Simply outdoor Hiroya Yamaguchi’s administrative center is a blackboard crowded with exploded stars, spaceship schematics and spectral traces. The A4 printouts difficult to understand virtually all of the loose area, excluding for a tiny nook the place he occasionally scribbles in white chalk. At this time, Yamaguchi, an affiliate professor at Japan’s Institute of House and Astronautical Science, is status in entrance of this blackboard, going through me. He is giving me a crash path at the X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Venture, or XRISM, a partnership between NASA, the Jap Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA) and the Eu House Company (ESA). The very first thing I be informed is I have been announcing the telescope’s title mistaken this entire time. Fortunately, I’ve most commonly been repeating the mistaken “ex-riz-um” in my head. It’s if truth be told pronounced “criz-um.”The second one is this area telescope was once introduced on September 6, 2023, sporting the heaviest weight of all: Expectation.Comparable: JAXA, NASA divulge 1st pictures from XRISM X-ray area telescopeJAXA’s two earlier X-ray telescopes, Suzaku and Hitomi, each skilled problems after release. Suzaku’s spectrometer malfunctioned after release, nevertheless it was once in a position to hold out a decade-long imaging challenge. Hitomi was once disastrous: After snapping its dawn symbol, the spacecraft went into an out of control spin and broke aside. To this point, XRISM has been appearing smartly, Yamaguchi says, and has already supplied scientists with an abundance of knowledge since dawn in January — together with some discoveries no person anticipated to search out. “There are such a large amount of surprises,” Yamaguchi laughs, glancing across the more than a few printouts caught to the blackboard.There’s, on the other hand, somewhat of an issue.Signal as much as our publication for the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!First, the excellent news: The telescope’s primary device, a comfortable X-ray spectrometer referred to as Get to the bottom of, is operating as anticipated. The marginally-worse information: An aperture door masking Get to the bottom of has now not opened. A couple of makes an attempt to open the door — or “gate valve” — have failed. Regardless of stories suggesting JAXA and NASA have made up our minds to “perform the spacecraft as is for a minimum of 18 months”, Yamaguchi informed me that “has now not been formally made up our minds.”A NASA spokesperson showed “NASA and JAXA proceed to carry ongoing discussions about the most efficient trail ahead to perform XRISM; the present, main choice is to assemble science for the following 18 months prior to making some other try to open the gate valve, however the businesses will proceed to evaluate possible choices.”With the door closed, an intriguing “What If?” scenario for challenge experts and X-ray astronomers items itself. On one hand, the spacecraft is operating beautifully and appearing it is able to handing over a heap of latest, thrilling information. Looking to open the door dangers harmful the spacecraft. Then again, opening the door may essentially trade our figuring out of the universe. 