 A brand new find out about discovered that the genetic code of the single-celled Amoebidium incorporates remnants of historical massive viruses, providing insights into the genetic evolution of advanced lifestyles. This discovery unearths that those viral genes, even though doubtlessly damaging, are saved inactive via chemical processes inside of Amoebidium’s DNA, suggesting a extra intricate dating between viruses and their hosts, which might have an effect on our working out of genetic evolution in different organisms, together with people.Microorganisms divulge how our single-celled predecessors included viral DNA into their very own genomes.Researchers have found out remnants of historical massive viruses within the genome of Amoebidium, a single-celled organism, suggesting that such viral sequences will have performed a job within the evolution of advanced lifestyles bureaucracy. This find out about highlights the dynamic dating between viruses and their hosts, additionally reflecting on human genetics.A shocking twist within the evolutionary historical past of advanced lifestyles has been exposed in a brand new find out about printed in Science Advances. Researchers at Queen Mary College of London have discovered {that a} single-celled organism, carefully associated with animals, incorporates remnants of historical massive viruses inside of its genetic code. This discovery supplies perception into how advanced organisms will have obtained a few of their genes and underscores the dynamic interaction between viruses and their hosts.The find out about excited by a microbe known as Amoebidium, a unicellular parasite present in freshwater environments. By means of inspecting Amoebidium’s genome, the researchers led via Dr. Alex de Mendoza Soler, Senior Lecturer at Queen Mary’s Faculty of Organic and Behavioural Sciences, discovered a stunning abundance of genetic subject material originating from massive viruses – probably the most biggest viruses identified to science. Those viral sequences had been closely methylated, a chemical tag that steadily silences genes.“It’s like discovering Trojan horses hiding within the Amoebidium’s DNA,” explains Dr de Mendoza Soler. “Those viral insertions are doubtlessly damaging, however Amoebidium appears to be holding them in test via chemically silencing them.”
A brand new find out about discovered that the genetic code of the single-celled Amoebidium incorporates remnants of historical massive viruses, providing insights into the genetic evolution of advanced lifestyles. This discovery unearths that those viral genes, even though doubtlessly damaging, are saved inactive via chemical processes inside of Amoebidium’s DNA, suggesting a extra intricate dating between viruses and their hosts, which might have an effect on our working out of genetic evolution in different organisms, together with people.Microorganisms divulge how our single-celled predecessors included viral DNA into their very own genomes.Researchers have found out remnants of historical massive viruses within the genome of Amoebidium, a single-celled organism, suggesting that such viral sequences will have performed a job within the evolution of advanced lifestyles bureaucracy. This find out about highlights the dynamic dating between viruses and their hosts, additionally reflecting on human genetics.A shocking twist within the evolutionary historical past of advanced lifestyles has been exposed in a brand new find out about printed in Science Advances. Researchers at Queen Mary College of London have discovered {that a} single-celled organism, carefully associated with animals, incorporates remnants of historical massive viruses inside of its genetic code. This discovery supplies perception into how advanced organisms will have obtained a few of their genes and underscores the dynamic interaction between viruses and their hosts.The find out about excited by a microbe known as Amoebidium, a unicellular parasite present in freshwater environments. By means of inspecting Amoebidium’s genome, the researchers led via Dr. Alex de Mendoza Soler, Senior Lecturer at Queen Mary’s Faculty of Organic and Behavioural Sciences, discovered a stunning abundance of genetic subject material originating from massive viruses – probably the most biggest viruses identified to science. Those viral sequences had been closely methylated, a chemical tag that steadily silences genes.“It’s like discovering Trojan horses hiding within the Amoebidium’s DNA,” explains Dr de Mendoza Soler. “Those viral insertions are doubtlessly damaging, however Amoebidium appears to be holding them in test via chemically silencing them.”
