“We’re stardust, we’re golden / We’re billion-year-old carbon.” So wrote Joni Mitchell, additionally noting that she dreamed of bomber jet planes becoming butterflies. The 1970 track has misplaced none of its relevance these days. It’s additionally a lyrical description of dry and undying realities of human life: we’re made out of components and the ones components were round for an unfathomably very long time (“one billion years” is poetic license and a critical understatement). As Mitchell says, many of the components that make up us – from carbon to iron – originated underneath the stipulations of intense force and warmth that exist within the core of stars, all of which is spewed out into the universe after they die.
Because the poets at NASA put it, “from the carbon in our DNA to the calcium in our bones, just about all the components in our our bodies have been solid within the fiery hearts and loss of life throes of stars.” And so they’ve been round a long way longer than we now have. Mild components began forming an estimated 14 billion years in the past, in truth, within the first couple of minutes after the Giant Bang, even though others didn’t come round until a couple of hundred thousand years later when the universe cooled down sufficient for electrons to stick in orbit round atomic nuclei.
The one components that preceded those have been a lot more effective: hydrogen, helium and a little of lithium — sure, the stuff additionally they prescribe for bipolar dysfunction, even though almost definitely now not sufficient to cheer you up at the hours of darkness, lonely vastness of the early universe.
Issues have got higher since then. A survey of over 150,000 stars, introduced in 2017, cataloged the distribution of the life-essential components of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus and sulfur.
“From the carbon in our DNA to the calcium in our bones, just about all the components in our our bodies have been solid within the fiery hearts and loss of life throes of stars.”
“We are actually ready to map the abundance of all the primary components discovered within the human frame throughout loads of 1000’s of stars in our Milky Manner,” mentioned Jennifer Johnson, a pace-setter of the learn about workforce and an observational astronomer founded at The Ohio State College, in a press free up on the time.
Extra not too long ago, a paper revealed simply this July within the magazine Science Advances main points the discovering of stardust liberally sprinkled on a close-by asteroid, this time with the bonus of close-range, lab-based learn about of this unique but oh-so-familiar substance.
Need extra well being and science tales on your inbox? Subscribe to Salon’s weekly e-newsletter Lab Notes.
Dr. Ann Nguyen of NASA, an area scientist and the director of the NanoSIMS Analysis Facility on the NASA Johnson Area Middle, is the lead writer some of the dozens of members from a couple of nations who helped to investigate samples of the asteroid Ryugu.
“Presolar stardust grains are mud that condensed from the gaseous outflows of stars that died billions of years sooner than our sun machine shaped,” she informed Salon in an e mail. “They’ve isotopic compositions which might be massively other than the isotopic compositions of any subject matter that shaped inside of our sun machine.”
The atypical isotopic ratios — proportions of specific variations of the weather discovered — permit the researchers to decide that they have got come from a long way, a long way away and likewise to know how they have been shaped.
Nguyen and her colleagues mapped the Ryugu samples for carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and silicon, all primary portions of who we’re these days — best, in fact, whilst those are components acquainted to Earthlings like us, the isotopic ratio tells us that those specific ones got here from in different places.
“Those grains seeded our sun machine and constituted one of the crucial unique construction blocks.”
