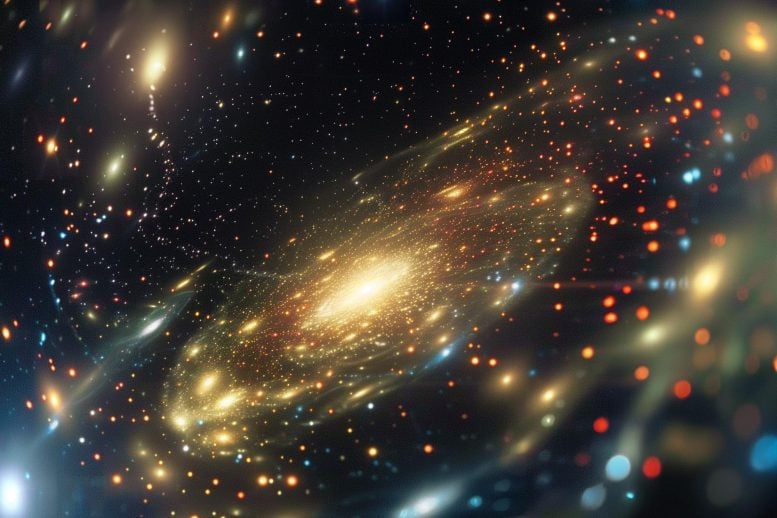
Contemporary findings via astronomers the usage of the Very Massive Telescope display that the obvious uniform density throughout galaxies is a results of oversimplified fashions slightly than exact galactic similarity. This discovery calls into query long-held ideals in regards to the interplay of stars and darkish subject in galaxy formation. Credit score: SciTechDaily.com
Contemporary findings via astronomers the usage of the Very Massive Telescope display that the obvious uniform density throughout galaxies is a results of oversimplified fashions slightly than exact galactic similarity. This discovery calls into query long-held ideals in regards to the interplay of stars and darkish subject in galaxy formation. Credit score: SciTechDaily.com
A global group of astronomers has debunked the idea that stars and darkish subject inexplicably catch up on every different in galaxies, revealing this perceived uniformity is because of oversimplified astronomical fashions.
Through using extra detailed fashions and in depth knowledge from the Very Massive Telescope, the group demonstrated the real complexity of galactic buildings, difficult the established working out of galaxy formation and evolution.
A longstanding ‘conspiracy’ in astronomy – that stars and darkish subject are interacting in inexplicable techniques – has been overturned via a world group of astronomers, in a paper printed on August 10 in Per month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS).
The authors are based totally in Australia, the United Kingdom, Austria, and Germany, and used the Very Massive Telescope in Chile.
The conspiracy emerged to give an explanation for a phenomenon that had perplexed astronomers for 1 / 4 of a century. The density of subject in numerous galaxies gave the look to be reducing on the similar charge from their middle to outer edges. This was once perplexing as a result of galaxies are numerous, with many various ages, shapes, sizes, and numbers of stars. So why would they’ve the similar density construction?
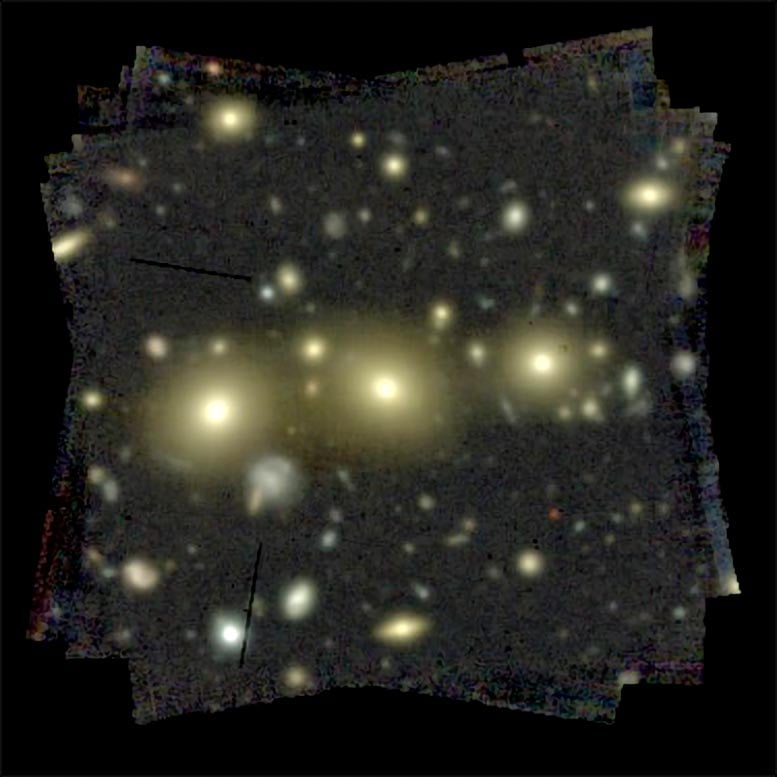 One of the most group’s Very Massive Telescope photographs appearing huge galaxies in a gaggle. The galaxies on the centre are every about 125 billion occasions the mass of our solar (together with their darkish subject). Credit score: Trevor Mendel, ANU
One of the most group’s Very Massive Telescope photographs appearing huge galaxies in a gaggle. The galaxies on the centre are every about 125 billion occasions the mass of our solar (together with their darkish subject). Credit score: Trevor Mendel, ANU
Rethinking Galactic Buildings
“This homogeneity recommended that darkish subject and stars should someway catch up on every different in an effort to produce such common mass buildings,” says Dr. Caro Derkenne, the primary creator of the paper and an ASTRO 3D researcher from Macquarie College.
