Astronomers have detected dynamic climate actions, reminiscent of large cyclones, at the uninhabitable exoplanet WASP-121 b the use of NASA’s Hubble Area Telescope. This discovery, a very powerful for learning far away planetary climate, is enabled by means of detailed observations and complicated computational fashions. Credit score: NASA, ESA, Quentin Changeat (ESA/STScI), Mahdi Zamani (ESA/Hubble)Stormy climate on show on a “sizzling Jupiter”The Jupiter-sized planet WASP-121 b is not any position to name house. For starters, it orbits very just about a celeb this is brighter and warmer than the Solar. The planet is so dangerously just about its megastar that its higher environment reaches a blazing 3,400 levels Fahrenheit – warmer than a metal blast furnace.A torrent of ultraviolet gentle from the host megastar is heating the planet’s higher environment, which is inflicting the magnesium and iron fuel to flee into house. Robust gravitational tidal forces from the megastar have altered the planet’s form in order that apparently extra soccer formed. Through combining a number of years of Hubble Area Telescope observations with pc modeling, astronomers have discovered proof for large cyclones swirling at the hellish planet. The cyclones are many times created and destroyed because of the massive temperature distinction between the star-facing aspect and darkish night-time aspect of the exoplanet.
Astronomers have detected dynamic climate actions, reminiscent of large cyclones, at the uninhabitable exoplanet WASP-121 b the use of NASA’s Hubble Area Telescope. This discovery, a very powerful for learning far away planetary climate, is enabled by means of detailed observations and complicated computational fashions. Credit score: NASA, ESA, Quentin Changeat (ESA/STScI), Mahdi Zamani (ESA/Hubble)Stormy climate on show on a “sizzling Jupiter”The Jupiter-sized planet WASP-121 b is not any position to name house. For starters, it orbits very just about a celeb this is brighter and warmer than the Solar. The planet is so dangerously just about its megastar that its higher environment reaches a blazing 3,400 levels Fahrenheit – warmer than a metal blast furnace.A torrent of ultraviolet gentle from the host megastar is heating the planet’s higher environment, which is inflicting the magnesium and iron fuel to flee into house. Robust gravitational tidal forces from the megastar have altered the planet’s form in order that apparently extra soccer formed. Through combining a number of years of Hubble Area Telescope observations with pc modeling, astronomers have discovered proof for large cyclones swirling at the hellish planet. The cyclones are many times created and destroyed because of the massive temperature distinction between the star-facing aspect and darkish night-time aspect of the exoplanet.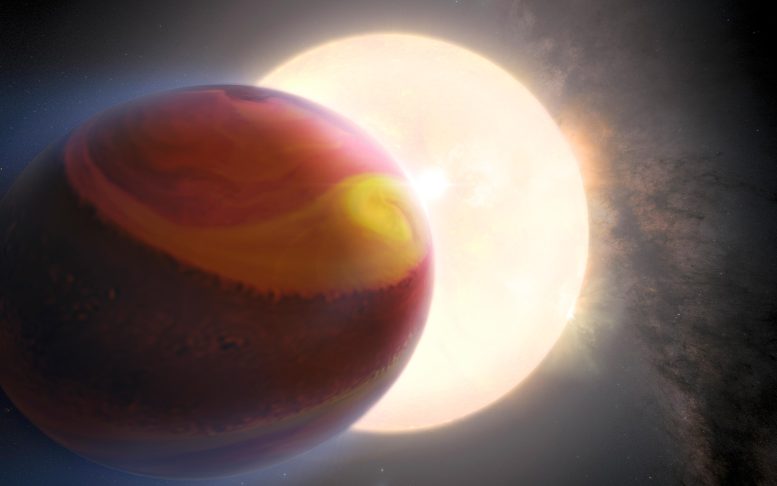 That is an artist’s thought of the exoplanet WASP-121 b, often referred to as Tylos. The exoplanet’s look is in keeping with Hubble simulation records of the item. The usage of Hubble observations, every other workforce of scientists had in the past reported the detection of heavy metals reminiscent of magnesium and iron escaping from the higher environment of the ultra-hot Jupiter exoplanet; marking it as the primary of such detection. The exoplanet is orbiting dangerously just about its host megastar, kind of 2.6% of the space of Earth to the Solar, striking it at the verge of being ripped aside by means of the megastar’s tidal forces. The robust gravitational forces have altered the planet’s form. Credit score: NASA, ESA, Quentin Changeat (ESA/STScI), Mahdi Zamani (ESA/Hubble)Hubble Area Telescope Observes Exoplanet Setting Converting Over 