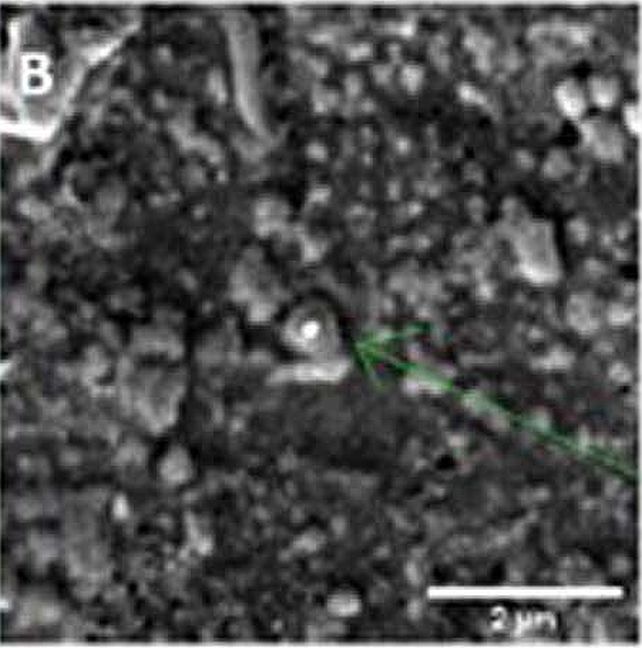
“It is because their isotopic ratios outcome from nucleosynthetic reactions that happened deep throughout the father or mother stars. A few of these grains have been integrated into our sun machine and survived processing at the asteroid or comet host,” Nguyen defined. For the reason that presolar grains are, on reasonable, 1 / 4 of a micrometer in diameter, this isn’t one thing you’ll be able to see in a telescope or different far-range research. As an alternative, the researchers used specialised apparatus able to measurements at the scale of a nanometer, all the way down to the atomic degree.
However you don’t simply kill a celeb and get a complete cabinet of components appropriate for whipping up no matter subject matter just right — whether or not Uranus or, with apologies, your anus — you’re after. Explicit sorts of stars and the way in which wherein they die free up other components into the universe.
“Stars of various plenty have other fates,” Nguyen informed Salon. “Stars with low to intermediate plenty (not up to about 8 sun plenty) evolve to the AGB section, while extra large stars evolve to change into supernovae. The extra large stars succeed in upper temperatures and pressures of their interiors, which permits for various nucleosynthetic reactions to happen.”
(The AGB section Nguyen discussed refers back to the so-called “asymptotic large department,” a lifestyles degree of moderately skimpy stars wherein they change into cool and luminous balls of sometimes explosively-igniting helium fusion round a carbon and oxygen core, then swell to change into a crimson large, lose mass to stellar winds, and might finally end up as very lovely protoplanetary nebulae — a essentially incomplete description of a fancy and every so often numerous procedure stretching out over round 100 thousand years.)
The workforce focused carbon, nitrogen and oxygen in particular as a result of their isotopic composition supplies transparent indications of what kind of celebrity they got here from: supernova, nova or AGB celebrity, as an example. And the chemical make-up of a presolar grain tells secrets and techniques concerning the chemistry of the celebrity it got here from. “For example,” Nguyen presented, “presolar oxides and silicates come from stars which might be oxygen-rich, and presolar SiC [a compound of silicon and carbon] and graphite [a form of carbon] come from carbon-rich stars.”
Good enough, however how did these items to find its technique to us so very way back? “We all know we’re fabricated from stardust as a result of bona fide examples of grains were recognized in asteroid and comet samples,” Nguyen defined. “Those grains seeded our sun machine and constituted one of the crucial unique construction blocks. The natural topic that I learn about shaped via abiotic processes and is other than prebiotic natural topic — however it’s conceivable that our bodies like Ryugu or comets delivered the elements vital for lifestyles on Earth. If this is the case, the presolar grains and natural topic would even have been delivered.”
Scientists have simply found out easy methods to open a caught canister of mud from 101955 Bennu, a carbon-filled near-Earth asteroid — broken fasteners had rendered it astronomer-proof, however now not for lengthy! And now Nguyen is deep in research of the Bennu samples from the NASA sample-return project, which returned to Earth in September however best absolutely printed its dusty secrets and techniques remaining month. Samples of the samples are actually being studied through scientists all over the place the sector and we’re getting tantalizing tidbits already (a number of water and phosphate). Most likely we will be able to quickly know extra concerning the foundation folks and the whole lot round us.
Within the interim, the ones folks with a way of awe can also be lovely glad figuring out our earth mud, and our our bodies, which is able to at some point go back to mud, do certainly derive from the glittering reaches of house and the unfathomable depth of stars of their loss of life throes.










:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-2150879228-fad22bc836f0447c83ae797e2b768ce0.jpg)