Like many conspiracies, no researcher may get a hold of a mechanism. If darkish subject and stars may have interaction on this means, then we might want to exchange our working out of the way galaxies shape and evolve. However in addition they couldn’t to find another reason why to give an explanation for what they have been seeing, till now.
 Lead creator, Dr. Caro Derkenne.
Lead creator, Dr. Caro Derkenne.
Derkenne and her colleagues discovered that the similarity in density will not be because of the galaxies themselves however to how astronomers have been measuring and modeling them.
Complicated Modeling Finds New Insights
The group seen 22 middle-aged galaxies (having a look again some 4 billion years up to now because of their long way) in abnormal element, the usage of the Eu Southern Observatory’s Very Massive Telescope in Chile. It enabled them to create extra advanced fashions that higher captured the range of galaxies within the universe.
“Prior to now, folks constructed easy fashions that had too many simplifications and assumptions,” says Derkenne.
“Galaxies are difficult, and we need to fashion them with freedom or we’re going to measure the fallacious issues. Our fashions ran at the OzStar supercomputer at Swinburne College, the usage of the an identical of about 8,000 hours of desktop computing time.”
Have an effect on Past Astronomy
Derkenne is now making use of her astronomy experience to advanced knowledge for the Australia Public Provider.
“Astronomy units you up actually neatly to grasp giant knowledge,” she says. “The actual global is messy, and we don’t all the time have all of the knowledge. No person is there to inform you the solutions or if you happen to’re fallacious or proper. You wish to have to acquire knowledge and analyze till you to find one thing that works.”
The venture used MUSE (Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer) at the VLT to investigate the galaxies from the MAGPI survey (Center Ages Galaxy Houses with Integral box spectroscopy). MUSE collects spectral knowledge cubes by which each unmarried pixel is in fact a spectrum.
“The MAGPI venture is a brilliant instance of the way coaching workshops and collaborative house inside of ASTRO 3D have applied Australia’s strategic partnership with the Eu Southern Observatory,” says ASTRO 3D Director Professor Emma Ryan-Weber.
“The advanced knowledge from the ESO Very Massive Telescope has no longer most effective solved a long-standing drawback in Astronomy, but in addition enabled younger scientists, corresponding to Dr. Caro Derkenne, a platform on which to release their careers to unravel real-world issues,” she says.
Reference: “The MAGPI Survey: Proof towards the bulge-halo conspiracy” via C Derkenne, R M McDermid, G Santucci, A Poci, S Thater, S Bellstedt, J T Mendel, C Foster, Okay E Harborne, C D P Lagos, E Wisnioski, S Croom, R-S Remus, L M Valenzuela, J van de Sande, S M Candy and B Ziegler, 10 August 2024, Per month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stae1836
The co-authors are from the World Centre for Radio Astronomy Analysis (ICRAR) in Western Australia, College of Durham, College of Vienna, the Australian Nationwide College, College of New South Wales Sydney, College of Sydney, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität, and College of Queensland.
Debunking a Galactic Conspiracy: Stars and Darkish Topic Don’t Engage in “Inconceivable Tactics”