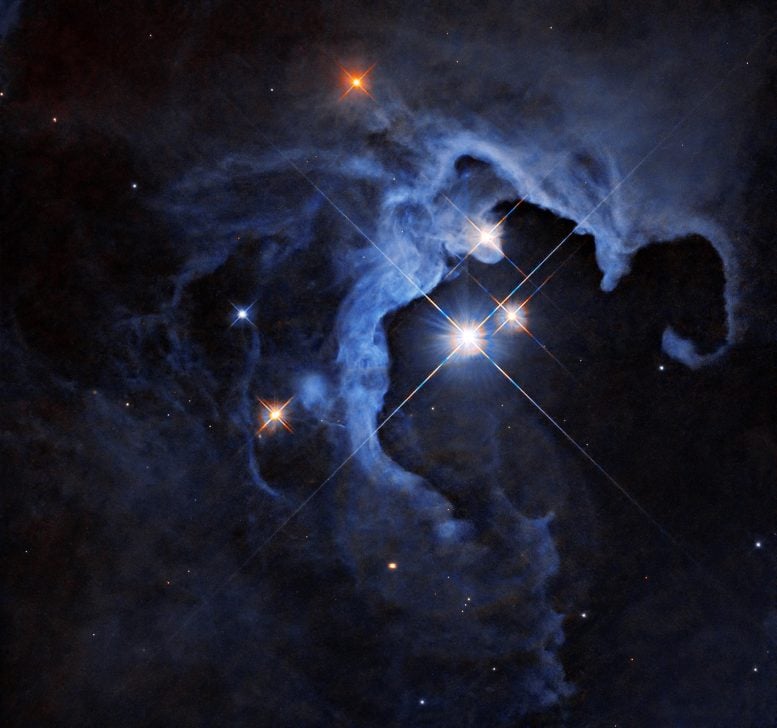
 This NASA Hubble House Telescope symbol captures a triple-star megastar gadget. Credit score: NASA, ESA, G. Duchene (Universite de Grenoble I); Symbol Processing: Gladys Kober (NASA/Catholic College of The us)NASA’s Hubble House Telescope captured a putting symbol of a trio of stars, together with the variable megastar HP Tau, in a mirrored image nebula. Those younger T Tauri stars, no longer but present process nuclear fusion, are nonetheless shrouded within the remnants of the mud and fuel clouds from which they shaped, highlighting the early phases of megastar formation and planetary disk construction.Corresponding to a glittering cosmic geode, a shocking trio of stars blaze from the hollowed-out hollow space of a mirrored image nebula on this new symbol captured by means of NASA’s Hubble House Telescope. This triple-star gadget consists of the variable megastar HP Tau, HP Tau G2, and HP Tau G3. HP Tau is referred to as a T Tauri megastar, a kind of younger variable megastar that hasn’t but began nuclear fusion however is starting to evolve right into a hydrogen-fueled megastar very similar to our Solar.T Tauri stars are normally more youthful than 10 million years outdated. When put next, our Solar is round 4.6 billion years outdated. They’re frequently discovered nonetheless enveloped within the clouds of mud and fuel from which they shaped.
