A seek for the primary stars that winked into life on the daybreak of the Universe has yielded some of the oldest stars we now have discovered but, proper subsequent door to our personal galaxy.It isn’t moderately a member of the primary stellar era. This glimmer within the darkness, referred to as LMC 119, used to be noticed within the Massive Magellanic Cloud that orbits the Milky Approach, and it is the first big name from the Universe’s moment era that is been present in some other galaxy.
“This big name supplies a novel window into the very early element-forming procedure in galaxies instead of our personal,” says astrophysicist Anirudh Chiti of the College of Chicago, who led the analysis.
“Now we have constructed up an concept of the way those stars that had been chemically enriched through the primary stars seem like within the Milky Approach, however we do not but know if a few of these signatures are distinctive, or if issues came about in a similar way throughout different galaxies.”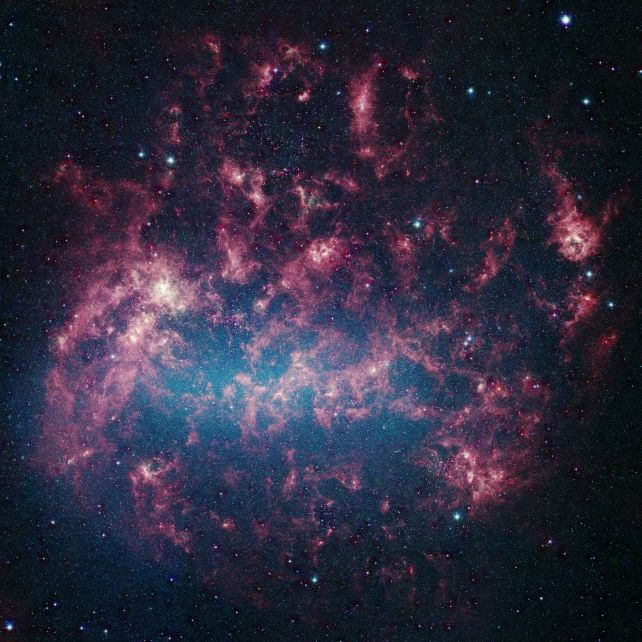 The Massive Magellanic Cloud. (NASA/JPL-Caltech/STScI)The primary stars within the Universe did not have a various vary of fabrics to paintings with. They shaped from the clouds of hydrogen and helium that coalesced within the early Universe within the wake of the Large Bang, turning their cores into fusion machines that blazed gentle around the darkness.
The Massive Magellanic Cloud. (NASA/JPL-Caltech/STScI)The primary stars within the Universe did not have a various vary of fabrics to paintings with. They shaped from the clouds of hydrogen and helium that coalesced within the early Universe within the wake of the Large Bang, turning their cores into fusion machines that blazed gentle around the darkness.
It used to be those stars, smashing hydrogen into helium, after which helium into carbon, and so forth, all of the method as much as iron for probably the most large stars, that began the manufacturing of the periodic desk of parts within the Universe. The celebrities’ violent explosions and collisions produced even heavier parts.
As soon as those parts had been available in the market within the Universe, they had been taken up into next generations of stars. A celebrity’s metallicity is likely one of the gauges that astronomers use to inform its age; decrease amounts of metals in a celebrity’s composition imply that it used to be born previous within the Universe, when there used to be a lot much less steel round. The Massive Magellanic Cloud in ultraviolet gentle. (NASA/Swift/S. Immler (Goddard) and M. Siegel (Penn State))The Holy Grail can be stars without a metallicity in any way – the ones of the primary era. However none were discovered but. We expect it is because maximum of the ones first stars had been so large that they burned out and died extraordinarily briefly.
The Massive Magellanic Cloud in ultraviolet gentle. (NASA/Swift/S. Immler (Goddard) and M. Siegel (Penn State))The Holy Grail can be stars without a metallicity in any way – the ones of the primary era. However none were discovered but. We expect it is because maximum of the ones first stars had been so large that they burned out and died extraordinarily briefly.
What we have now discovered within the Milky Approach is stars astronomers suppose belong to the second one era – with so little metallicity that they should were born best from the fabric that used to be left after the primary era exploded into stardust.
They’re extraordinarily uncommon – not up to one big name in 100,000 is a second-generation big name – however they are price searching for, the researchers say. And discovering one out of doors the Milky Approach would possibly let us know if the fabrics floating across the early Universe had been frivolously disbursed.
“Of their outer layers, those stars maintain the weather close to the place they shaped,” Chiti says. “If you’ll be able to discover a very outdated big name and get its chemical composition, you’ll be able to perceive what the chemical composition of the universe used to be like the place that big name shaped, billions of years in the past.”
To search out extragalactic historic stars, Chiti and his colleagues became their consideration to the Massive Magellanic Cloud, a satellite tv for pc of the Milky Approach that orbits at a distance of round 160,000 light-years. That is the place they discovered LMC 119, a celebrity so deficient in heavier parts that it should be a member of the second one era of stars. Symbol of the Milky Approach compiled from Gaia information, with the Massive and Small Magellanic Clouds within the backside proper. (ESA/Gaia/DPAC)Curiously, the crew present in LMC 119 some of the solutions they had been searching for. It does vary in composition to the Milky Approach second-generation stars – it has considerably much less carbon and iron.
Symbol of the Milky Approach compiled from Gaia information, with the Massive and Small Magellanic Clouds within the backside proper. (ESA/Gaia/DPAC)Curiously, the crew present in LMC 119 some of the solutions they had been searching for. It does vary in composition to the Milky Approach second-generation stars – it has considerably much less carbon and iron.
“That used to be very intriguing, and it means that most likely carbon enhancement of the earliest era, as we see within the Milky Approach, used to be now not common. We will must do additional research, nevertheless it suggests there are variations from position to put,” Chiti says.
“I feel we are filling out the image of what the early detail enrichment procedure appeared like in numerous environments.”
The researchers consider extra of those historic stars could be lurking available in the market within the Massive Magellanic Cloud. Discovering them may yield new clues concerning the infancy of the Universe, and the diversities in evolutionary paths taken through stars separated throughout house and time.The analysis has been revealed in Nature Astronomy.
Considered one of The Oldest Stars in The Universe Discovered Proper Beside Milky Approach