and Supplementary Desk 12). Subtype comparisons on CSF t-tau and p-tau ranges, in addition to age and intercourse, indicated most commonly equivalent variations as seen in the principle analyses for the replication cohorts (Fig. 3b–d and Supplementary Desk 13). Replication cohort 4 additionally had CSF over the serum albumin ratios to be had (Fig. 3e), which is a marker for blood–mind barrier leakage; this was once greater within the blood–mind barrier subtype most effective (P < 0.0001). General, those effects means that the subtypes we came upon in the principle analyses also are found in different cohorts.Fig. 3: Replication of AD subtypes in six cohorts.
a, Median hippocampal quantity as the share of general intracranial quantity (TIV) in comparison to subtypes within the dementia level. b, Choroid plexus quantity as the share of TIV in comparison to subtypes within the dementia level. c, Cortical atrophy related to AD subtypes within the dementia level in comparison to controls (n = 160). β signifies imply cortical thickness in mm, averaged over the correct and left hemispheres and altered for age and intercourse. d, Medical development from MCI to dementia in step with subtype (left; except for subtype 3 because of n = 2) and time from dementia to dying in step with subtypes (proper). All atrophy measures are according to people with dementia most effective. a,b, The boxplots depict the median within the middle; the bounds point out the primary and 3rd quartiles, whilst the whiskers prolong up and down to one.5 occasions the interquartile vary (restricted to exact seen knowledge issues), and the issues point out person individual values (subtype 1, n = 37; subtype 2, n = 45; subtype 3, n = 12; subtype 4, n = 40; subtype 5, n = 25). See Supplementary Tables 6a,b and eight for the detailed statistical metrics.When trying out AD genetic chance variants, we discovered enrichment for ABCA7, PICALM, IL-34 and CLNK. Whilst ABCA7 and IL-34 are expressed within the choroid plexus73,74, PICALM is expressed within the blood–mind barrier75. Each ABCA7 and PICALM have a task in lipid metabolism76,77 and feature been related to amyloid clearance together with LRP1 (ref. 78). IL-34 has been related to impaired macrophage function79, which might intervene with the macrophage uptake of amyloid fibrils80. At the side of the reduced ranges of BACE1 and amyloid-β40 on this subtype in comparison to controls (Desk 1), suggesting reduced amyloid metabolism, those genetic elements means that impaired clearance mechanisms give a contribution to AD pathogenesis in subtype 4.Taken in combination, those effects recommend that choroid plexus disorder is every other contributor to AD, in a selected subgroup of sufferers.Subtype 5 blood–mind barrier dysfunctionSubtype 5 (n = 56, 13.4%) was once extremely very similar to our in the past recognized blood–mind barrier disorder subtype with greater ranges of 640 proteins that integrated blood proteins comparable to albumin, fibrinogens, plasminogen, prothrombin and lots of immunoglobulins, comparable to IgG1, all proteins that leak into the mind when the blood–mind barrier is compromised81. Pathways related to greater proteins integrated blood coagulation, B cell-mediated immunity and acute inflammatory reaction. No transcription issue enrichment was once seen for proteins with greater CSF ranges. On MRI, this subtype had extra microbleeds than controls (P = 0.01; Desk 1), in contrast to the opposite subtypes. Maximum proteins related to subtype 5 (1,013, 61%) had, then again, reduced CSF ranges in comparison to controls, and those have been related to neuroplasticity and converged at the transcription elements SUZ12 and REST. This means that the blood–mind barrier subtype additionally has hypoplasticity, just like the choroid plexus subtype. Neuronal plasticity processes will also be impaired by means of leakage of blood proteins, together with fibrin, that have been in particular greater on this subtype82. Moreover, in comparison to our earlier find out about, we discovered further proteins altered within the blood–mind barrier subtype, that have been related to pericytes, cells that usually quilt capillaries, and with explicit vascular cellular varieties, comparable to decrease ranges of PDGFRB, CDH2 (N-cadherin), MFGE8 (medin), HTRA1, LAMB1 (laminin), EDN1, LRP1 and JAM3, in addition to greater ranges of CDH5 (VE-cadherin), ANXA3, ICAM1, AMBP, VWF and PTPRB (Supplementary Desk 4, columns AV-AX). All of those were in the past related to deposition of blood proteins within the parenchyma75,83,84,85,86,87. The low PDGFRb ranges we seen would