This NASA Hubble House Telescope symbol captures a triple-star megastar gadget. Credit score: NASA, ESA, G. Duchene (Universite de Grenoble I); Symbol Processing: Gladys Kober (NASA/Catholic College of The us)NASA’s Hubble House Telescope captured a putting symbol of a trio of stars, together with the variable megastar HP Tau, in a mirrored image nebula. Those younger T Tauri stars, no longer but present process nuclear fusion, are nonetheless shrouded within the remnants of the mud and fuel clouds from which they shaped, highlighting the early phases of megastar formation and planetary disk construction.Corresponding to a glittering cosmic geode, a shocking trio of stars blaze from the hollowed-out hollow space of a mirrored image nebula on this new symbol captured by means of NASA’s Hubble House Telescope. This triple-star gadget consists of the variable megastar HP Tau, HP Tau G2, and HP Tau G3. HP Tau is referred to as a T Tauri megastar, a kind of younger variable megastar that hasn’t but began nuclear fusion however is starting to evolve right into a hydrogen-fueled megastar very similar to our Solar.T Tauri stars are normally more youthful than 10 million years outdated. When put next, our Solar is round 4.6 billion years outdated. They’re frequently discovered nonetheless enveloped within the clouds of mud and fuel from which they shaped.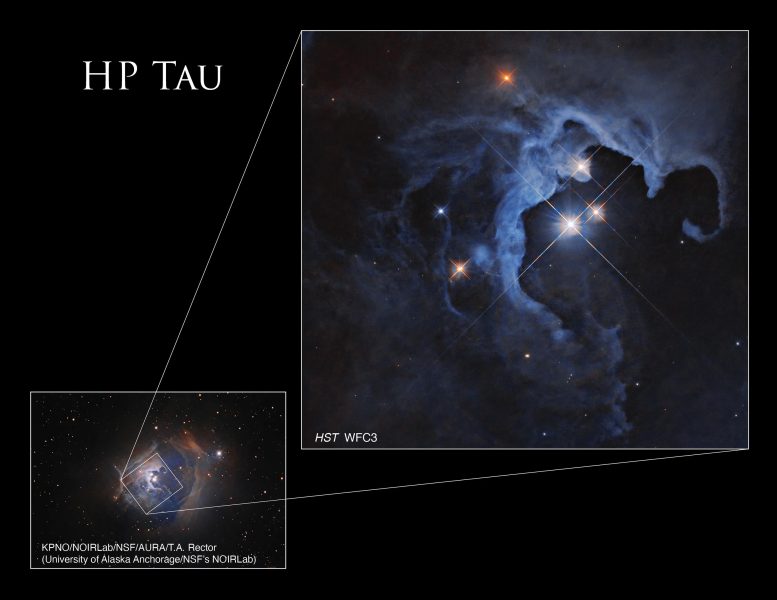 The field within the ground-based symbol unearths the site of Hubble’s view inside the wider context of this triple-star gadget. Credit score: NASA, ESA, G. Duchene (Universite de Grenoble I); Symbol Processing: Gladys Kober (NASA/Catholic College of The us); Inset: KPNO/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/T.A. Rector (College of Alaska Anchorage/NSF’s NOIRLab)As with every variable stars, HP Tau’s brightness adjustments through the years. T Tauri stars are identified to have each periodic and random fluctuations in brightness. The random permutations could also be because of the chaotic nature of a creating younger megastar, similar to instabilities within the accretion disk of mud and fuel across the megastar, subject material from that disk falling onto the megastar and being fed on, and flares at the megastar’s floor. The periodic adjustments could also be because of massive sunspots rotating out and in of view.Curving across the stars, a cloud of fuel and dirt shines with their mirrored mild. Mirrored image nebulae don’t emit visual mild of their very own, however shine as the sunshine from within reach stars bounces off the fuel and dirt, like fog illuminated by means of the glow of a automobile’s headlights.HP Tau is positioned roughly 550 light-years away within the constellation Taurus. Hubble studied HP Tau as a part of an investigation into protoplanetary disks, the disks of subject material round stars that coalesce into planets over thousands and thousands of years.
The field within the ground-based symbol unearths the site of Hubble’s view inside the wider context of this triple-star gadget. Credit score: NASA, ESA, G. Duchene (Universite de Grenoble I); Symbol Processing: Gladys Kober (NASA/Catholic College of The us); Inset: KPNO/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/T.A. Rector (College of Alaska Anchorage/NSF’s NOIRLab)As with every variable stars, HP Tau’s brightness adjustments through the years. T Tauri stars are identified to have each periodic and random fluctuations in brightness. The random permutations could also be because of the chaotic nature of a creating younger megastar, similar to instabilities within the accretion disk of mud and fuel across the megastar, subject material from that disk falling onto the megastar and being fed on, and flares at the megastar’s floor. The periodic adjustments could also be because of massive sunspots rotating out and in of view.Curving across the stars, a cloud of fuel and dirt shines with their mirrored mild. Mirrored image nebulae don’t emit visual mild of their very own, however shine as the sunshine from within reach stars bounces off the fuel and dirt, like fog illuminated by means of the glow of a automobile’s headlights.HP Tau is positioned roughly 550 light-years away within the constellation Taurus. Hubble studied HP Tau as a part of an investigation into protoplanetary disks, the disks of subject material round stars that coalesce into planets over thousands and thousands of years.
Cosmic Geode: Hubble Captures the Beginning of a Solar-like Superstar















