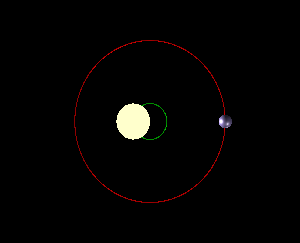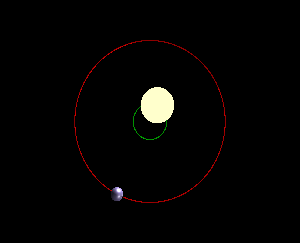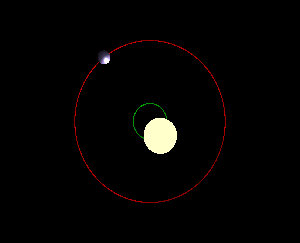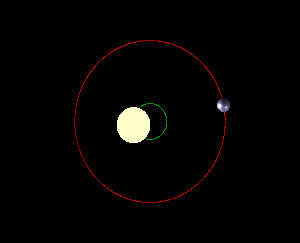
We are taught that the planets of our solar system change position while orbiting the sun. But does the sun itself move within the solar system? Although the sun is far from static, it orbits the Milky Way at staggering speeds, dragging the solar system along with it. The sun appears to move across the sky, but this is due to the Earth’s rotation, not the sun’s actual motion. As a result of Earth’s tilt and elliptical orbit, the sun’s position changes in the sky from our perspective, but it’s not the sun itself moving. Each planet orbits the sun at its own pace, with Mercury having the shortest year and Neptune the longest. The sun shifts position within the solar system due to the gravitational influences of the planets. The planets and the sun orbit a point of mutual gravity called a “barycenter,” with the sun being much more massive, causing the barycenters to be located deep within the sun. Jupiter’s gravitational pull has a noticeable effect on the sun, causing a small wobble as it orbits. This wobble can be detected using the Doppler effect and can also be used to detect exoplanets outside the solar system.
Does the sun move in the solar system?