It’s been a very long time since Fritz Zwicky, a Swiss astronomer, offered the time period ‘darkish subject’ to the arena in 1930. Over the past 9 many years, our figuring out of house and cosmic entities has complicated considerably.
But something stays unchanged — darkish subject used to be a thriller then, and it nonetheless is nowadays.
On the other hand, findings from a brand new learn about promise to modify that. The learn about authors suggest that the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) has the possible to locate scalar area darkish subject, a type of darkish subject manufactured from ultra-light scalar boson debris.
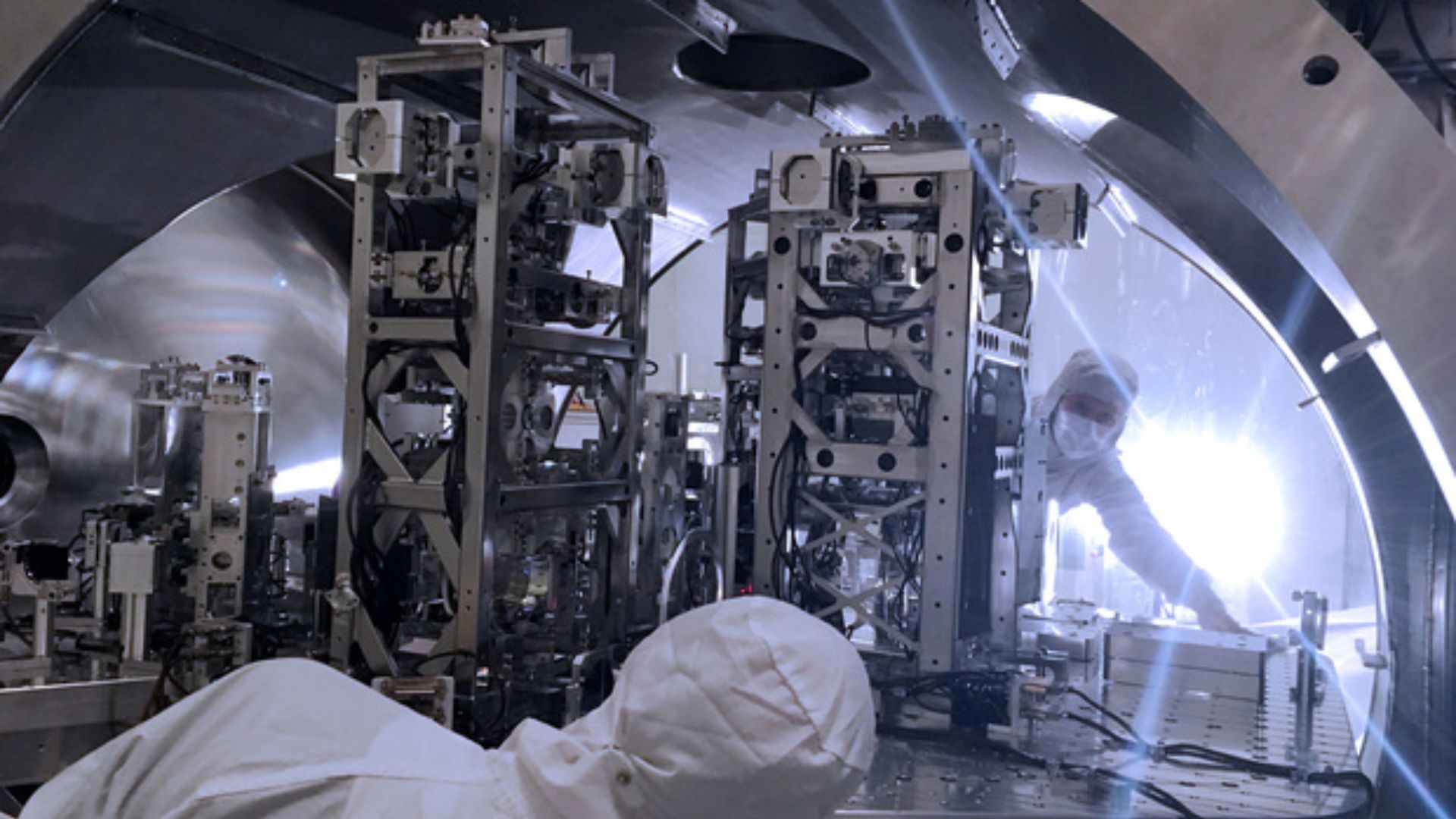
LIGO is a physics observatory that detects gravitational waves. It used to be advanced and deployed through researchers at Caltech and MIT within the early 2000s. This large instrument made headlines in 2015 when it showed the presence of gravitational waves for the primary time.
Here’s how LIGO can practice the invisible darkish subject
The theoretical ultralight boson debris that make up the scalar area darkish subject are believed to engage with subject and lightweight. Even if this interplay is vulnerable, it might outcome at midnight subject appearing wave-like homes.
In step with the researchers, LIGO can harness the wave-like patterns of the debris to locate scalar-field darkish subject. “Some theories recommend darkish subject behaves extra like a wave than a particle,” Dr. Alexandre Sébastien Göttel, lead learn about writer and a analysis affiliate at Cardiff College, stated.
“Those waves would motive tiny oscillations in standard subject, which can also be detected through gravitational wave detectors (corresponding to LIGO),” Göttel added. He and his workforce additionally examined this principle the use of a theoretical style.
This style tested a imaginable interplay between scalar area darkish subject waves and LIGO with the assistance of simulation instrument, which predicted how scalar area darkish subject would possibly impact LIGO’s output.
This research helped them determine the indicators they will have to search for in LIGO’s information. Subsequent, they studied LIGO’s information the use of a method known as logarithmic spectral research to search out patterns throughout the indicators that might point out the presence of scalar area darkish subject.
The result of the simulation
Even if the researchers couldn’t to find sturdy proof of the darkish subject, they had been ready to determine new higher limits at the coupling energy, i.e., how strongly darkish subject may have interaction with the LIGO parts.
The brand new limits represented a ten,000-fold development within the coupling energy price in comparison to what used to be proposed through previous research.
“We set new higher limits for the coupling constants of scalar area darkish subject as a serve as of its mass, which improves upon bounds from earlier direct searches through as much as 4 orders of magnitude in a frequency band from 10 to 180 Hz,” the learn about authors observe.
Those findings recommend that LIGO has a better probability of detecting darkish subject than more than a few different approaches.
Additionally, as detectors extra complicated than LIGO are advanced, scientists will have the ability to take a look at more than a few scalar darkish subject theories with out making use of any oblique seek means.
The learn about is printed within the magazine Bodily Assessment Letters.
Darkish subject detection nearer as LIGO’s attainable boosted 10,000 occasions