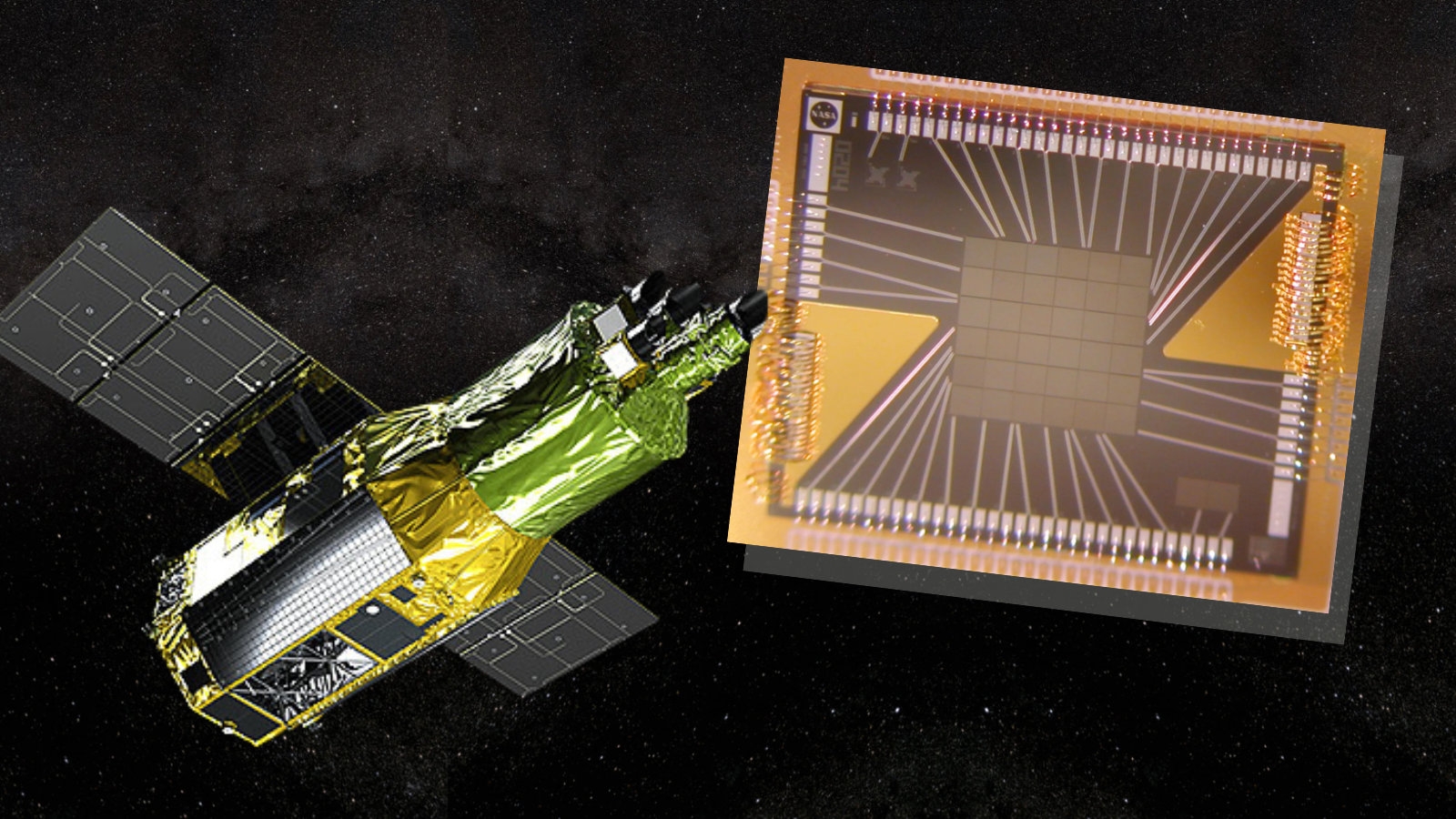 (Left) The NASA/JAXA X-ray telescope XRISM; (proper) the 6-by-6-pixel microcalorimeter array on the middle of Get to the bottom of, an device on XRISM. (Symbol credit score: NASA/XRISM/Caroline Kilbourne/JAXA/Robert Lea (created with Canva))Remedy for ‘X’X-rays supply a technique to probe probably the most maximum lively phenomena within the universe — however, as a result of Earth’s setting blocks X-rays, space-based telescopes are a prerequisite.”We are unraveling the composition of the universe,” Aurora Simionescu, an astrophysicist on the Netherlands Institute for House Analysis, tells me. “That is what X-rays do.”There are greater than a dozen X-ray telescopes recently in area, with NASA’s Chandra observatory, one in every of its so-called Nice Observatories, in all probability essentially the most widely recognized as a result of the fantastic perspectives it has supplied of the X-ray universe. XRISM, with its skill to look essentially the most detailed X-ray spectra but, hopes to carve out a identical legacy. Yamaguchi issues out, on the other hand, that despite the fact that Chandra and XRISM follow the similar a part of the electromagnetic spectrum, they are intended to take action in numerous tactics. That comes right down to the instrumentation on board.Get to the bottom of is what is referred to as a microcalorimeter spectrometer. The detection equipment converts X-rays to warmth, measuring minute adjustments in temperature — we are speaking adjustments in millikelvins — to resolve the quantity and effort of X-rays seen coming from a selected area of area. Power is measured in electron volts (eV). The device due to this fact needs to be cooled right down to only a few levels above absolute 0. That is less warm even than the cosmic microwave background, which is leftover radiation from the start of time. This radiation is scattered throughout our universe, but hidden to the human eye as a result of how completely frigid it’s. “You might be mainly virtually 30 occasions less warm than the coldest a part of outer area,” says Simionescu. The extraordinary cooling impact is accomplished via chemical and mechanical manner.Chandra makes use of a special taste of X-ray detector, which options an array of charge-coupled gadgets, or CCDs. This converts X-ray photons to electrons, fairly than to warmth.Measuring calories is especially helpful, as a result of you’ll plot the collection of X-rays that extend your telescope in opposition to their calories stage — developing what researchers name a “spectrum.” XRISM’s Get to the bottom of has an edge on this case. It is in a position to measure energies about 20 to 30 occasions upper than Chandra can, and with better solution. “This permits XRISM to review a lot more element concerning the atomic physics and the rate construction of the X-ray assets,” says Patrick Slane, director of the Chandra X-ray Heart.
