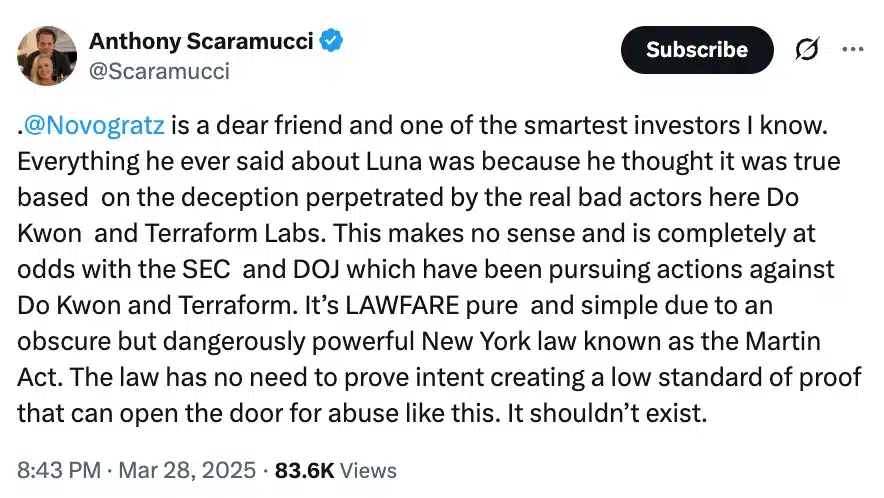
A brand new set of predictions for the so-called “blaze megastar,” T Corona Borealis suggests the megastar would possibly cross nova on both March 27, November 10, or June 25, 2026. Then again, different astronomers are skeptical about those predictions, which might be according to an implied development within the explosive device’s orbital configuration,”T Corona Borealis [T CrB] is a singular object that has fascinated novice {and professional} astronomers for greater than a century,” Léa Planquart of the Institut d’Astronomie et d’Astrophysique on the Université Libre de Bruxelles in Belgium, instructed Area.com.T CrB is a symbiotic binary, a vampire device wherein a white dwarf is siphoning subject matter from a pink massive megastar. A white dwarf is the dense, compact core remnant of a as soon as sun-like megastar, packing a mass an identical to that of a celeb right into a quantity concerning the measurement of Earth. A pink massive represents an previous degree in a celeb’s evolution, when a sun-like megastar begins to expire of its hydrogen gas provide and starts to swell. Its distended surroundings then turns into simple prey to the gravity of the some distance smaller, however denser, white dwarf.Subject material captured from the pink massive bureaucracy a spiraling disk across the white dwarf, in the long run depositing that subject matter onto the white dwarf’s floor. As soon as sufficient subject matter has constructed up, a thermonuclear explosion ignites. It does no longer wreck the white dwarf, however we will be able to see the sunshine of the explosion throughout hundreds of light-years.We name this a nova, after the Latin for “new megastar.”Generally, T CrB languishes at about magnitude +10, this means that it’s so faint that it might best be observed via moderate-aperture telescopes or huge binoculars. Then again, when it is going nova, it brightens to naked-eye visibility, and therefore in short turns into observed as a “new megastar” within the evening sky.T CrB is if truth be told much more particular than that, as a result of it’s one among best 11 recognized “recurrent” novas, which might be observed to move nova time and again, with gaps of lower than 100 years between explosions. In the past, on February 9, 1946 and Would possibly 12, 1866, the white dwarf within the T CrB device went nova. It additionally went nova round Christmastime in 1787, even supposing the precise date is not recognized, and there could also be an offer {that a} nova hooked up to this megastar used to be observed someday within the autumn evening sky of 1217.Breaking house information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Previous to the 1946 nova, T CrB brightened fairly in 1938, sooner than dimming once more simply sooner than going nova. The similar development