HELSINKI — China plans to release an exoplanet observatory in 2028 with the purpose of constructing a leap forward detection of a possible 2d Earth.
Round 5,000 exoplanets had been discovered since 1995, however no Earth-sized planets within the liveable zones of sun-like stars had been noticed.
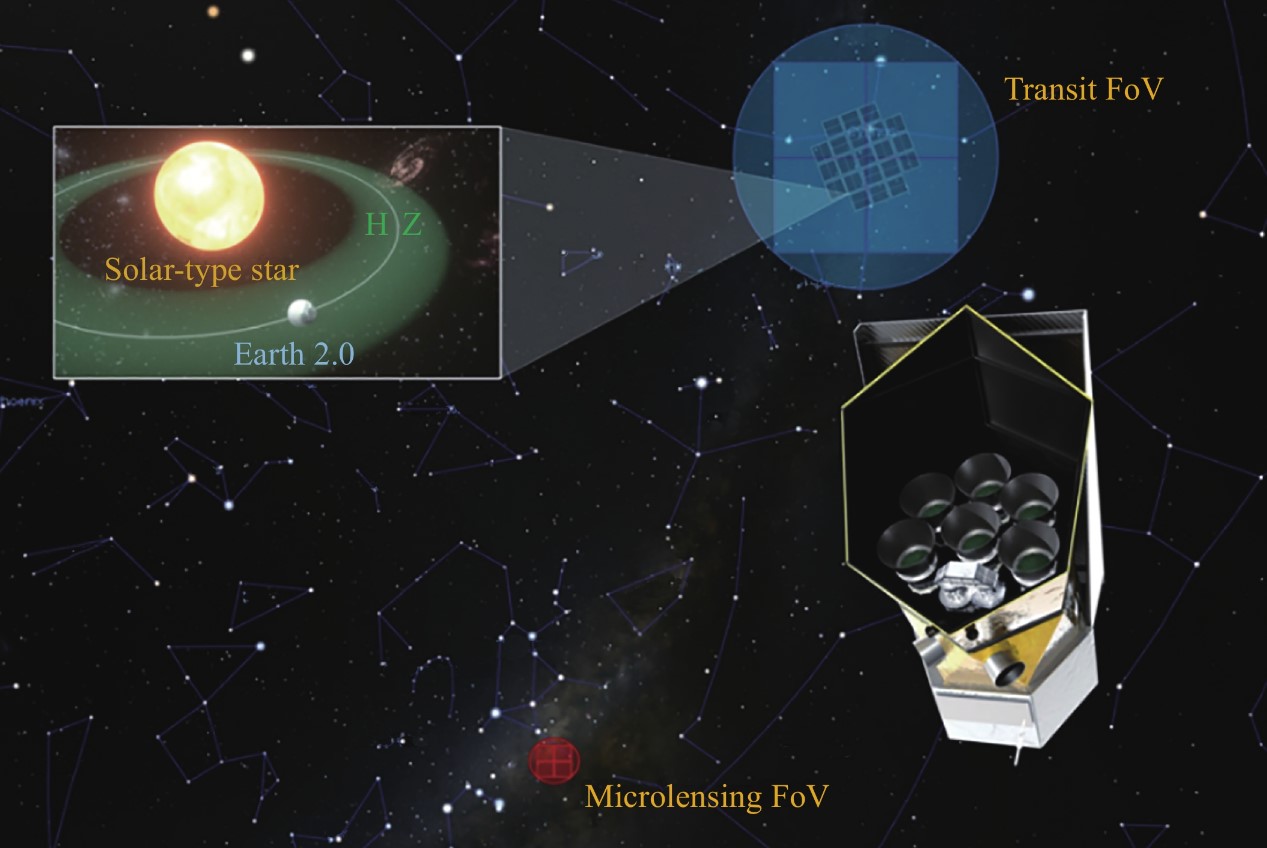
Earth 2.0, or ET, proposed by way of the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory beneath the Chinese language Academy of Sciences (CAS), intends to make use of six 28-centimeter-aperture wide-field optical telescopes to watch about 2 million stars within the Kepler challenge famous person subject and different, greater within reach areas, often tracking for transits of so-called exo-Earths over 4 years.
The challenge is now concentrated on release in 2028, in keeping with a brand new paper authored by way of the challenge essential investigator and others and printed within the Chinese language Magazine of Area Science.
The spacecraft shall be introduced to Solar-Earth Lagrange level 2—the similar gravitationally solid area of house because the James Webb Area Telescope—which is able to supply a solid orbit, a continuing view of deep house, and decreased interference from Earth.
There, ET’s optimized transit telescopes will ship excessive photometric precision—the accuracy and consistency with which the telescopes can measure the brightness of stars—that may permit for the detection of small, rocky planets, in the past past the scope of missions similar to NASA’s Kepler exoplanet observatory.
Whilst Earth-like planets had been detected, those had been present in reasonably quick orbits round reasonably brilliant stars or low mass purple dwarfs, which emit sturdy radiation. ET will be capable to stare at its goal patches of sky for lengthy classes. This prolonged commentary time will permit it to locate planets with longer orbital classes within the liveable zones round sun-like stars, and thus probably select up indicators of exo-Earths.