(Left) The NASA/JAXA X-ray telescope XRISM; (proper) the 6-by-6-pixel microcalorimeter array on the middle of Get to the bottom of, an device on XRISM. (Symbol credit score: NASA/XRISM/Caroline Kilbourne/JAXA/Robert Lea (created with Canva))Remedy for ‘X’X-rays supply a technique to probe probably the most maximum lively phenomena within the universe — however, as a result of Earth’s setting blocks X-rays, space-based telescopes are a prerequisite.”We are unraveling the composition of the universe,” Aurora Simionescu, an astrophysicist on the Netherlands Institute for House Analysis, tells me. “That is what X-rays do.”There are greater than a dozen X-ray telescopes recently in area, with NASA’s Chandra observatory, one in every of its so-called Nice Observatories, in all probability essentially the most widely recognized as a result of the fantastic perspectives it has supplied of the X-ray universe. XRISM, with its skill to look essentially the most detailed X-ray spectra but, hopes to carve out a identical legacy. Yamaguchi issues out, on the other hand, that despite the fact that Chandra and XRISM follow the similar a part of the electromagnetic spectrum, they are intended to take action in numerous tactics. That comes right down to the instrumentation on board.Get to the bottom of is what is referred to as a microcalorimeter spectrometer. The detection equipment converts X-rays to warmth, measuring minute adjustments in temperature — we are speaking adjustments in millikelvins — to resolve the quantity and effort of X-rays seen coming from a selected area of area. Power is measured in electron volts (eV). The device due to this fact needs to be cooled right down to only a few levels above absolute 0. That is less warm even than the cosmic microwave background, which is leftover radiation from the start of time. This radiation is scattered throughout our universe, but hidden to the human eye as a result of how completely frigid it’s. “You might be mainly virtually 30 occasions less warm than the coldest a part of outer area,” says Simionescu. The extraordinary cooling impact is accomplished via chemical and mechanical manner.Chandra makes use of a special taste of X-ray detector, which options an array of charge-coupled gadgets, or CCDs. This converts X-ray photons to electrons, fairly than to warmth.Measuring calories is especially helpful, as a result of you’ll plot the collection of X-rays that extend your telescope in opposition to their calories stage — developing what researchers name a “spectrum.” XRISM’s Get to the bottom of has an edge on this case. It is in a position to measure energies about 20 to 30 occasions upper than Chandra can, and with better solution. “This permits XRISM to review a lot more element concerning the atomic physics and the rate construction of the X-ray assets,” says Patrick Slane, director of the Chandra X-ray Heart. 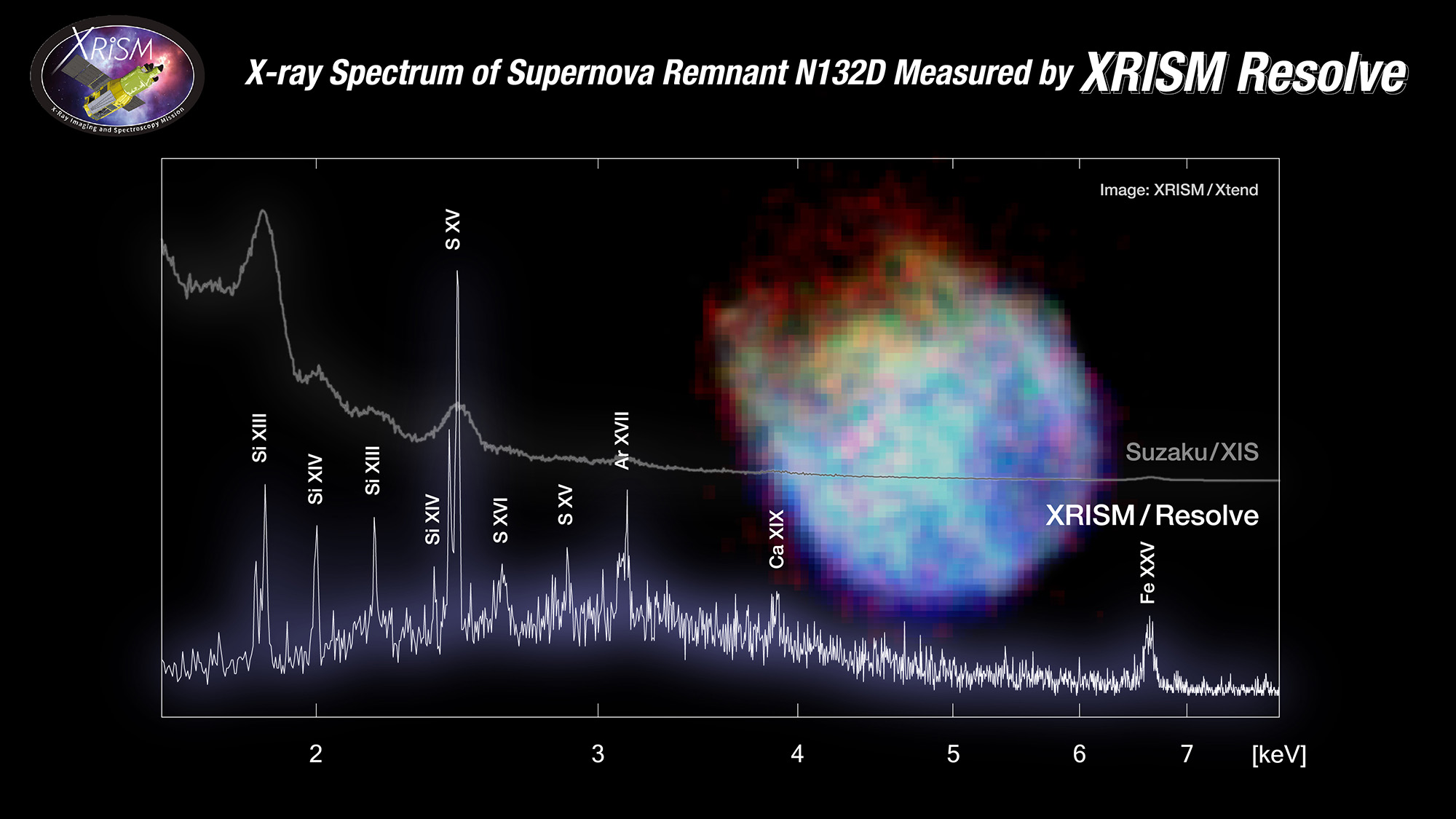 Suzuki’s spectrum of a supernova remnant in comparison to XRISM’s model. See how XRISM’s is in a position to select up ins and outs that Suzuki could not discover? (Symbol credit score: JAXA)Chandra, on the other hand, has benefits of its personal. It is also built with the very best quality X-ray mirrors ever constructed, Slane says, because of this its imaging high quality a long way exceeds XRISM’s. The important thing this is the mirrors give Chandra an angular solution of 0.5 arcseconds, which necessarily permits