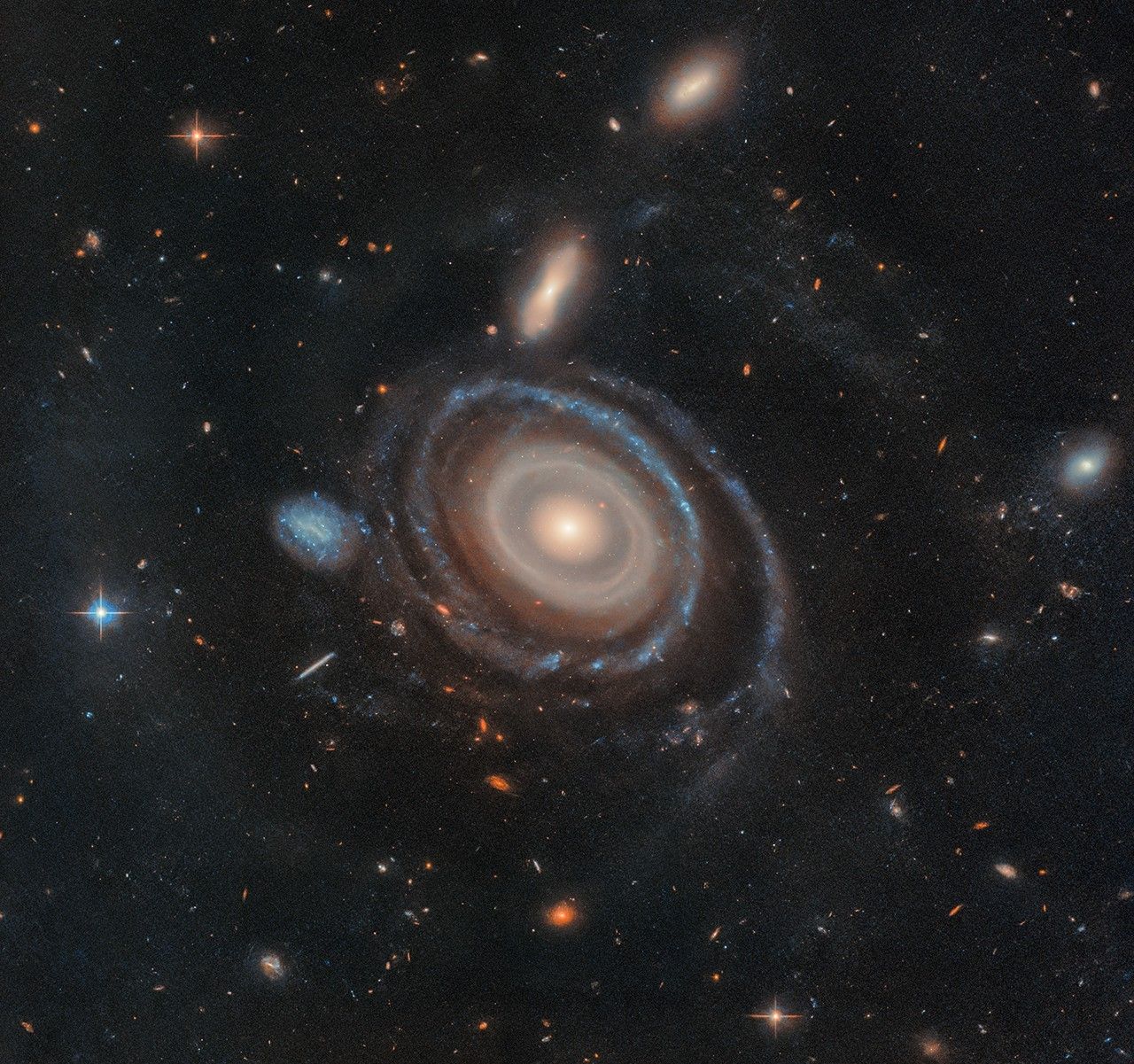
NASA’s Hubble Area Telescope has captured a cosmic bullseye! The gargantuan galaxy LEDA 1313424 is rippling with 9 star-filled rings after an “arrow” — a much smaller blue dwarf galaxy — shot via its middle. Astronomers the use of Hubble recognized 8 visual rings, greater than in the past detected by means of any telescope in any galaxy, and showed a 9th the use of knowledge from the W. M. Keck Observatory in Hawaii. Earlier observations of alternative galaxies display a most of 2 or 3 rings.
