Issues are taking a look up for digging deep on Mars. Growth is palpable on how absolute best to extract subsurface ice to generate drinkable water, rocket gasoline and different helpful sources at the Pink Planet.However uninteresting down from the topside of Mars to achieve to be had icy reservoirs isn’t any slam dunk.Tackling that problem is the corporate Honeybee Robotics, which calls its method the RedWater thought. Comparable: Mars ice deposits may just pave the way in which for human explorationDual functions  Honeybee Robotics’ ice drilling {hardware} for Mars encompasses coiled tubing and the “RodWell” approach. (Symbol credit score: Honeybee Robotics)”RedWater has confirmed to be the precise structure for deep drilling on Mars,” mentioned Kris Zacny, vice chairman of the exploration era workforce at Honeybee Robotics in Altadena, California.Zacny mentioned that RedWater can serve twin functions, drilling for clinical exploration and water mining. “It is a win-win. We’re at a place the place this era can also be infused into [the] subsequent Mars missions,” he advised House.com. Contemporary revelations about subsurface water ice at the Pink Planet mesh neatly with RedWater. Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Glacier ice Through the years, knowledge amassed through Mars orbiters has published {that a} 3rd of the Martian floor incorporates ice close to the outside, in addition to extra deeply buried ice sheets. For instance, previous this 12 months, observations through the Ecu House Company’s Mars Categorical probe prompt that layers of water ice stretch a number of miles beneath floor in some puts in the world. Including to the Mars ice tale is that this month’s record on the fifty fifth Lunar and Planetary Science Convention of a in the past unseen volcano. The brand new analysis speculates that, underneath that a great deal eroded function, glacier ice is most likely nonetheless reward, preserved close to the outside in a somewhat heat equatorial area on Mars. Comparable: The seek for water on Mars (pictures) Finish-to-end checking out
Honeybee Robotics’ ice drilling {hardware} for Mars encompasses coiled tubing and the “RodWell” approach. (Symbol credit score: Honeybee Robotics)”RedWater has confirmed to be the precise structure for deep drilling on Mars,” mentioned Kris Zacny, vice chairman of the exploration era workforce at Honeybee Robotics in Altadena, California.Zacny mentioned that RedWater can serve twin functions, drilling for clinical exploration and water mining. “It is a win-win. We’re at a place the place this era can also be infused into [the] subsequent Mars missions,” he advised House.com. Contemporary revelations about subsurface water ice at the Pink Planet mesh neatly with RedWater. Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Glacier ice Through the years, knowledge amassed through Mars orbiters has published {that a} 3rd of the Martian floor incorporates ice close to the outside, in addition to extra deeply buried ice sheets. For instance, previous this 12 months, observations through the Ecu House Company’s Mars Categorical probe prompt that layers of water ice stretch a number of miles beneath floor in some puts in the world. Including to the Mars ice tale is that this month’s record on the fifty fifth Lunar and Planetary Science Convention of a in the past unseen volcano. The brand new analysis speculates that, underneath that a great deal eroded function, glacier ice is most likely nonetheless reward, preserved close to the outside in a somewhat heat equatorial area on Mars. Comparable: The seek for water on Mars (pictures) Finish-to-end checking out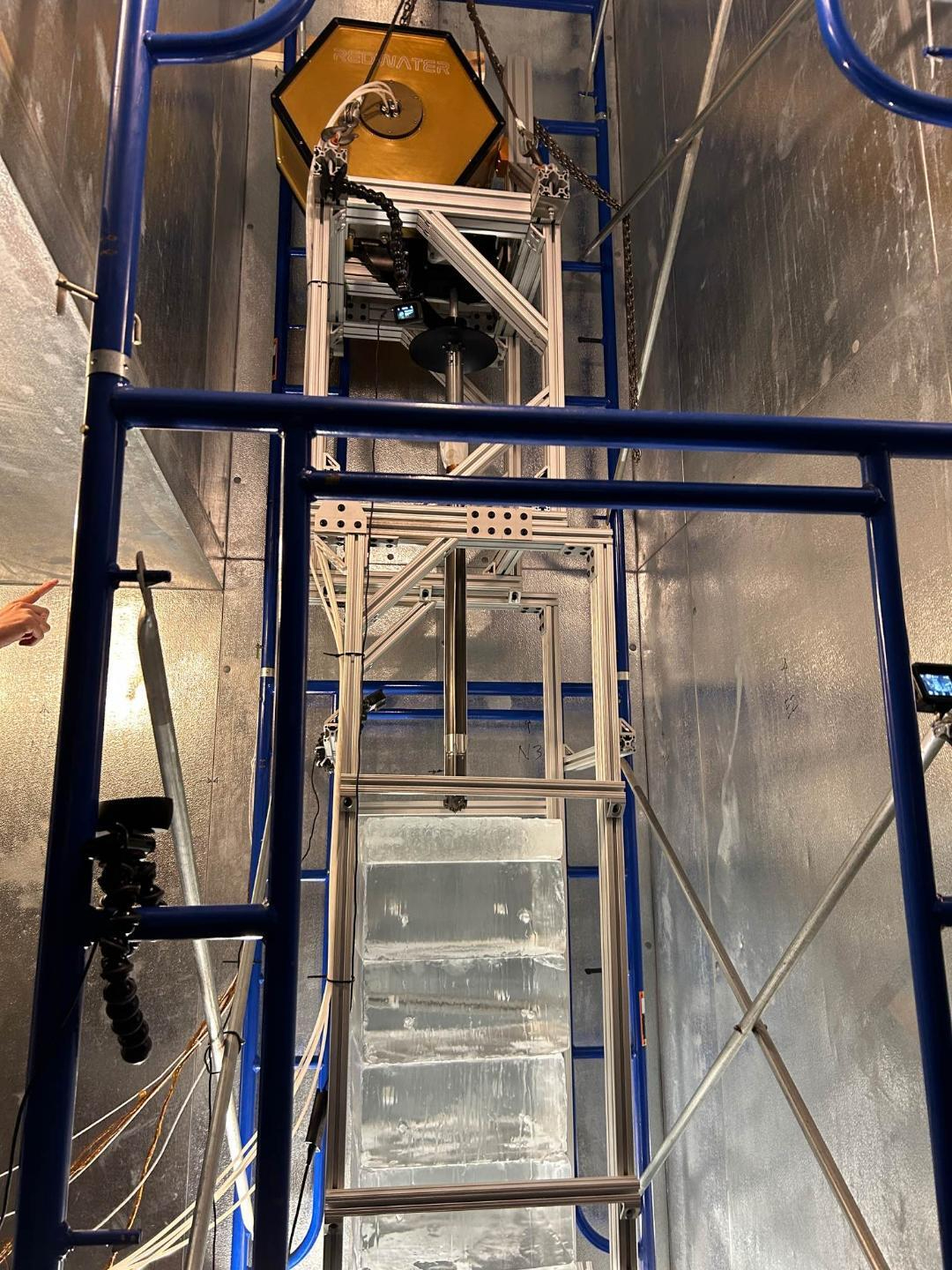  The RedWater gadget undergoes end-to-end checking out in Honeybee Robotics’ bloodless chamber to simulate the super-cold stipulations on Mars. (Symbol credit score: Honeybee Robotics)In the meantime, Honeybee technologists have just lately finished end-to-end checking out of a RedWater gadget within the corporate’s bloodless chamber, mentioned Joey Palmowski, a programs engineer on the corporate.That paintings used to be undertaken thru a NASA Subsequent House Applied sciences for Exploration Partnerships (NextSTEP-2) grant, Palmowski advised House.com.The RedWater gadget makes use of two confirmed terrestrial applied sciences, already put into motion in fortify of polar operations in each Greenland and Antarctica. They’re coiled tubing that unspools from the outside into underlying ice, and what is termed the Rodriguez Smartly, or “RodWell” thought. RodWell is a technique of melting a neatly in subsurface ice and pumping the liquid water to the outside.To chop to the chase: Water ice within the type of debris-covered glaciers or ice sheets, possibly loads of meters thick, has been detected and mapped within the mid-latitudes of Mars. That is a good spot for a long run human expeditionary outpost. SWIM staff Nathaniel Putzig is affiliate director and senior scientist on the Planetary Science Institute’s workplace in Lakewood, Colorado. As co-lead of the Subsurface Water Ice Mapping (SWIM) on Mars venture staff, Putzig and co-workers are busy charting the positioning and intensity of mid-latitude ice on Mars.They are now wrapping up a 3rd section of the SWIM paintings, which explicitly aimed to lend a hand determine focused on priorities for the possible Global Mars Ice Mapper (I-MIM) undertaking thought.Ice-scouting