has additionally been observed in T CrB this time round, with it brightening by means of 0.7 magnitudes in 2015 sooner than dimming once more in 2023. This is the reason astronomers are expecting a brand new nova.Jean Schneider of Paris Observatory, has additionally spotted what he believes to be a development between the timing of the T CrB nova occasions. The pink massive and white dwarf take 227.5687 days to orbit one any other, and Schneider believes that each and every nova takes position after a time equivalent to a precise entire selection of orbits. In different phrases, one thing concerning the place of the white dwarf and the pink massive is triggering the nova outbursts, he says.But, as a result of their orbits are round, no unmarried place must have an impact. So, Schneider proposes the presence of a 3rd object within the T CrB device on a much broader, elliptical orbit. Each 79–80 years, he says the 3rd object is with reference to the white dwarf, which means that the white dwarf can feed off each the pink massive and this hypothetical 3rd object on the similar time. This might support the velocity of subject falling onto the white dwarf, growing the prerequisites for a nova.Up to now, this 3rd object, if it exists, has remained undetected, however Schneider tells Area.com that “it may well be detected by means of astrometry, radial pace, direct imaging, a transit or microlensing.”Certainly, Schneider wonders whether or not it hasn’t already been detected however simply no longer identified. On April 21, 2016, the T CrB device all of sudden higher in visible brightness by means of 0.5 magnitudes.”I’ve the next, qualitative interpretation, which is that sooner than then, the 3rd frame used to be out of doors the pixel comparable to the visible measurements,” he mentioned. In different phrases, the 3rd object moved shut sufficient to the opposite two parts of the T CrB device that from our viewpoint it used to be sharing a pixel with them in pictures, including its brightness to the mixed gentle of the pink massive and white dwarf.Then again, different astronomers don’t seem to be but satisfied. Léa Planquart has studied T CrB and different recurrent novas, and in January printed a paper describing the mass switch between the pink massive and the white dwarf according to radial pace observations with the HERMES spectrograph at the 1.2-meter Mercator telescope at Los angeles Palma in Chile. Radial pace right here, for context, refers back to the Doppler shifted motions of the person stars and the subject being transferred between the pink massive, what is referred to as the “accretion disk” and the white dwarf.”Jean Schneider has recommended the presence of a 3rd spouse in an eccentric orbit with a duration of 80 years,” Planquart instructed Area.com. “Such further orbital movement is, then again, no longer