Chandra to tell apart between items within the sky which might be shut in combination. Evaluate that to XRISM, which has an angular solution of one.7 arcminutes. Due to that feat of engineering, Slane says Chandra can select X-ray level assets about 200 occasions extra simply than XRISM may. In follow, this makes NASA’s telescope extraordinarily helpful for that specialize in the ones level assets — far away, smaller goals like neutron stars, planets and comets. XRISM is just right for “prolonged” goals, just like the diffuse fuel between and inside of galaxies.Which, eventually, brings us to XRISM’s gate valve: The closed door successfully blockading low calories X-rays from attaining the detector. As of now, the telescope is constant to discover the high-energy X-ray universe as a result of the ones wavelengths aren’t suffering from the gate catch 22 situation — in reality, Yamaguchi and Simionescu each say it is already returning improbable effects at upper energies.But when the door is caught for just right, scientists must take care of portions of our cosmos closing inaccessible… no less than, till some other X-ray telescope comes alongside, which might be the Athena challenge within the mid-2030s.XRISMgate-gateThe gate valve was once designed to care for a near-vacuum inside the telescope’s cryostat — necessarily the refrigerator that guarantees its tools stay extraordinarily chilly — whilst XRISM was once stationed on Earth. As soon as a telescope reaches orbit, keeping up this type of vacuum is not a subject. In area, area itself creates the vacuum. Because of this, the gate valve was once designed to turn open in a two-step procedure after release, by means of a collection of actuators. Briefly, the actuators would slide again to permit the door — manufactured from a beryllium window and metal mesh — to turn open. That did not occur. JAXA has attempted to finesse the equipment open on 3 other events, nevertheless it hasn’t budged. The following try can be a far riskier one, doubtlessly requiring the spacecraft to heat up from its extraordinarily low temperatures and be shaken about. The function? Dislodging the actuators with power. That is a chance the distance businesses working XRISM will want to weigh up. With the gate valve closed, they are already banking information. And it is superb information.”Essentially the most stunning factor is while you have a look at the information, and it appears to be like not anything like what you anticipated — and this is occurring with the present XRISM information,” says Simionescu.
Suzuki’s spectrum of a supernova remnant in comparison to XRISM’s model. See how XRISM’s is in a position to select up ins and outs that Suzuki could not discover? (Symbol credit score: JAXA)Chandra, on the other hand, has benefits of its personal. It is also built with the very best quality X-ray mirrors ever constructed, Slane says, because of this its imaging high quality a long way exceeds XRISM’s. The important thing this is the mirrors give Chandra an angular solution of 0.5 arcseconds, which necessarily permits Chandra to tell apart between items within the sky which might be shut in combination. Evaluate that to XRISM, which has