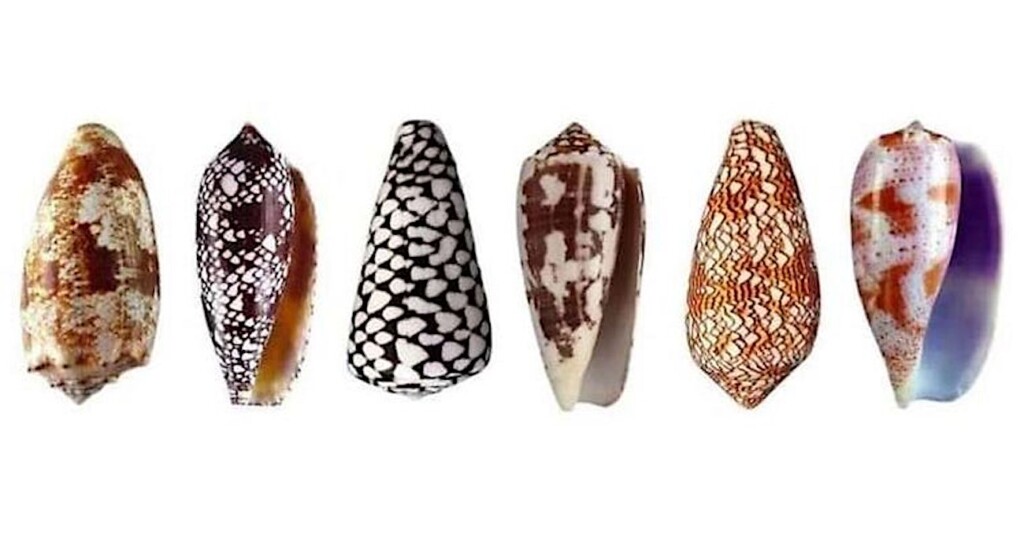
6 bad cone snails – Pictures by means of Almed2 and H Zell compiled by means of Mario NET, CC BY-SA 4.0
6 bad cone snails – Pictures by means of Almed2 and H Zell compiled by means of Mario NET, CC BY-SA 4.0
Fatal poison from cone snails is usually a newfound secret to meaking higher medication to regard diabetes, consistent with a brand new find out about.
The toxin, from some of the venomous creatures on this planet, may additionally result in new drugs for extra prerequisites led to by means of hormone issues, stated the researchers.
They known an element inside the venom from the Conus geographus that mimics a human hormone referred to as somatostatin—which regulates the degrees of blood sugar and several other different hormones within the human frame.
The crew, led by means of scientists from the College of Utah in america, stated the somatostatin-like toxin is helping the snail hunt its prey. In people, somatostatin acts like a brake pedal for lots of processes within the frame, fighting ranges of blood sugar, a number of hormones, and plenty of different vital molecules from emerging dangerously prime.
The cone snail toxin, referred to as consomatin, works in a similar fashion—however consomatin is extra solid and explicit than the human hormone, which makes it a “promising” blueprint for drug design, consistent with the effects revealed within the magazine Nature Communications.
Via measuring how consomatin interacts with somatostatin’s goals in human cells in a dish, the researchers came upon that consomatin interacts with some of the similar proteins that somatostatin does.
Importantly, regardless that, whilst somatostatin without delay interacts with a number of proteins, consomatin most effective interacts with one. The sort of fine-tuned concentrated on implies that the cone snail toxin impacts hormone-determined blood sugar ranges, however no longer the degrees of a number of different molecules.
They concluded that the cone snail toxin was once extra exactly focused than probably the most explicit artificial medication designed to keep watch over hormone ranges, corresponding to medication that keep watch over enlargement hormone.
Even supposing the snail toxin could also be bad to make use of as a healing, the find out about of its construction may result in the design of protected medication for endocrine issues.