The RedWater gadget undergoes end-to-end checking out in Honeybee Robotics’ bloodless chamber to simulate the super-cold stipulations on Mars. (Symbol credit score: Honeybee Robotics)In the meantime, Honeybee technologists have just lately finished end-to-end checking out of a RedWater gadget within the corporate’s bloodless chamber, mentioned Joey Palmowski, a programs engineer on the corporate.That paintings used to be undertaken thru a NASA Subsequent House Applied sciences for Exploration Partnerships (NextSTEP-2) grant, Palmowski advised House.com.The RedWater gadget makes use of two confirmed terrestrial applied sciences, already put into motion in fortify of polar operations in each Greenland and Antarctica. They’re coiled tubing that unspools from the outside into underlying ice, and what is termed the Rodriguez Smartly, or “RodWell” thought. RodWell is a technique of melting a neatly in subsurface ice and pumping the liquid water to the outside.To chop to the chase: Water ice within the type of debris-covered glaciers or ice sheets, possibly loads of meters thick, has been detected and mapped within the mid-latitudes of Mars. That is a good spot for a long run human expeditionary outpost. SWIM staff Nathaniel Putzig is affiliate director and senior scientist on the Planetary Science Institute’s workplace in Lakewood, Colorado. As co-lead of the Subsurface Water Ice Mapping (SWIM) on Mars venture staff, Putzig and co-workers are busy charting the positioning and intensity of mid-latitude ice on Mars.They are now wrapping up a 3rd section of the SWIM paintings, which explicitly aimed to lend a hand determine focused on priorities for the possible Global Mars Ice Mapper (I-MIM) undertaking thought.Ice-scouting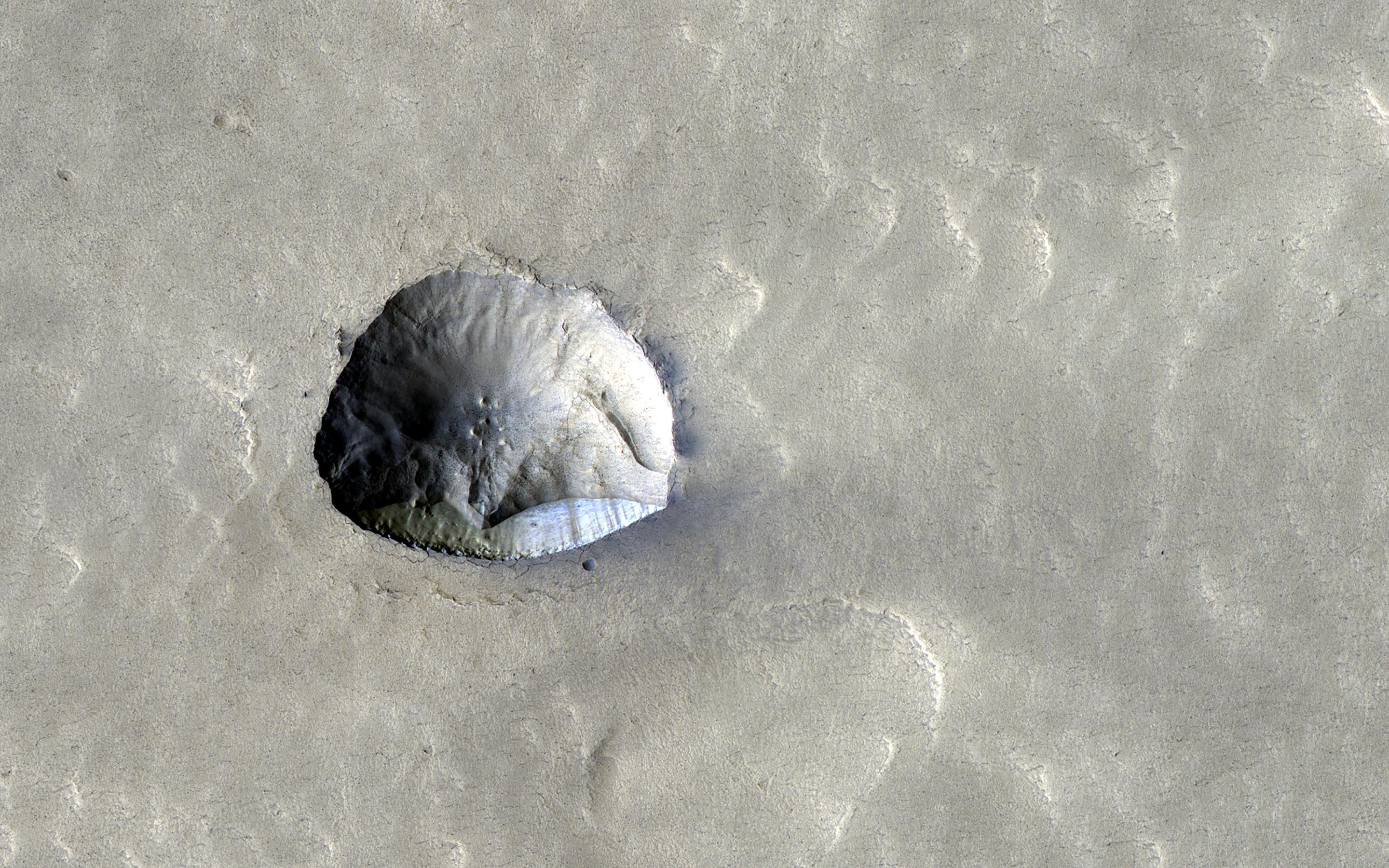  Kind of a 3rd of Mars has ice slightly under the planet’s floor. Many have an effect on craters within the mid-latitudes of the Pink Planet are full of easy subject matter this is most likely ice coated with some filth. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona)A radar-carrying orbiter, the I-MIM is a projected NASA endeavor in partnership with the Italian area company, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA), and the Canadian House Company to increase an ice-scouting Mars orbiter. I-MIM’s key objective is to symbolize the level and quantity of water ice within the mid- and low-latitude areas of the planet.Putzig mentioned he senses that NASA and the opposite global companions are apprehensive to pursue the I-MIM undertaking. However, there was important funds uncertainty in regards to the enterprise, Putzig noticed, undoubtedly at the NASA aspect and possibly with different businesses as neatly. “This makes it tough for the global companions to finalize their agreements and start actively designing and development the undertaking {hardware} and tools,” Putzig famous. Sought after: lateral and vertical knowledge There are uncertainties inside present-day datasets, Putzig mentioned, so extra analysis — and particularly new orbital radar sounding functions — are wanted at Mars. As soon as in hand, that data can definitively determine and symbolize buried ice at landing-site scales for huge areas around the mid-latitudes of Mars, Putzig added.”That mentioned, one may just in idea ship landed missions to raised latitudes or to places the place recent affects have uncovered ice and be confident of encountering ice within the subsurface the usage of a drill with out first obtaining that further knowledge,” mentioned Putzig. “Then again, even for such places, the lateral and vertical extent and focus of the ice will stay poorly constrained with out new tools.”Arduous details
Kind of a 3rd of Mars has ice slightly under the planet’s floor. Many have an effect on craters within the mid-latitudes of the Pink Planet are full of easy subject matter this is most likely ice coated with some filth. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona)A radar-carrying orbiter, the I-MIM is a projected NASA endeavor in partnership with the Italian area company, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA), and the Canadian House Company to increase an ice-scouting Mars orbiter. I-MIM’s key objective is to symbolize the level and quantity of water ice within the mid- and low-latitude areas of the planet.Putzig mentioned he senses that NASA and the opposite global companions are apprehensive to pursue the I-MIM undertaking. However, there was important funds uncertainty in regards to the enterprise, Putzig noticed, undoubtedly at the NASA aspect and possibly with different businesses as neatly. “This makes it tough for the global companions to finalize their agreements