detected in our decade-long radial-velocity tracking.”In different phrases, radial pace measurements display no proof for a 3rd megastar, even supposing Planquart can not rule out a low-mass frame corresponding to a big exoplanet.Jeremy Shears, who’s the Director of the British Astronomical Affiliation’s Variable Megastar Segment, additionally has doubts. “Maximum astronomers are skeptical about this prediction, as am I,” he instructed Area.com. “The most efficient factor to do is to stay looking at each and every transparent evening.”Must there be no 3rd object, and if the development observed by means of Schneider within the dates of earlier novas is only a twist of fate, then what is occurring to T CrB?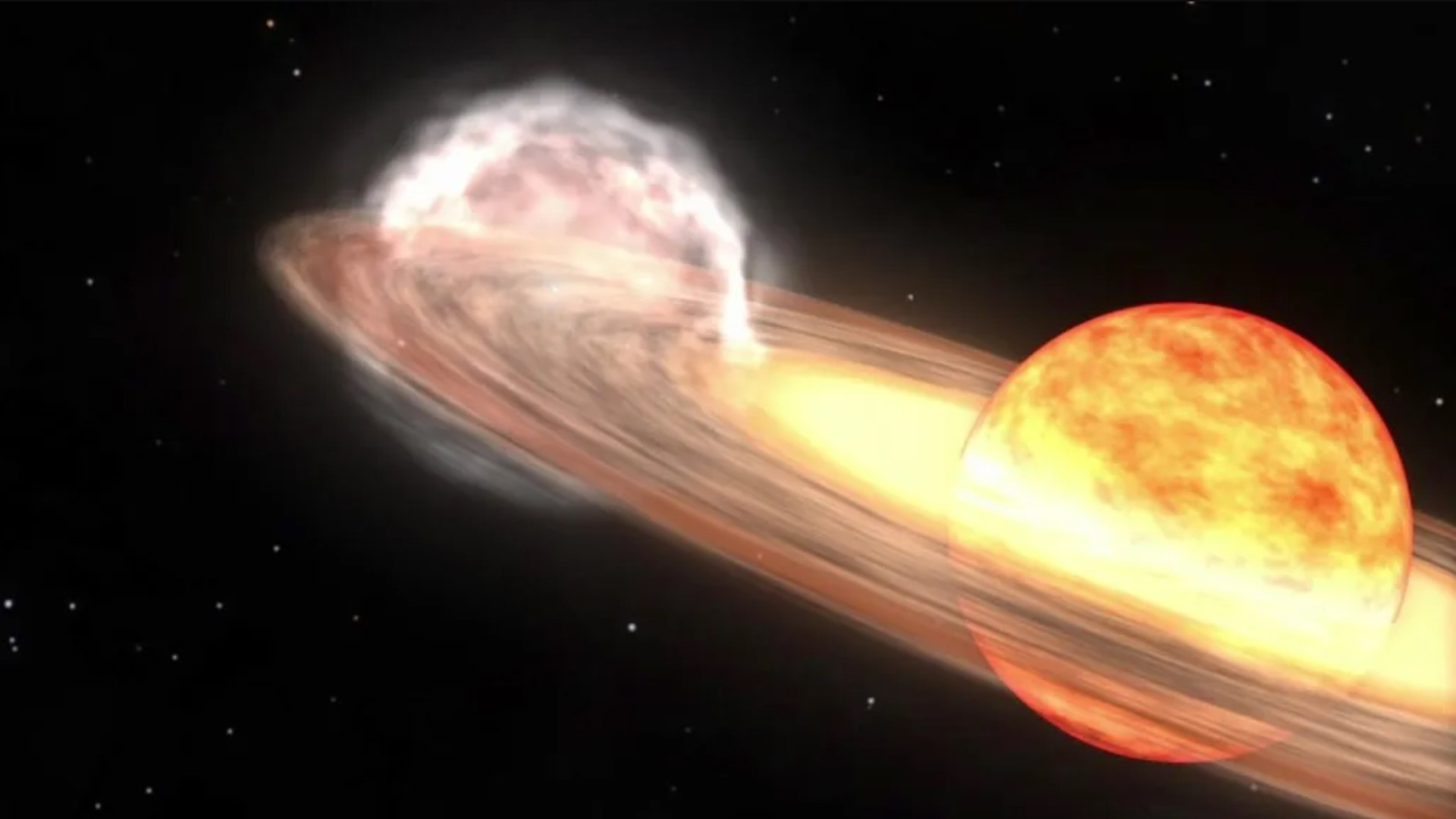 An artist’s depiction of what the nova would possibly appear to be. (Symbol credit score: NASA)
An artist’s depiction of what the nova would possibly appear to be. (Symbol credit score: NASA)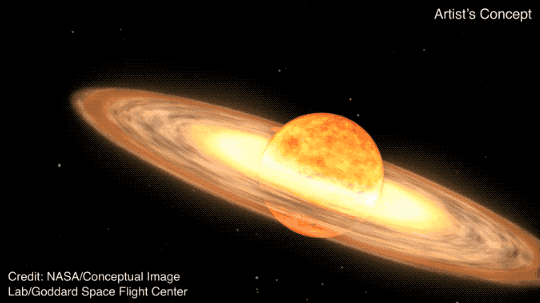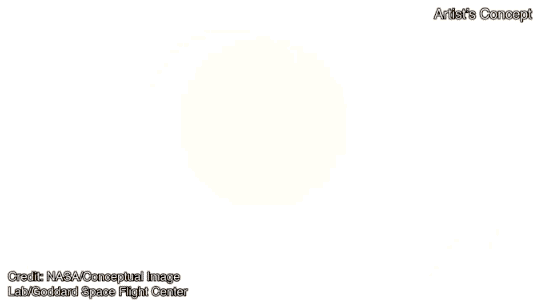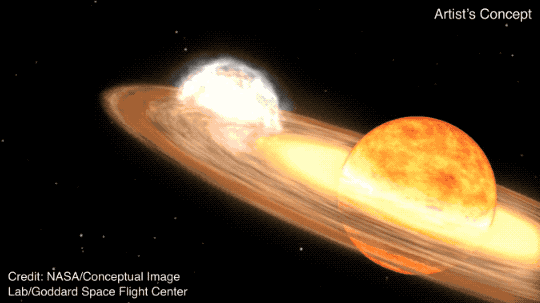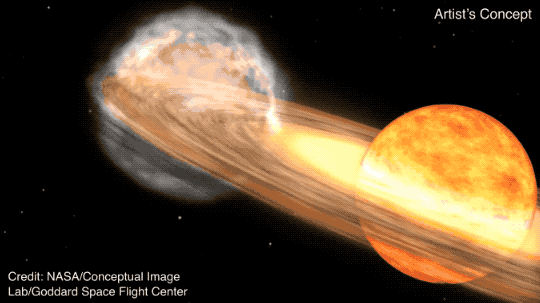 (Symbol credit score: NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle)Planquart’s observations shed some gentle at the subject, specifically the brightening observed in 1938 and 2015, adopted by means of a dimming, maximum just lately observed in 2023.”We learned that from 2015 to 2023, the accretion disk across the white dwarf had reached its most extension and changed into warmer and extra luminous, resulting in higher brightness,” Planquart mentioned. This enhanced what Planquart calls “the vampirization impact,” expanding the switch of subject to the white dwarf in a “super-active section.” Then, in 2023, the accretion disk cooled go into reverse once more, ensuing within the dimming, even supposing subject continues to glide from the disk to the white dwarf at a slower price.”It’s most probably that this enhanced task is essential to cause the nova explosion, because it lets in the fabric to amass extra impulsively,” mentioned Planquart.Then, in 2023, the accretion disk cooled go into reverse once more, ensuing within the dimming, even supposing subject continues to glide from the disk to the white dwarf at a slower price. Then again, the main points are nonetheless reasonably unclear — what reasons the state alternate within the accretion disk that ends up in the super-active section, and precisely what is occurring at the floor of the white dwarf between the disk cooling once more and the nova explosion?Even though Schneider’s precise date predictions might or won’t come to move, the development of the super-active section adopted by means of quiescence and dimming means that the nova is solely across the nook. “We might be expecting to peer the explosion within the coming months — or most likely subsequent 12 