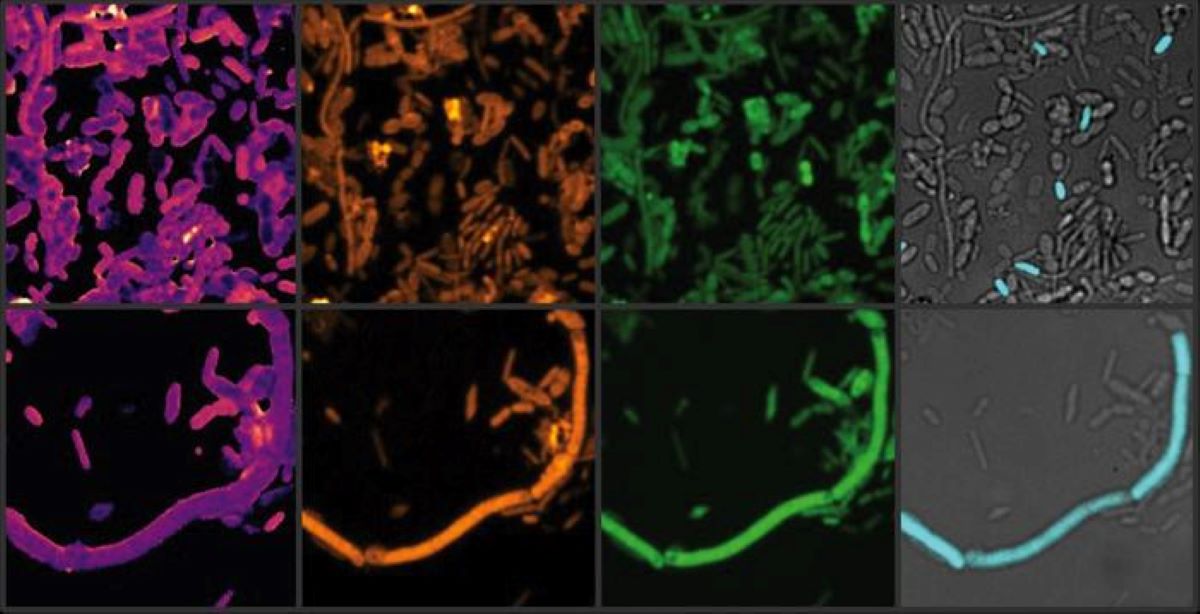
Abstract: COVID-19-induced cognitive impairment is related to the protein IL-1β. Researchers discovered that vaccination can scale back mind irritation and reminiscence loss in rodent fashions. This means vaccines would possibly decrease the danger of lengthy COVID mind fog. Extra analysis is had to ascertain those findings in people.Key Information:IL-1β Protein: Connected to cognitive impairment and diminished neurogenesis.Vaccination Advantages: Reduces mind irritation and cognitive signs.Analysis Findings: Vaccinated fashions confirmed much less reminiscence loss and mind serve as affect.Supply: College of Western OntarioSince the outset of the COVID-19 pandemic, 10 to 30 % of the overall inhabitants has skilled some type of virus-induced cognitive impairment, together with hassle concentrating, mind fog, or reminiscence loss. This led a workforce of researchers to discover the mechanism at the back of this phenomenon and pinpoint a selected protein that seems to be riding those cognitive adjustments. A brand new find out about revealed in Nature Immunology, led through researchers at Western and Washington College College of Drugs in St. Louis, Missouri, additionally checked out how vaccination would possibly lend a hand scale back the affects of reminiscence loss following COVID-19 infections.  The workforce seen that the fashions with greater ranges of IL-1β skilled lack of neurogenesis, the method through which new neurons are shaped within the mind, and in addition displayed reminiscence loss. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsThe analysis workforce, together with Schulich College of Drugs & Dentistry professor Dr. Robyn Klein, who joined Western from Washington College used rodent fashions to higher know how COVID-19 affects cognitive impairment. “We seemed sparsely at their brains all through acute an infection after which later after restoration to find what used to be peculiar in relation to the other immune cells trafficking into the mind and their results on neural cells,” mentioned Klein, who holds the Canada Excellence Analysis Chair in Neurovirology and Neuroimmunology. Klein mentioned she used to be involved through reviews of cognitive impairment within the early days of the pandemic, which led researchers to query whether or not the virus used to be invading the central anxious machine. Klein’s earlier paintings studied viruses that invade the mind. “We had prior to now proven that the virus may now not be detected in human or hamster brains, and this find out about additionally confirmed that the virus used to be now not invading the central anxious machine,” mentioned Klein. The discovering way another mechanism is resulting in cognitive impairment. The workforce recognized SARS-CoV-2 an infection greater ranges of mind Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), a cytokine protein that affects the immune machine. The workforce seen that the fashions with greater ranges of IL-1β skilled lack of neurogenesis, the method through which new neurons are shaped within the mind, and in addition displayed reminiscence loss. Vaccination reduces cognitive signs The workforce concluded IL-1β used to be one doable mechanism riding SARS-CoV-2-induced cognitive impairment, and puzzled whether or not this can be averted through vaccination. Researchers then investigated how vaccinated fashions have been impacted. They discovered a promising correlation between vaccination and diminished cognitive impairments like reminiscence loss. The researchers confirmed that prior vaccination diminished irritation of the mind and decreased ranges of IL-1β. Because of this, the vaccinated fashions skilled much less of an affect on reminiscence and mind serve as. Klein says there may be nonetheless extra paintings to be performed to completely know how vaccinations are attaining this outcome, and whether or not it’ll translate to people. “We all know there’s anecdotal proof that people who’ve been vaccinated have a miles decrease chance of creating this lengthy COVID mind fog,” mentioned Klein. The vaccine used within the find out about isn’t the similar because the vaccines to be had to other people, Klein wired, that means extra research will want to be carried out to additional examine the relationship between vaccination and diminished lengthy COVID affects. “What we do know is that in the event you’re vaccinated you could have a lot much less irritation,” mentioned Klein. Vaccination is ready reducing the danger of the affects of an infection, now not totally combating an infection, she added. As an example, a vaccine can give protection to folks from creating serious pneumonia, however that doesn’t imply it totally protects towards pneumonia. The similar is most probably true for cognitive affects. “Other folks want to needless to say about vaccines,” Klein mentioned. “They want to know what vaccines can do and what they may be able to’t do.” About this reminiscence and COVID-19 analysis newsAuthor: Cynthia Fazio
