The presence of parasitic microbes has for the primary time been discovered actually changing the metabolism in their hosts.The culprits are tiny, parasitic archaea of the species Candidatus Nanohaloarchaeum antarcticus that parasitize different single-celled organisms, the host archaeon species Halorubrum lacusprofundi.
And researchers have discovered that those parasites are very selective concerning the assets they thieve from the frame in their host.
“In different phrases,” says marine microbiologist Joshua Hamm of the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Analysis (NIOZ), “Ca. N. antarcticus is a choosy eater.”
Archaea are single-celled organisms which might be very similar to micro organism, however belong to a wholly other area of organisms. Ca. N. antarcticus belongs to a bunch of archaea referred to as DPANN – small archaea. A few of these parasitize different single-celled organisms, slurping up their hosts’ lipids as construction fabrics for their very own membranes.
A couple of years in the past, a staff of scientists discovered that Ca. N. antarcticus does not simply parasitize any outdated microbe – it is particularly, and strangely, reliant on H. lacusprofundi for lipids and different metabolites that it can not make itself.
Led by means of NIOZ microbiologist Su Ding, a staff of researchers took a far nearer have a look at each organisms to higher perceive Ca. N. antarcticus’ dependency. Their paintings concerned examining the lipids, or fatty compounds, discovered each in host-parasite pairs, and in H. lacusprofundi that experience now not been parasitized by means of Ca. N. antarcticus.
This used to be best conceivable the use of a brand new analytical method evolved by means of Ding that allowed the researchers to peer all of the lipids provide, even lipids they hadn’t but known. Earlier tactics best allowed scientists to peer lipids in the event that they knew what they had been on the lookout for.
Their findings had been unexpected. Originally, the parasites analyzed did not slurp all of the lipids willy-nilly from their hosts. They had been discovered to be selectively taking best sure compounds for their very own use, and leaving the remainder untouched. Choosy eaters certainly.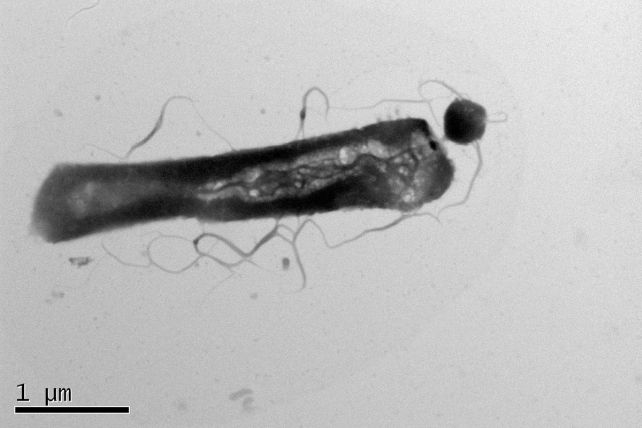 H. lacusprofundi, at the left, being parasitized by means of Ca. N. antarcticus. (Joshua N. Hamm)Secondly, the metabolism of H. lacusprofundi displays marked variations between parasitized and non-parasitized people. The amounts of the lipids provide fluctuate for a parasitized microbe, with an important depletion within the lipids taken by means of Ca. N. antarcticus, however an building up in different lipids within the host’s tiny frame.
H. lacusprofundi, at the left, being parasitized by means of Ca. N. antarcticus. (Joshua N. Hamm)Secondly, the metabolism of H. lacusprofundi displays marked variations between parasitized and non-parasitized people. The amounts of the lipids provide fluctuate for a parasitized microbe, with an important depletion within the lipids taken by means of Ca. N. antarcticus, however an building up in different lipids within the host’s tiny frame.
The researchers say that is most probably a reaction to the higher metabolic load generated by means of the parasite’s presence. As well as, the host species has an odd membrane for archaea. Whilst it supplies H. lacusprofundi with an ecological benefit when it comes to being extra energy-efficient, it may additionally permit the parasite to break out with its fussy style in fat.
The researchers additionally famous that one of the adjustments in inflamed hosts’ membrane composition is also a defensive reaction to the parasite.
Additional analysis will likely be required to know the mechanisms in the back of each the parasite’s number of lipids, and the host’s defensive reaction, however simply understanding {that a} parasitic archaeon can trade its host’s metabolism has some fascinating implications.
Bolstering defenses and changing lipid manufacturing based on a parasite, the researchers say, will have implications for the way the host responds to different exterior influences, akin to converting temperatures or acidity ranges.
“Now not best does [the discovery] shed a break of day at the interactions between other archaea; it provides a wholly new perception within the basics of microbial ecology,” Hamm says.
“Particularly that now we have now demonstrated that those parasitic microbes can impact the metabolism of alternative microbes, which in flip may just modify how they are able to reply to their setting. Long run paintings is had to decide to what extent this will likely have an effect on the steadiness of the microbial neighborhood in converting stipulations.”The staff’s analysis has been printed in Nature Communications.
'Choosy' Parasites Adjust Hosts' Metabolism by means of Selectively Eating on Their Lipid Buffet