A little bit over a decade in the past, a robot rover on Mars after all exposed a solution to a urgent query. It is now transparent that the pink planet does, certainly, have natural subject material buried within the sediment of its historic lakebeds.
Since then, now we have persevered to search out natural molecules on Mars dispensed in some way that implies carbon chemistry is in style throughout our small rusty neighbor.
This doesn’t suggest now we have discovered indicators of alien lifestyles. A long way from it; there are lots of non-biological processes that may produce natural molecules. However precisely the place the fabric got here from has posed just a little of a puzzle.
Now, a workforce of researchers led by means of planetary scientist Yuichiro Ueno of the Tokyo Institute of Era has exposed proof of its origins within the setting, the place carbon dioxide bathed in ultraviolet daylight reacted to shape a mist of carbon molecules that rained onto the planet’s floor.
Whilst it is not reasonably as exciting as Martian biology, the dicovery may just lend a hand us determine how the elements for lifestyles ended up proper right here on our house planet of Earth, billions of years in the past.
“Such carbon-based complicated molecules are the prerequisite of lifestyles, the development blocks of lifestyles, one would possibly say,” says chemist Matthew Johnson of the College of Copenhagen.
“So, this can be a bit just like the previous debate about which got here first, the hen or the egg. We display that the natural subject material discovered on Mars has been shaped thru atmospheric photochemical reactions – with out lifestyles this is. That is the ‘egg’, a prerequisite of lifestyles. It nonetheless is still proven whether or not or now not this natural subject material led to lifestyles at the pink planet.”
The perception that photolysis – the method wherein molecules are damaged aside by means of mild – performs a task within the natural chemistry discovered at the floor of Mars has been kicking round for some time. Johnson and two colleagues printed a paper at the speculation in 2013, in line with simulations, and others have due to this fact investigated additional.
What we want, regardless that, is tricky proof from Mars that is in line with the simulation effects.
The photolysis of CO2 produces carbon monoxide and oxygen atoms. However there are two isotopes, or lots, of strong carbon. Via a ways the most typical is carbon-12, which accommodates six protons and 6 neutrons. The following heaviest is carbon-13, which accommodates six protons and 7 neutrons.
Photolysis works quicker at the lighter isotope. So, when UV mild photolytically splits the combination of C-12 and C-13 carbon dioxide within the setting, molecules containing C-12 are depleted quicker, leaving a noticeable ‘extra’ of C-13 carbon dioxide at the back of.
This atmospheric carbon-13 enrichment had already been recognized a couple of years in the past. The researchers analyzed a meteorite that got here from Mars and landed in Antarctica, containing carbonate minerals that shaped from the CO2 within the Martian setting.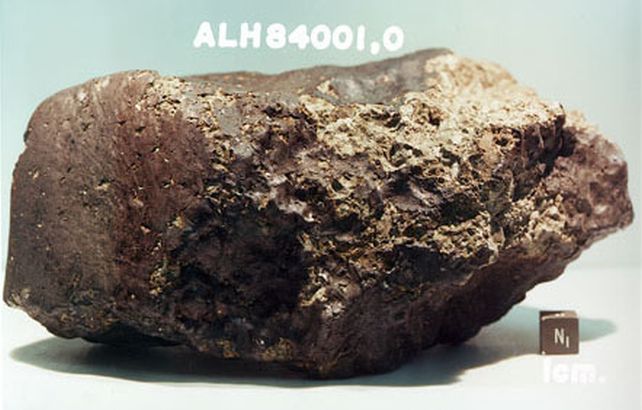 The meteorite Allan Hills 84001, from which the atmospheric isotopes had been derived. (NASA)”The smoking gun this is that the ratio of carbon isotopes in it precisely suits our predictions within the quantum chemical simulations, however there used to be a lacking piece within the puzzle,” Johnson explains.
The meteorite Allan Hills 84001, from which the atmospheric isotopes had been derived. (NASA)”The smoking gun this is that the ratio of carbon isotopes in it precisely suits our predictions within the quantum chemical simulations, however there used to be a lacking piece within the puzzle,” Johnson explains.
“We had been lacking the opposite made of this chemical procedure to verify the speculation, and that’s the reason what now we have now received.”
That lacking puzzle piece used to be present in information received by means of the Interest rover within the Gale crater. Within the samples of carbonate minerals discovered at the flooring on Mars is a carbon-13 depletion that completely mirrors the carbon-13 enrichment discovered within the Martian meteorite.
“There is not any opposite direction to provide an explanation for each the carbon-13 depletion within the natural subject material and the enrichment within the Martian meteorite, each relative to the composition of volcanic CO2 emitted on Mars, which has a continuing composition, equivalent as for Earth’s volcanoes, and serves as a baseline,” Johnson says.
That is robust proof that the carbon natural subject material discovered by means of Interest shaped from the carbon monoxide produced by means of photolysis, the researchers say. And this provides us a clue concerning the starting place of natural subject material on Earth.
Billions of years in the past, when the Sun Gadget used to be however a babe, Earth, Venus, and Mars all had very equivalent atmospheres, suggesting the similar procedure most likely took place right here on our house planet.
The 3 planets have since advanced alongside very other paths, and Mars and Venus appear reasonably inhospitable to lifestyles as we understand it in their very own idiosyncratic tactics. However the rusted barren region surroundings of Mars has now given us a clue about our personal origins.
“We now have now not but discovered this ‘smoking gun’ subject material right here on Earth to end up that the method happened. Possibly as a result of Earth’s floor is a lot more alive, geologically and actually, and subsequently repeatedly converting,” Johnson says.
“However this can be a giant step that we have got now discovered it on Mars, from a time when the 2 planets had been very equivalent.”The workforce’s findings were printed in Nature Geoscience.
Chemistry Discovery on Mars Hints at The Origins of Lifestyles on Earth