and start actively designing and development the undertaking {hardware} and tools,” Putzig famous. Sought after: lateral and vertical knowledge There are uncertainties inside present-day datasets, Putzig mentioned, so extra analysis — and particularly new orbital radar sounding functions — are wanted at Mars. As soon as in hand, that data can definitively determine and symbolize buried ice at landing-site scales for huge areas around the mid-latitudes of Mars, Putzig added.”That mentioned, one may just in idea ship landed missions to raised latitudes or to places the place recent affects have uncovered ice and be confident of encountering ice within the subsurface the usage of a drill with out first obtaining that further knowledge,” mentioned Putzig. “Then again, even for such places, the lateral and vertical extent and focus of the ice will stay poorly constrained with out new tools.”Arduous details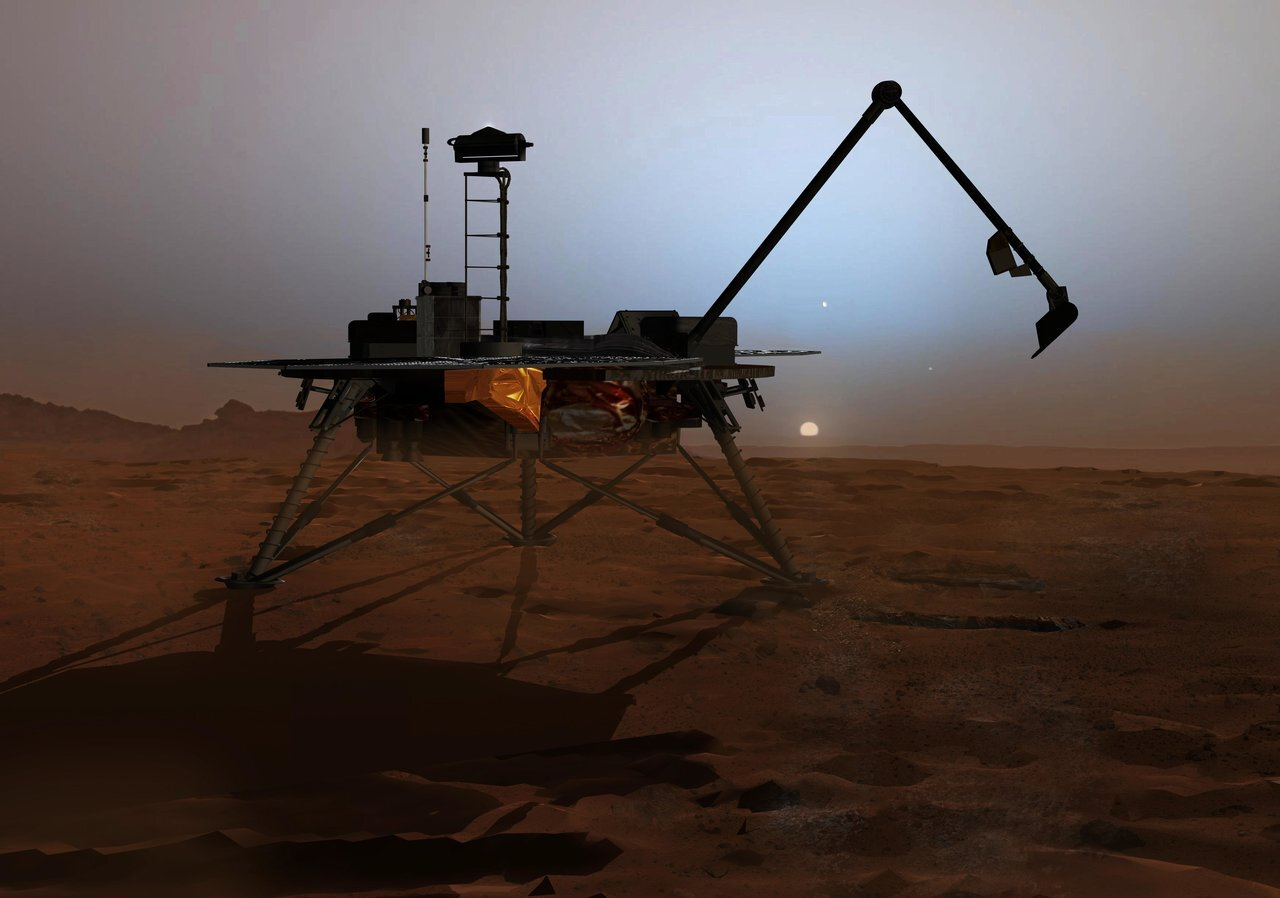  Artist’s representation of NASA’s Phoenix Mars lander undertaking, which in 2008 scooped up soil and probed for ice within the Martian arctic. (Symbol credit score: NASA)Drilling even 1 meter (3.3 ft) into ice can also be tough, defined Isaac Smith, an affiliate professor at York College in Toronto, Ontario. He is additionally a senior scientist on the Planetary Science Institute, headquartered in Tucson, Arizona.Such drilling on Earth calls for lots of thermal or electric energy and numerous human energy. “It is particularly arduous when the ice is far less warm than minus 40 levels Celsius (minus 40 levels Fahrenheit), like every ice on Mars,” Smith mentioned. That used to be discovered to be the case with the NASA Phoenix Mars lander undertaking in 2008, mentioned Smith. The legged desk bound spacecraft plopped down in the world farther north than any earlier undertaking, at a latitude similar to that of northern Alaska, then scooped up Martian soil and checked for — and located — water ice. “That ice-cemented soil [at the Phoenix lander locale] is in reality arduous to dig in, however any individual who lives in Canada throughout wintry weather is aware of to not cross digging in a yard when the bottom is frozen,” Smith identified.Frozen in time In moderation sampling any ice on Mars would yield a bonanza of science returns, Smith mentioned. “Polar ice can provide you with an in depth document of local weather historical past; mid-latitude ice can grow to be a useful resource for long run area exploration and is the following frontier for searching for