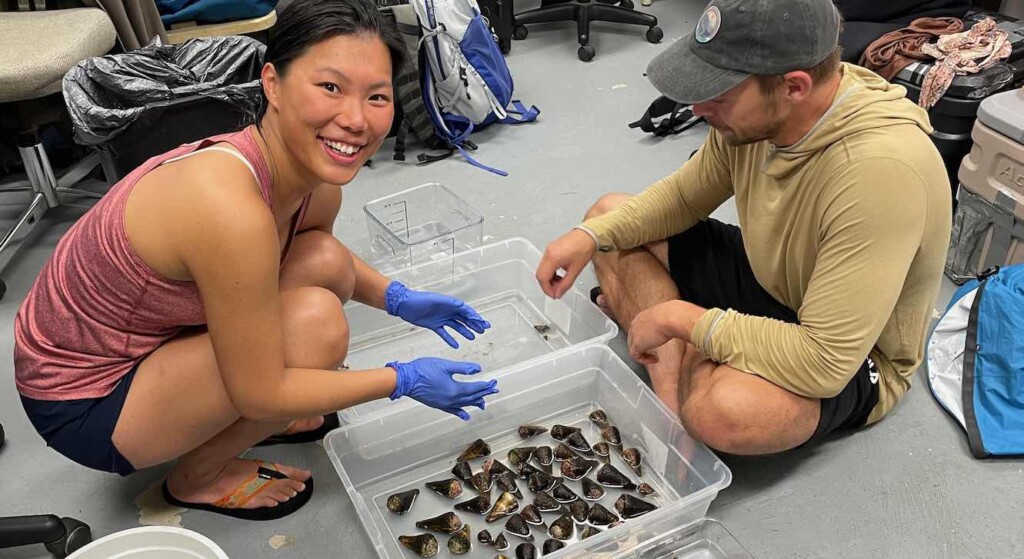 Ho Yan Yeung and Thomas Koch inspecting cone snails – Credit score: Safavi Lab / SWNS
Ho Yan Yeung and Thomas Koch inspecting cone snails – Credit score: Safavi Lab / SWNS
Consomatin lasts some distance longer within the frame than the human hormone, because of the inclusion of an extraordinary amino acid that makes it tough to wreck down. Finding out that function could be helpful to pharmaceutical researchers taking a look to make medication that may have long-lasting advantages.
Senior creator Professor Helena Safavi, of the College of Utah says the toxin’s precision will also be “extremely helpful” when treating illness.
“Venomous animals have, via evolution, fine-tuned venom elements to hit a specific goal within the prey and disrupt it. If you are taking one person part out of the venom aggregate and have a look at the way it disrupts standard body structure, that pathway is regularly in reality related in illness.”
She described it as “somewhat of a shortcut” for medicinal chemists as a result of consomatin stocks an evolutionary lineage with somatostatin, however over hundreds of thousands of years of evolution, the cone snail became its personal hormone right into a weapon.
MORE DIABETES GOOD NEWS: Diabetes-Reversing Drug Boosts Insulin-Generating Cells by means of 700%
Consomatin’s fatal results hinge on its skill to stop blood sugar ranges from emerging. It lowers the extent of blood sugar so briefly that the cone snail’s prey turns into non-responsive. Then, its 2d part assists in keeping blood sugar ranges from getting better.
“We predict the cone snail evolved this extremely selective toxin to paintings at the side of the insulin-like toxin to convey down blood glucose to a in reality low stage,” stated Dr. Ho Yan Yeung of the College of Utah, the find out about’s lead creator.
She defined that the truth that a number of portions of the cone snail’s venom goal blood sugar law hints that it might come with many different molecules that do identical issues.
POPULAR: New Synthetic Pancreas for Sort 2 Diabetes Manages Blood Sugar Two times as Smartly as Jabs –Now Authorized in UK
“It implies that there would possibly no longer most effective be insulin and somatostatin-like toxins within the venom,” stated Dr. Yeung. “There may doubtlessly be different toxins that experience glucose-regulating houses too.”
It will appear sudden {that a} snail is in a position to outperform the most productive human chemists in its drug design, however Prof. Safavi says that the cone snails have evolutionary time on their aspect.
“We’ve been looking to do medicinal chemistry and drug building for a couple of hundred years, every so often badly.”
RECYCLING OYSTER SHELLS: Eating places To find Firms to Take Their Spent Oyster Shells to Repair Oyster Reefs
“Cone snails have had numerous time to do it in reality smartly—and they’re simply in reality excellent chemists.”
SEND THIS COOL DISCOVERY To Seashell-Loving Pals On Social Media…
Cone Snail Poison is Fatal However Might Now Result in Higher Diabetes and Hormone Medication