months,” mentioned Planquart.When that occurs, what are we able to be expecting to peer within the evening sky? In 1946, T CrB reached magnitude +2, which means it used to be simply visual to the bare eye, equivalent in brightness to the celebrities of the Giant Dipper. Shears expects it to be simply as brilliant this time round.T CrB is positioned within the constellation of Corona Borealis, the Northern Crown, which is recently visual within the evening sky throughout the entire of the Northern Hemisphere and from as some distance south as South Africa and Australia (albeit low down within the sky from southerly places).”At the present T CrB is 10th magnitude, so it is just visual in massive binoculars,” mentioned Shears. “But if it rises [in brightness] it is going to turn into visual in usual binoculars after which the bare eye.”And the upward push in brightness will likely be fast. “It’s just a subject of a couple of hours for the upward push to happen — exactly what number of isn’t referred to as the upward push hasn’t ever been stuck sooner than,” mentioned Shears. “That’s why it’s so thrilling. We are hoping that with such a lot of observers this time round, we might certainly catch it because it awakes from its shut eye.”Certainly there will likely be many observers, as astronomers wait and watch to catch a glimpse of this uncommon nova and be told extra about what is occurring at the floor of this white dwarf when it hosts a large thermonuclear explosion. “When it explodes, it is going to be one of the crucial broadly noticed gadgets, focused by means of telescopes international,” mentioned Planquart.As for what the long run holds for T CrB, a fair higher explosion is at the horizon. The mass of the white dwarf within the T CrB device is 1.37 instances the mass of our solar. That is very with reference to the Chandrasekhar restrict, which is 1.44 sun plenty, and is the purpose at which the thermonuclear detonation overcomes the white dwarf and blows it to smithereens as a Kind Ia supernova. Because it ceaselessly steals mass from its spouse pink massive and grows within the procedure, it hurries up its personal loss of life.”As white dwarfs means the Chandrasekhar restrict their radius shrinks and their floor gravity is higher,” Ken Hinkle, an astronomer at NOIRLab in Tucson, Arizona, instructed Area.com. “This leads to the fast time between eruptions.”Because the white dwarf inches nearer to the Chandrasekhar restrict, the nova occasions will turn into extra common, till someday … increase! However it is going to take loads of hundreds, if no longer tens of millions, of years for the white dwarf to get to that degree, so there is no rush so as to add it in your calendar. Within the interim, we will stay looking at the sky for its newest nova.Jean Schneider’s paper used to be printed in Analysis Notes of the AAS.