an angular solution of one.7 arcminutes. Due to that feat of engineering, Slane says Chandra can select X-ray level assets about 200 occasions extra simply than XRISM may. In follow, this makes NASA’s telescope extraordinarily helpful for that specialize in the ones level assets — far away, smaller goals like neutron stars, planets and comets. XRISM is just right for “prolonged” goals, just like the diffuse fuel between and inside of galaxies.Which, eventually, brings us to XRISM’s gate valve: The closed door successfully blockading low calories X-rays from attaining the detector. As of now, the telescope is constant to discover the high-energy X-ray universe as a result of the ones wavelengths aren’t suffering from the gate catch 22 situation — in reality, Yamaguchi and Simionescu each say it is already returning improbable effects at upper energies.But when the door is caught for just right, scientists must take care of portions of our cosmos closing inaccessible… no less than, till some other X-ray telescope comes alongside, which might be the Athena challenge within the mid-2030s.XRISMgate-gateThe gate valve was once designed to care for a near-vacuum inside the telescope’s cryostat — necessarily the refrigerator that guarantees its tools stay extraordinarily chilly — whilst XRISM was once stationed on Earth. As soon as a telescope reaches orbit, keeping up this type of vacuum is not a subject. In area, area itself creates the vacuum. Because of this, the gate valve was once designed to turn open in a two-step procedure after release, by means of a collection of actuators. Briefly, the actuators would slide again to permit the door — manufactured from a beryllium window and metal mesh — to turn open. That did not occur. JAXA has attempted to finesse the equipment open on 3 other events, nevertheless it hasn’t budged. The following try can be a far riskier one, doubtlessly requiring the spacecraft to heat up from its extraordinarily low temperatures and be shaken about. The function? Dislodging the actuators with power. That is a chance the distance businesses working XRISM will want to weigh up. With the gate valve closed, they are already banking information. And it is superb information.”Essentially the most stunning factor is while you have a look at the information, and it appears to be like not anything like what you anticipated — and this is occurring with the present XRISM information,” says Simionescu. The galaxy cluster Abell 2319 captured in X-ray gentle (proven in pink) via the XRISM area telescope. (Symbol credit score: JAXA/NASA/XRISM Xtend; background, DSS)Nonetheless, it is a tricky destroy for Simionescu. She’s in particular desirous about finding out X-rays from “galactic atmospheres” — the stuff XRISM was once constructed to have a look at with an open gate valve. With the gate closed, that a part of the X-ray universe stays locked away. She totally has the same opinion with the verdict to not chance looking to open the gate — no less than for now. However that does not imply it isn’t painful, figuring out what might be.”I’m completely gutted that we will’t see under 2 keV,” Simionescu says.And what may lie under?Some X-ray area telescopes, just