Key questions and wandering Earths
The challenge will hone in on 3 key questions: the superiority of exo-Earths within the galaxy, the formation and evolution of Earth-like planets, and the foundation of free-floating planets.
The challenge is well-placed to give a contribution considerably to the seek for Exo-Earths, in keeping with Jessie Christiansen, leader scientist on the NASA Exoplanet Science Institute at Caltech/IPAC.
“Given our advanced wisdom in regards to the frequency of Earth-like planets, the ET staff had been in a position to design a survey this is a lot more most likely than Kepler used to be or [the European Space Agency’s] PLATO shall be to locate those planets.
“This essentially comes to a far greater stellar pattern on which the challenge will download high-precision photometry had to locate Earths, completed with each a bigger subject of view than Kepler and excessive precision to a fainter magnitude,” Christiansen informed SpaceNews.
The query of rogue planets shall be investigated the usage of a 35 cm microlensing telescope. That software will stare at round 30 million stars within the Galactic bulge to locate microlensing occasions brought about when free-floating, or “rogue” planets. Those occasions happen when planets produce gravitational lensing results at the gentle of background stars, picked up by way of noting function anomalies within the famous person’s brightness curve. The hope is to discover a “wandering Earth,” floating freed from stars within the void of deep house.
Tech growth, have an effect on on analysis
Growth on ET goes nicely, in keeping with the paper. It describes complicated growth on key applied sciences for the challenge, together with the CMOS detector for photometric precision, satellite tv for pc balance and thermal regulate. All are near-ready for flight.
As soon as at Solar-Earth L2 and entirely operational, ET can start filling state of the art paintings in looking for exo-Earths, one thing that another way would possibly not occur for some time.
“These days the one challenge scheduled to fly within the subsequent decade that can locate Earth-like planets is NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope, and that may best locate them with microlensing – a fleeting dimension of a far off sign that disappears unexpectedly and doesn’t seem once more. Those planets shall be helpful for statistically working out the liveable actual property of the galaxy, however received’t constitute the precious, person planets that we need to symbolize intimately with different telescopes.”
The Roman Area Telescope is anticipated to release in 2027.
“Past that, NASA’s subsequent flagship challenge, the Liveable Worlds Observatory (HWO), is 20-plus years away. If ET is funded and flies within the subsequent decade, it could possibly locate within reach, characterizable liveable planets a decade previous than another way deliberate.”
Now not best does the challenge promise candidate exo-Earths, it is going to permit for practice up observations of such applicants to tease out additional traits.
ET will paintings with China’s LAMOST ground-based optical telescope to hold out spectral observations of commentary objectives, but in addition different groups and observatories around the globe and in house.
This may increasingly result in exact dimension of the mass, density and atmospheric composition of any exo-Earth candidate, contributing to an in-depth learn about of habitability traits, in keeping with the paper.
“Sport-changer”
Wang Chi, director of the Nationwide Area Science Middle (NSSC) beneath CAS, printed in April that the ET challenge have been decided on from a subject of astronomical analysis and house exploration missions. Lunar farside astronomy, excessive house physics, a sun observatory and gravitational wave missions have been additionally licensed.
Each and every of the chosen missions seems to push the limits of data. And ET generally is a game-changer, in keeping with Christiansen.
“We’ve been attempting to find Earth 2.0 for a very long time, and feature been stymied at each and every junction thus far,” says Christiansen. “If ET is in a position to after all and robustly discover a rocky planet within the liveable zone of a Solar-like famous person, it might be an improbable success.
“If this is a planet we will learn about with different telescopes, similar to JWST or, sooner or later, HWO, it is going to be a game-changer.”
ObjectiveDescription1. Uncover Exo-EarthsTo be the primary challenge to find Earth-like exoplanets (Exo-Earths) within the liveable zones of sun-like stars, and measure their prevalence charges.2. Amplify Pattern of Earth-like PlanetsTo considerably build up the identified pattern of Earth-like planets, particularly the ones with lengthy orbital classes, for detailed inhabitants research and formation research.3. Find out about Planetary Formation and EvolutionTo discover the formation mechanisms and evolutionary processes of Earth-like planets and different small, rocky exoplanets by way of undertaking statistical inhabitants research.4. Come across Unfastened-Floating PlanetsTo be the primary challenge to find and measure the frequency of free-floating (rogue) Earth-like planets, contributing to the working out of planetary machine formation.5. Behavior Microlensing SurveysTo make the most of microlensing to locate long-period chilly planets and free-floating planets, together with detailed characterization in their mass and different houses.6. Mix Transit and Microlensing MethodsTo use a mix of transit and microlensing the right way to fortify the possibility of finding quite a lot of exoplanets, together with the ones tricky to locate by way of different approach.7. Allow Long term Exoplanet ResearchTo supply objectives and important information for long run direct imaging missions and different exoplanet research, supporting the following technology of house exploration missions.A desk presenting the important thing targets of the Earth 2.0/ET challenge.
Similar