(Symbol credit score: NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle)Planquart’s observations shed some gentle at the subject, specifically the brightening observed in 1938 and 2015, adopted by means of a dimming, maximum just lately observed in 2023.”We learned that from 2015 to 2023, the accretion disk across the white dwarf had reached its most extension and changed into warmer and extra luminous, resulting in higher brightness,” Planquart mentioned. This enhanced what Planquart calls “the vampirization impact,” expanding the switch of subject to the white dwarf in a “super-active section.” Then, in 2023, the accretion disk cooled go into reverse once more, ensuing within the dimming, even supposing subject continues to glide from the disk to the white dwarf at a slower price.”It’s most probably that this enhanced task is essential to cause the nova explosion, because it lets in the fabric to amass extra impulsively,” mentioned Planquart.Then, in 2023, the accretion disk cooled go into reverse once more, ensuing within the dimming, even supposing subject continues to glide from the disk to the white dwarf at a slower price. Then again, the main points are nonetheless reasonably unclear — what reasons the state alternate within the accretion disk that ends up in the super-active section, and precisely what is occurring at the floor of the white dwarf between the disk cooling once more and the nova explosion?Even though Schneider’s precise date predictions might or won’t come to move, the development of the super-active section adopted by means of quiescence and dimming means that the nova is solely across the nook. “We might be expecting to peer the explosion within the coming months — or most likely subsequent 12 months,” mentioned Planquart.When that occurs, what are we able to be expecting to peer within the evening sky? In 1946, T CrB reached magnitude +2, which means it used to be simply visual to the bare eye, equivalent in brightness to the celebrities of the Giant Dipper. Shears expects it to be simply as brilliant this time round.T CrB is positioned within the constellation of Corona Borealis, the Northern Crown, which is recently visual within the evening sky throughout the entire of the Northern Hemisphere and from as some distance south as South Africa and Australia (albeit low down within the sky from southerly places).”At the present T CrB is 10th magnitude, so it is just visual in massive binoculars,” mentioned Shears. “But if it rises [in brightness] it is going to turn into visual in usual binoculars after which the bare eye.”And the upward push in brightness will likely be fast. “It’s just a subject of a couple of hours for the upward push to happen — exactly what number of isn’t referred to as the upward push hasn’t ever been stuck sooner than,” mentioned Shears. “That’s why it’s so thrilling. We are hoping that with such a lot of observers this time round, we might certainly catch it because it awakes from its shut eye.”Certainly there will likely be many observers, as astronomers wait and watch to catch a glimpse of this uncommon nova and be told extra about what is occurring at the floor of this white dwarf when it hosts a large thermonuclear explosion. “When it explodes, it is going to be one of the crucial broadly noticed gadgets, focused by means of telescopes international,” mentioned Planquart.As for what the long run holds for T CrB, a fair higher explosion is at the horizon. The mass of the white dwarf within the T CrB device is 1.37 instances the mass of our solar. That is very with reference to the Chandrasekhar restrict, which is 1.44 sun plenty, and is the purpose at which the thermonuclear detonation overcomes the white dwarf and blows it to smithereens as a Kind Ia supernova. Because it ceaselessly steals mass from its spouse pink massive and grows within the procedure, it hurries up its personal loss of life.”As white dwarfs means the Chandrasekhar restrict their radius shrinks and their floor gravity is higher,” Ken Hinkle, an astronomer at NOIRLab in Tucson, Arizona, instructed Area.com. “This leads to the fast time between eruptions.”Because the white dwarf inches nearer to the Chandrasekhar restrict, the nova occasions will turn into extra common, till someday … increase! However it is going to take loads of hundreds, if no longer tens of millions, of years for the white dwarf to get to that degree, so there is no rush so as to add it in your calendar. Within the interim, we will stay looking at the sky for its newest nova.Jean Schneider’s paper used to be printed in Analysis Notes of the AAS.
Cling onto your hats! Is the ‘blaze megastar’ T Corona Borealis about to move increase?