possibly replicate lack of pericytes, which is in step with mind tissue measures of PDGFRb in rodent fashions and postmortem AD83,88. A reduced choice of pericytes may additionally provide an explanation for the reduced ranges of LRP1 we seen on this subtype, which would possibly obstruct amyloid clearance around the blood–mind barrier78. On the other hand, the low concentrations we seen within the blood–mind barrier subtype may just replicate lack of different vascular cells, comparable to arterial easy muscle cells, which additionally specific PDGFRb86.When it comes to genetic chance, this subtype had the perfect share of APOE e4 carriers, even if the variation with different subtypes didn’t succeed in statistical importance (Desk 1). This subtype was once additional enriched for the IL-34, ECHDC3 and APP variants. IL-34 was once additionally related to the choroid plexus subtype, suggesting that it contributes to AD pathogenesis thru processes associated with the mind barrier. ECHDC3 has been related to lipid metabolism57. Some variants in APP were related to vascular disruption or greater prevalence of cerebral amyloid angiopathy, thru amyloid fragments which are tougher to clear89. The perception that this subtype has blood–mind barrier disorder, means that this commonplace APP variant would possibly give a contribution to AD chance thru vascular integrity.In combination, those knowledge supply further insights into the underlying pathophysiological processes related to the blood–mind barrier disorder AD subtype.Predicting AD subtypes in replication cohortsWe then studied if the subtypes may well be recognized in six impartial replication datasets with to be had CSF TMT MS. To this finish, we skilled random wooded area classifiers at the present dataset after which used those classifiers to expect subtype labels for people within the replication cohorts, together with sufferers from over 9 other nations in Europe and america (Strategies). All 5 subtypes have been seen in maximum replication cohorts with prime subtype-specific possibilities and similar frequencies as within the discovery cohort: on moderate 27.9% had subtype 1, 35.5% subtype 2, 5.8% subtype 3, 17.1% subtype 4 and 16.6% subtype 5 (Fig. 3a and Supplementary Desk 12). Subtype comparisons on CSF t-tau and p-tau ranges, in addition to age and intercourse, indicated most commonly equivalent variations as seen in the principle analyses for the replication cohorts (Fig. 3b–d and Supplementary Desk 13). Replication cohort 4 additionally had CSF over the serum albumin ratios to be had (Fig. 3e), which is a marker for blood–mind barrier leakage; this was once greater within the blood–mind barrier subtype most effective (P < 0.0001). General, those effects means that the subtypes we came upon in the principle analyses also are found in different cohorts.Fig. 3: Replication of AD subtypes in six cohorts.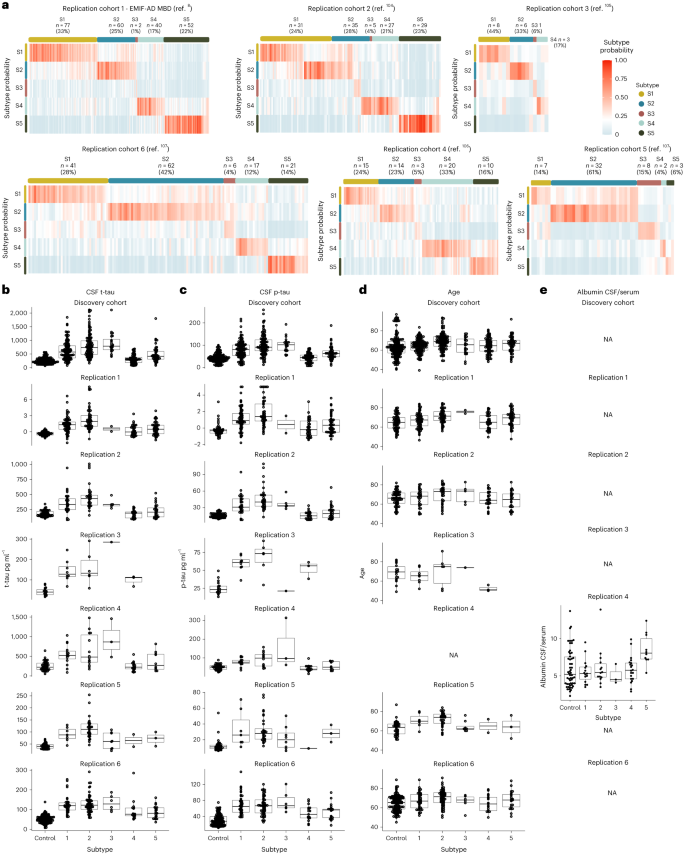 a, Subtype likelihood for each and every person in six replication cohorts. Most people confirmed prime likelihood for one subtype most effective. b–e, Subtype comparisons on CSF t-tau ranges (b), p-tau (c), age (d) and the CSF over serum albumin ratio (e) for each and every replication cohort when to be had. b–e, The boxplots depict the median within the middle, the bounds point out the primary and 3rd quartiles, the whiskers prolong up and down to one.5 occasions the interquartile vary (restricted to exact seen knowledge issues) and the issues point out person individual values. The choice of people according to team within the boxplots are indexed in Supplementary Tables 12 and 13, and gives the statistical metrics for the comparisons. NA, now not acceptable.
a, Subtype likelihood for each and every person in six replication cohorts. Most people confirmed prime likelihood for one subtype most effective. b–e, Subtype comparisons on CSF t-tau ranges (b), p-tau (c), age (d) and the CSF over serum albumin ratio (e) for each and every replication cohort when to be had. b–e, The boxplots depict the median within the middle, the bounds point out the primary and 3rd quartiles, the whiskers prolong up and down to one.5 occasions the interquartile vary (restricted to exact seen knowledge issues) and the issues point out person individual values. The choice of people according to team within the boxplots are indexed in Supplementary Tables 12 and 13, and gives the statistical metrics for the comparisons. NA, now not acceptable.
Cerebrospinal fluid proteomics in sufferers with Alzheimer’s illness finds 5 molecular subtypes with distinct genetic chance profiles – Nature Growing old