New analysis suggests there are places at the floor of Saturn’s moon, Enceladus, the place spacecraft may just land to scoop up pristine lines of the important thing substances for lifestyles. It is believed that those biosignatures come from subsurface oceans throughout the global’s icy shell. Enceladus has lengthy been identified to harbor natural molecules — compounds made from carbon, oxygen and nitrogen — in its subsurface oceans. Ahead of it plunged to the outside of Saturn in 2017, the Cassini spacecraft flew thru plumes of subject matter erupting thru fissures within the floor of Enceladus, detecting natural molecules like methane and ethane in addition to different complicated compounds attaining large altitudes.Round 90% of the bigger grains on this subject matter, introduced hundreds of miles over Enceladus, do not in truth get away the Saturnian gadget. Quite, they fall again to the outside of the Saturnian moon, scientists now say, the place they may be able to theoretically be accrued and tested by means of spacecraft.”We will be able to be told so much about possible biosignatures in Enceladus’ ocean by means of sending a venture to the outside of Enceladus. In the past, it was once concept that to be able to pattern the most up to date subject matter from the Enceladus ocean, you need to fly during the plume and measure plume grains and gases,” Amanda R. Hendrix , a senior scientist at The Planetary Science Institute and analysis chief, mentioned in a remark. “However now we all know that you’ll land at the floor and be assured that your tools can measure moderately pristine plume organics — sourced from the sea.”Similar: Indicators of lifestyles capturing from Saturn’s moon Enceladus can be detectable by means of spacecraft, scientists say Some natural molecules in Enceladus’ plumes that may be the fingerprints of organic lifestyles, alternatively, could also be destroyed by means of ultraviolet (UV) from the solar. That suggests there’s a want to get to those molecules whilst they continue to be unspoiled.”We all know that Enceladus’ ocean is liveable due to Cassini measurements. We all know there’s liquid water, power, and the chemical substances carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus and sulfur. Those are the substances essential for lifestyles as we are aware of it,” Hendrix mentioned. “If we wish to to find out if any ocean-derived biosignatures are provide within the plume grains, we’d like those grains to be as pristine and unexposed to UV as imaginable.”Trying to find pristine subject matter on Enceladus To find a spot on Enceladus the place such pristine subject matter can be to be had, Hendrix and the crew analyzed knowledge from the Hubble Area Telescope and Cassini spacecraft to look how deep photons of UV gentle can penetrate the outside of the moon. “What we discover on this find out about is that there are puts on Enceladus’ floor the place shall we land with a spacecraft and take a pattern — and we might be measuring moderately pristine organics,” Hendrix mentioned. “That’s for the reason that sun ultraviolet (UV) photons simply don’t penetrate very deeply into the icy floor.”The crew found out that destructive UV photons simplest penetrate round 100 micrometers into the icy floor of Enceladus, which is solely the width of a couple of human hairs. “In order that very best a part of the outside will get uncovered to these destructive UV photons, however just a share of the organics are chemically reworked, after which quickly sufficient that subject matter is roofed up by means of brisker plume subject matter,” Hendrix defined. “And the deeper grains don’t go through extra transformation — for the reason that UV photons are averted from interacting with the deeper subject matter. The freshly deposited plume grains act as a protect for the underlying subject matter. They act like a sunscreen!”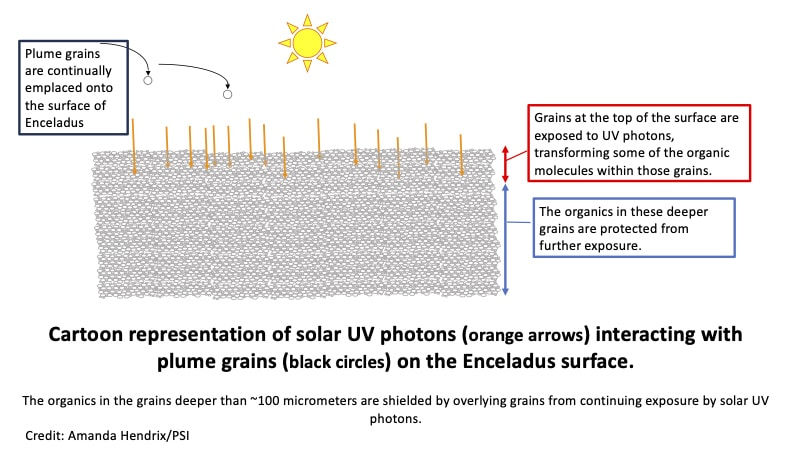 A demonstration presentations UV gentle affecting grains of subject matter on the floor of Enceladus however now not deeper subject matter. (Symbol credit score: Amanda Hendrix/ PSI)The consequences collected by means of the crew are helpful as a result of they inform scientists that missions to Enceladus may have an abundance of organics to pattern with no need to delve too deep.”As a result of UV gentle readily alters natural molecules, the intensity that such gentle travels into the outside of an ice-covered global truly issues. With the fast UV penetration depths discovered, our effects make certain that there’s considerable natural subject matter locked away and preserved within the ices of Enceladus that may be traced again to its ocean,” Christopher Area, analysis co-author and a scientist at Penn State College, mentioned within the remark. “It’s awe-inspiring to assume that with identified era, we will be able to readily get admission to a lot of natural subject matter from a liveable extraterrestrial ocean.”The crew’s analysis was once revealed Dec. 18 within the magazine Communications Earth & Atmosphere.
A demonstration presentations UV gentle affecting grains of subject matter on the floor of Enceladus however now not deeper subject matter. (Symbol credit score: Amanda Hendrix/ PSI)The consequences collected by means of the crew are helpful as a result of they inform scientists that missions to Enceladus may have an abundance of organics to pattern with no need to delve too deep.”As a result of UV gentle readily alters natural molecules, the intensity that such gentle travels into the outside of an ice-covered global truly issues. With the fast UV penetration depths discovered, our effects make certain that there’s considerable natural subject matter locked away and preserved within the ices of Enceladus that may be traced again to its ocean,” Christopher Area, analysis co-author and a scientist at Penn State College, mentioned within the remark. “It’s awe-inspiring to assume that with identified era, we will be able to readily get admission to a lot of natural subject matter from a liveable extraterrestrial ocean.”The crew’s analysis was once revealed Dec. 18 within the magazine Communications Earth & Atmosphere.
Discovering lifestyles on Saturn’s moon Enceladus could be more straightforward than we concept