like the ESA’s XMM-Newton, can see decrease calories X-rays, right down to under 2 keV. For example, it has seen the Coma Cluster, which incorporates over 1,000 galaxies, at energies as little as 0.3 keV. And XRISM’s different device, Xtend, could also be in a position to get right down to decrease energies. However those are CCD detectors too and now not as helpful for acquiring spectra. Outdoor of XRISM, there is no X-ray telescope orbiting the Earth with capacity to seem throughout “prolonged” items at low energies with excessive solution, which is especially necessary for Simionescu’s paintings.Right through an internet name, she stocks a wide-field X-ray symbol of M87, the primary black hollow to be imaged via people in visual gentle. The picture was once snapped via Chandra in 2019. “That is my favourite object on the planet,” she says excitedly.The distance surrounding that black hollow is a maelstrom. Simionescu’s cursor bounces across the sky as she issues out the huge jet emanating from the black hollow in addition to spaces of dense fuel and an extended filament that stretches light-years into the cosmos. She describes a graph of the spectra seen via Chandra at M87 — all under 2 keV — and notes how it is all “a mumbo jumbo” of emission traces from oxygen, neon, nickel and different gases.With the gate open, that will trade.”It’s good to inform what’s the composition of the fuel, how is it being moved, how is it being driven out via the black hollow — which is all data that, at the moment, you can’t get,” she says.It is fascinating to imagine the bounce ahead with XRISM in opposition to the backdrop of uncertainty that surrounds NASA’s Chandra challenge. Sadly, the sector of X-ray astronomy might be with out Chandra within the close to long term. The distance telescope’s operations, that have lasted for 25 years, face excessive funds cuts in 2024. Astronomers say the proposed funds would consequence within the challenge’s cancellation. “If Chandra had been to be canceled, we’d lose an amazing useful resource for all of contemporary astrophysics,” Slane says.That may be an ignominious finish for the Nice Observatory, which stays helpful for long term discoveries, together with running in tandem with XRISM. If JAXA does unjam its door, Chandra can be the most important software to observe up XRISM’s observations.In the meantime, the ghosts of Suzaku and Hitomi will linger till the following try at opening the door. For now, the sector of X-ray astronomy is serious about what is to return. The worst case state of affairs is not all that dangerous, relying the way you have a look at it.”We’re taking improbable information that no one has ever been in a position to take prior to,” Simionescu says. “The spectra are all completely impressive.”