The workforce seen that the fashions with greater ranges of IL-1β skilled lack of neurogenesis, the method through which new neurons are shaped within the mind, and in addition displayed reminiscence loss. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsThe analysis workforce, together with Schulich College of Drugs & Dentistry professor Dr. Robyn Klein, who joined Western from Washington College used rodent fashions to higher know how COVID-19 affects cognitive impairment. “We seemed sparsely at their brains all through acute an infection after which later after restoration to find what used to be peculiar in relation to the other immune cells trafficking into the mind and their results on neural cells,” mentioned Klein, who holds the Canada Excellence Analysis Chair in Neurovirology and Neuroimmunology. Klein mentioned she used to be involved through reviews of cognitive impairment within the early days of the pandemic, which led researchers to query whether or not the virus used to be invading the central anxious machine. Klein’s earlier paintings studied viruses that invade the mind. “We had prior to now proven that the virus may now not be detected in human or hamster brains, and this find out about additionally confirmed that the virus used to be now not invading the central anxious machine,” mentioned Klein. The discovering way another mechanism is resulting in cognitive impairment. The workforce recognized SARS-CoV-2 an infection greater ranges of mind Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), a cytokine protein that affects the immune machine. The workforce seen that the fashions with greater ranges of IL-1β skilled lack of neurogenesis, the method through which new neurons are shaped within the mind, and in addition displayed reminiscence loss. Vaccination reduces cognitive signs The workforce concluded IL-1β used to be one doable mechanism riding SARS-CoV-2-induced cognitive impairment, and puzzled whether or not this can be averted through vaccination. Researchers then investigated how vaccinated fashions have been impacted. They discovered a promising correlation between vaccination and diminished cognitive impairments like reminiscence loss. The researchers confirmed that prior vaccination diminished irritation of the mind and decreased ranges of IL-1β. Because of this, the vaccinated fashions skilled much less of an affect on reminiscence and mind serve as. Klein says there may be nonetheless extra paintings to be performed to completely know how vaccinations are attaining this outcome, and whether or not it’ll translate to people. “We all know there’s anecdotal proof that people who’ve been vaccinated have a miles decrease chance of creating this lengthy COVID mind fog,” mentioned Klein. The vaccine used within the find out about isn’t the similar because the vaccines to be had to other people, Klein wired, that means extra research will want to be carried out to additional examine the relationship between vaccination and diminished lengthy COVID affects. “What we do know is that in the event you’re vaccinated you could have a lot much less irritation,” mentioned Klein. Vaccination is ready reducing the danger of the affects of an infection, now not totally combating an infection, she added. As an example, a vaccine can give protection to folks from creating serious pneumonia, however that doesn’t imply it totally protects towards pneumonia. The similar is most probably true for cognitive affects. “Other folks want to needless to say about vaccines,” Klein mentioned. “They want to know what vaccines can do and what they may be able to’t do.” About this reminiscence and COVID-19 analysis newsAuthor: Cynthia Fazio
Supply: College of Western Ontario
Touch: Cynthia Fazio – College of Western Ontario
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Closed get entry to.
“Vaccination reduces central anxious machine IL-1β and reminiscence deficits after COVID-19 in mice” through Robyn Klein et al. Nature ImmunologyAbstractVaccination reduces central anxious machine IL-1β and reminiscence deficits after COVID-19 in miceUp to twenty-five% of people inflamed with serious acute respiration syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) showcase postacute cognitive sequelae.Even though tens of millions of circumstances of coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19)-mediated reminiscence disorder are gathering international, the underlying mechanisms and the way vaccination lowers chance are unknown. Interleukin-1 (IL-1), a key part of innate immune protection towards SARS-CoV-2 an infection, is increased within the hippocampi of people with COVID-19.Right here we display that intranasal an infection of C57BL/6J mice with SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant ends up in central anxious machine infiltration of Ly6Chi monocytes and microglial activation.Accordingly, SARS-CoV-2, however now not H1N1 influenza virus, will increase ranges of mind IL-1β and induces chronic IL-1R1-mediatedloss of hippocampal neurogenesis, which promotes postacute cognitive deficits. Vaccination with a low dose of adenoviral-vectored spike protein prevents hippocampal manufacturing of IL-1β all through step forward SARS-CoV-2 an infection, lack of neurogenesis and next reminiscence deficits.Our find out about identifies IL-1β as one doable mechanism riding SARS-CoV-2-induced cognitive impairment in a brand new mouse fashion this is averted through vaccination.
COVID-19 Vaccines Might Cut back Virus-Precipitated Reminiscence Issues – Neuroscience Information