The microbe Amoebidium appalachense present process its developmental lifestyles cycle within the laboratory. The nuclei divide inside of a cellular till adulthood (~40h within the video), when each and every nucleus turns into a unmarried cellular and the colony breaks giving upward push to the progeny. Credit score: Alex de MendozaOngoing Analysis and ImplicationsThe researchers then investigated how common this phenomenon may well be. They in comparison the genomes of a number of Amoebidium isolates and located vital variation within the viral content material. This implies that the method of viral integration and silencing is ongoing and dynamic.“Those findings problem our working out of the connection between viruses and their hosts,” says Dr. de Mendoza Soler. “Historically, viruses are noticed as invaders, however this find out about suggests a extra advanced tale. Viral insertions will have performed a job within the evolution of advanced organisms via offering them with new genes. And that is allowed via the chemical taming of those intruders’ DNA.”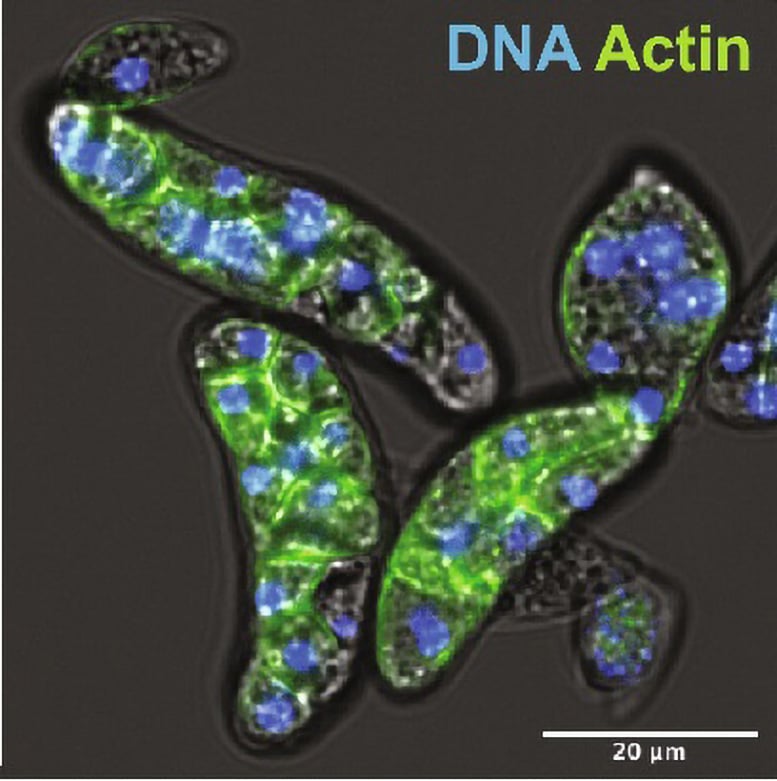 Amoebidium appalachense cells stained for DNA (in blue, appearing the nucleus) and actin (in inexperienced), highlighting the cellular membranes within the cellularization step of the colony. Credit score: Alex de MendozaFurthermore, the findings in Amoebidium be offering intriguing parallels to how our personal genomes engage with viruses. Very similar to Amoebidium, people and different mammals have remnants of historical viruses, known as Endogenous Retroviruses, built-in into their DNA. Whilst those remnants had been up to now considered inactive “junk DNA,” some would possibly now be really helpful. Alternatively, in contrast to the enormous viruses present in Amoebidium, Endogenous Retroviruses are a lot smaller, and the human genome is considerably higher. Long run analysis can discover those similarities and variations to know the advanced interaction between viruses and sophisticated lifestyles bureaucracy.Reference: “DNA methylation allows recurrent endogenization of huge viruses in an animal relative” via Luke A. Sarre, Iana V. Kim, Vladimir Ovchinnikov, Marine Olivetta, Hiroshi Suga, Omaya Dudin, Arnau Sebé-Pedrós and Alex de Mendoza, 12 July 2024, Science Advances.
Amoebidium appalachense cells stained for DNA (in blue, appearing the nucleus) and actin (in inexperienced), highlighting the cellular membranes within the cellularization step of the colony. Credit score: Alex de MendozaFurthermore, the findings in Amoebidium be offering intriguing parallels to how our personal genomes engage with viruses. Very similar to Amoebidium, people and different mammals have remnants of historical viruses, known as Endogenous Retroviruses, built-in into their DNA. Whilst those remnants had been up to now considered inactive “junk DNA,” some would possibly now be really helpful. Alternatively, in contrast to the enormous viruses present in Amoebidium, Endogenous Retroviruses are a lot smaller, and the human genome is considerably higher. Long run analysis can discover those similarities and variations to know the advanced interaction between viruses and sophisticated lifestyles bureaucracy.Reference: “DNA methylation allows recurrent endogenization of huge viruses in an animal relative” via Luke A. Sarre, Iana V. Kim, Vladimir Ovchinnikov, Marine Olivetta, Hiroshi Suga, Omaya Dudin, Arnau Sebé-Pedrós and Alex de Mendoza, 12 July 2024, Science Advances.
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ado6406
Discovery of Historic Massive Virus Remnants Gives New Clues to the Origins of Complicated Existence