The galaxy cluster Abell 2319 captured in X-ray gentle (proven in pink) via the XRISM area telescope. (Symbol credit score: JAXA/NASA/XRISM Xtend; background, DSS)Nonetheless, it is a tricky destroy for Simionescu. She’s in particular desirous about finding out X-rays from “galactic atmospheres” — the stuff XRISM was once constructed to have a look at with an open gate valve. With the gate closed, that a part of the X-ray universe stays locked away. She totally has the same opinion with the verdict to not chance looking to open the gate — no less than for now. However that does not imply it isn’t painful, figuring out what might be.”I’m completely gutted that we will’t see under 2 keV,” Simionescu says.And what may lie under?Some X-ray area telescopes, just like the ESA’s XMM-Newton, can see decrease calories X-rays, right down to under 2 keV. For example, it has seen the Coma Cluster, which incorporates over 1,000 galaxies, at energies as little as 0.3 keV. And XRISM’s different device, Xtend, could also be in a position to get right down to decrease energies. However those are CCD detectors too and now not as helpful for acquiring spectra. Outdoor of XRISM, there is no X-ray telescope orbiting the Earth with capacity to seem throughout “prolonged” items at low energies with excessive solution, which is especially necessary for Simionescu’s paintings.Right through an internet name, she stocks a wide-field X-ray symbol of M87, the primary black hollow to be imaged via people in visual gentle. The picture was once snapped via Chandra in 2019. “That is my favourite object on the planet,” she says excitedly.The distance surrounding that black hollow is a maelstrom. Simionescu’s cursor bounces across the sky as she issues out the huge jet emanating from the black hollow in addition to spaces of dense fuel and an extended filament that stretches light-years into the cosmos. She describes a graph of the spectra seen via Chandra at M87 — all under 2 keV — and notes how it is all “a mumbo jumbo” of emission traces from oxygen, neon, nickel and different gases.With the gate open, that will trade.”It’s good to inform what’s the composition of the fuel, how is it being moved, how is it being driven out via the black hollow — which is all data that, at the moment, you can’t get,” she says.It is fascinating to imagine the bounce ahead with XRISM in opposition to the backdrop of uncertainty that surrounds NASA’s Chandra challenge. Sadly, the sector of X-ray astronomy might be with out Chandra within the close to long term. The distance telescope’s operations, that have lasted for 25 years, face excessive funds cuts in 2024. Astronomers say the proposed funds would consequence within the challenge’s cancellation. “If Chandra had been to be canceled, we’d lose an amazing useful resource for all of contemporary astrophysics,” Slane says.That may be an ignominious finish for the Nice Observatory, which stays helpful for long term discoveries, together with running in tandem with XRISM. If JAXA does unjam its door, Chandra can be the most important software to observe up XRISM’s observations.In the meantime, the ghosts of Suzaku and Hitomi will linger till the following try at opening the door. For now, the sector of X-ray astronomy is serious about what is to return. The worst case state of affairs is not all that dangerous, relying the way you have a look at it.”We’re taking improbable information that no one has ever been in a position to take prior to,” Simionescu says. “The spectra are all completely impressive.”
‘Completely gutted’: How a jammed door is locking astronomers out of the X-ray universe