“This was once a serendipitous discovery,” stated Imad Pasha, the lead researcher and a doctoral pupil at Yale College in New Haven, Connecticut. “I used to be having a look at a ground-based imaging survey and after I noticed a galaxy with a number of transparent rings, I used to be instantly interested in it. I needed to forestall to research it.” The crew later nicknamed the galaxy the “Bullseye.”
Hubble and Keck’s follow-up observations additionally helped the researchers end up which galaxy plunged in the course of the middle of the Bullseye — a blue dwarf galaxy to its center-left. This slightly tiny interloper traveled like a dart in the course of the core of the Bullseye about 50 million years in the past, leaving rings in its wake like ripples in a pond. A skinny path of gasoline now hyperlinks the pair, regardless that they’re these days separated by means of 130,000 light-years.
“We’re catching the Bullseye at an excessively particular second in time,” stated Pieter G. van Dokkum, a co-author of the brand new find out about and a professor at Yale. “There’s an excessively slim window after the affect when a galaxy like this is able to have such a lot of rings.”
Galaxies collide or slightly pass over one every other fairly continuously on cosmic timescales, however this can be very uncommon for one galaxy to dive in the course of the middle of every other. The blue dwarf galaxy’s instantly trajectory in the course of the Bullseye later brought about subject matter to transport each inward and outward in waves, surroundings off new areas of big name formation.
How large is the Bullseye? Our Milky Approach galaxy is set 100,000 light-years in diameter, and the Bullseye is sort of two-and-a-half occasions greater, at 250,000 light-years throughout.
The researchers used Hubble’s crisp imaginative and prescient to rigorously to pinpoint the site of maximum of its rings, since many are piled up on the middle. “This may were not possible with out Hubble,” Pasha stated.
They used Keck to verify yet another ring. The crew suspects a tenth ring additionally existed, however has pale and is not detectable. They estimate it could lie thrice farther out than the widest ring in Hubble’s symbol.
Pasha additionally discovered a shocking connection between the Bullseye and a fashioned principle: The galaxy’s rings seem to have moved outward nearly precisely as predicted by means of fashions.
“That principle was once evolved for the day that any person noticed such a lot of rings,” van Dokkum stated. “It’s immensely pleasing to verify this long-standing prediction with the Bullseye galaxy.”
If considered from above, it might be extra glaring that the galaxy’s rings aren’t frivolously spaced like the ones on a dart board. Hubble’s symbol presentations the galaxy from a slight attitude. “If we have been to appear down on the galaxy immediately, the rings would glance round, with rings bunched up on the middle and progressively turning into extra spaced out the farther out they’re,” Pasha defined.
To visualise how those rings will have shaped, take into accounts losing a pebble right into a pond. The primary ring ripples out, turning into the widest over the years, whilst others proceed to shape after it.
The researchers suspect that the primary two rings within the Bullseye shaped temporarily and unfold out in wider circles. The formation of extra rings will have been reasonably staggered, because the blue dwarf galaxy’s flythrough affected the primary rings extra considerably.
Person stars’ orbits have been in large part undisturbed, regardless that teams of stars did “pile up” to shape distinguishable rings over tens of millions of years. The gasoline, then again, was once carried outward, and combined with mud to shape new stars, additional brightening the Bullseye’s rings.
There’s much more analysis to be executed to determine which stars existed prior to and after the blue dwarf’s “fly via.” Astronomers will now additionally have the ability to toughen fashions appearing how the galaxy might proceed to adapt over billions of years, together with the disappearance of extra rings.
Even supposing this discovery was once an opportunity discovering, astronomers can anticipate finding extra galaxies like this one quickly. “As soon as NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope starts science operations, fascinating items will come out a lot more simply,” van Dokkum defined. “We will be able to learn the way uncommon those impressive occasions in point of fact are.”
The crew’s paper was once revealed at the February 4, 2025 in The Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
The Hubble Area Telescope has been running for over 3 a long time and continues to make ground-breaking discoveries that form our basic figuring out of the universe. Hubble is a mission of world cooperation between NASA and ESA (Eu Area Company). NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Heart in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope and project operations. Lockheed Martin Area, founded in Denver, additionally helps project operations at Goddard. The Area Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, which is operated by means of the Affiliation of Universities for Analysis in Astronomy, conducts Hubble science operations for NASA.
Discover Extra
Media Touch:
Claire Andreoli (claire.andreoli@nasa.gov)
NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Heart, Greenbelt, MD
Claire Blome and Ray Villard
Area Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, MD