3 YearsBy combining a number of years of observations from NASA’s Hubble Area Telescope at the side of carrying out pc modeling, astronomers have discovered proof for large cyclones and different dynamic climate process swirling on a sizzling, Jupiter-sized planet 880 light-years away.The planet, known as WASP-121 b, isn’t liveable. However this result’s the most important early step in learning climate patterns on far away worlds, and most likely sooner or later discovering probably liveable exoplanets with solid, long-term climates.For the previous few a long time, detailed telescopic and spacecraft observations of neighboring planets in our sun machine display that their turbulent atmospheres aren’t static however continuously converting, similar to climate on Earth. This variability must additionally practice to planets round different stars, too. But it surely takes a number of detailed staring at and computational modeling to in truth measure such adjustments.A Leap forward in Exoplanet Climate ObservationTo make the invention, a world workforce of astronomers assembled and reprocessed Hubble observations of WASP-121 b taken in 2016, 2018, and 2019.They discovered that the planet has a dynamic environment, converting over the years. The workforce used subtle modeling tactics to show that those dramatic temporal diversifications may well be defined by means of climate patterns within the exoplanet’s environment.
That is an artist’s thought of the exoplanet WASP-121 b, often referred to as Tylos. The exoplanet’s look is in keeping with Hubble simulation records of the item. The usage of Hubble observations, every other workforce of scientists had in the past reported the detection of heavy metals reminiscent of magnesium and iron escaping from the higher environment of the ultra-hot Jupiter exoplanet; marking it as the primary of such detection. The exoplanet is orbiting dangerously just about its host megastar, kind of 2.6% of the space of Earth to the Solar, striking it at the verge of being ripped aside by means of the megastar’s tidal forces. The robust gravitational forces have altered the planet’s form. Credit score: NASA, ESA, Quentin Changeat (ESA/STScI), Mahdi Zamani (ESA/Hubble)Hubble Area Telescope Observes Exoplanet Setting Converting Over 3 YearsBy combining a number of years of observations from NASA’s Hubble Area Telescope at the side of carrying out pc modeling, astronomers have discovered proof for large cyclones and different dynamic climate process swirling on a sizzling, Jupiter-sized planet 880 light-years away.The planet, known as WASP-121 b, isn’t liveable. However this result’s the most important early step in learning climate patterns on far away worlds, and most likely sooner or later discovering probably liveable exoplanets with solid, long-term climates.For the previous few a long time, detailed telescopic and spacecraft observations of neighboring planets in our sun machine display that their turbulent atmospheres aren’t static however continuously converting, similar to climate on Earth. This variability must additionally practice to planets round different stars, too. But it surely takes a number of detailed staring at and computational modeling to in truth measure such adjustments.A Leap forward in Exoplanet Climate ObservationTo make the invention, a world workforce of astronomers assembled and reprocessed Hubble observations of WASP-121 b taken in 2016, 2018, and 2019.They discovered that the planet has a dynamic environment, converting over the years. The workforce used subtle modeling tactics to show that those dramatic temporal diversifications may well be defined by means of climate patterns within the exoplanet’s environment.
This visualization presentations the temperature forecast spanning 130 exoplanet-days, throughout first light, midday, sundown, and middle of the night for the exoplanet WASP-121 b, often referred to as Tylos. The brighter yellow areas depict spaces within the day aspect of the exoplanet the place temperatures leap smartly above 2,100 levels Kelvin (3,320 levels Fahrenheit); because of the shut proximity to its host megastar, kind of 2.6% of the space of Earth to the Solar. Because of the intense temperature distinction between the day and evening aspects, astronomers suspect evaporated iron and different heavy metals escaping into the upper layers of the ambience at the day aspect partly fall again onto decrease layers, making it rain iron at evening. One of the heavy metals additionally get away the planet’s gravity from the higher environment. Credit score: NASA, ESA, Quentin Changeat (ESA/STScI), Mahdi Zamani (ESA/Hubble)The workforce discovered that WASP-121 b’s environment presentations notable variations between observations. Maximum dramatically, there may well be large climate fronts, storms, and big cyclones which are many times created and destroyed because of the massive temperature distinction between the star-facing aspect and darkish aspect of the exoplanet. Additionally they detected an obvious offset between the exoplanet’s freshest area and the purpose in the world closest to the megastar, in addition to variability within the chemical composition of the exoplanet’s environment (as measured by way of spectroscopy).The workforce reached those conclusions by means of the use of computational fashions to assist provide an explanation for seen adjustments within the exoplanet’s environment. “The exceptional main points of our exoplanet environment simulations permits us to as it should be type the elements on ultra-hot planets like WASP-121 b,” defined Jack Skinner, a postdoctoral fellow on the California Institute of Era in Pasadena, California, and co-leader of this find out about. “Right here we make a vital step ahead by means of combining observational constraints with environment simulations to grasp the time-varying climate on those planets.”“It is a massively thrilling end result as we transfer ahead for staring at climate patterns on exoplanets,” mentioned one of the vital most important investigators of the workforce, Quentin Changeat, a Eu Area Company Analysis Fellow on the Area Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland. “Learning exoplanets’ climate is important to figuring out the complexity of exoplanet atmospheres on different worlds, particularly within the seek for exoplanets with liveable stipulations.”
This visualization presentations the elements patterns at the exoplanet WASP-121 b, often referred to as Tylos. This video has been slowed to look at the patterns within the exoplanet’s environment in nearer element. Credit score: NASA, ESA, Quentin Changeat (ESA/STScI), Mahdi Zamani (ESA/Hubble)WASP-121 b: A Case Learn about in Exoplanetary AtmospheresWASP-121 b is so just about its mother or father megastar that the orbital duration is only one.27 days. This shut proximity implies that the planet is tidally locked in order that the similar hemisphere all the time faces the megastar, in the similar method that our Moon all the time has the similar aspect pointed at Earth. Sunlight hours temperatures manner 3,450 levels Fahrenheit (2,150 levels Kelvin) at the star-facing aspect of the planet.The workforce used 4 units of Hubble archival observations of WASP-121 b. Your complete records set integrated observations of WASP-121 b transiting in entrance of its megastar (taken in June 2016); WASP-121 b passing in the back of its megastar, often referred to as a secondary eclipse (taken in November 2016); and the brightness of WASP-121 b as a serve as of its part perspective to the megastar (the various quantity of sunshine gained at Earth from an exoplanet because it orbits its mother or father megastar, very similar to our Moon’s phase-cycle). Those records have been taken in March 2018 and February 2019, respectively.“The assembled data-set represents a vital quantity of staring at time for a unmarried planet and is recently the one constant set of such repeated observations,” mentioned Changeat. The guidelines that we extracted from the ones observations was once used to deduce the chemistry, temperature, and clouds of the ambience of WASP-121 b at other instances. This equipped us with a good looking image of the planet converting over the years.”Hubble’s distinctive functions are also obvious within the extensive expanse of science methods it’ll allow thru its Cycle 31 observations, which started on December 1. About two-thirds of Hubble’s time will likely be dedicated to imaging research, whilst the rest is allocated to spectroscopy research, like the ones used for WASP-121 b. Extra information about Cycle 31 science are in a fresh announcement.Reference: “Is the ambience of the ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-121b variable?” by means of Quentin Changeat, Jack W. Skinner, James Y-Ok. Cho, Joonas Nättilä, Ingo P. Waldmann, Ahmed F. Al-Refaie, Achrène Dyrek, Billy Edwards, Thomas Mikal-Evans, Max Joshua, Giuseppe Morello, Nour Skaf, Angelos Tsiaras, Olivia Venot and Kai Hou Yip, 2 January 2023, Astrophysics > Earth and Planetary Astrophysics.
arXiv:2401.01465The Hubble Area Telescope is a undertaking of world cooperation between NASA and ESA. NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Heart in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Area Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble and Webb science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by means of the Affiliation of Universities for Analysis in Astronomy, in Washington, D.C.
Cyclones in Area? See How Hubble Exposed Excessive Climate on a Far-off Planet




/wion/media/media_files/2025/03/30/B1xgUHuPTxMh8iNXB0N4.png)