lifestyles on Mars,” Smith instructed. “Simply as getting rock samples may give clues to Mars’ early historical past, ice will give us clues to Mars’ fresh historical past.”All just right information, however achieving depths of tens of meters or extra is a large process, Smith mentioned. Doing so could be very power in depth, he mentioned, and calls for numerous human intervention, even on Earth. “For the foreseeable long run, it’ll need to be accomplished through robots on Mars, almost certainly over lengthy sessions, requiring additional ranges of robustness, which provides value, and a few energy supply that we should not have but,” Smith mentioned. “It is possible in the long run, and Honeybee Robotics is almost certainly the corporate to construct it.”
Artist’s representation of NASA’s Phoenix Mars lander undertaking, which in 2008 scooped up soil and probed for ice within the Martian arctic. (Symbol credit score: NASA)Drilling even 1 meter (3.3 ft) into ice can also be tough, defined Isaac Smith, an affiliate professor at York College in Toronto, Ontario. He is additionally a senior scientist on the Planetary Science Institute, headquartered in Tucson, Arizona.Such drilling on Earth calls for lots of thermal or electric energy and numerous human energy. “It is particularly arduous when the ice is far less warm than minus 40 levels Celsius (minus 40 levels Fahrenheit), like every ice on Mars,” Smith mentioned. That used to be discovered to be the case with the NASA Phoenix Mars lander undertaking in 2008, mentioned Smith. The legged desk bound spacecraft plopped down in the world farther north than any earlier undertaking, at a latitude similar to that of northern Alaska, then scooped up Martian soil and checked for — and located — water ice. “That ice-cemented soil [at the Phoenix lander locale] is in reality arduous to dig in, however any individual who lives in Canada throughout wintry weather is aware of to not cross digging in a yard when the bottom is frozen,” Smith identified.Frozen in time In moderation sampling any ice on Mars would yield a bonanza of science returns, Smith mentioned. “Polar ice can provide you with an in depth document of local weather historical past; mid-latitude ice can grow to be a useful resource for long run area exploration and is the following frontier for searching for lifestyles on Mars,” Smith instructed. “Simply as getting rock samples may give clues to Mars’ early historical past, ice will give us clues to Mars’ fresh historical past.”All just right information, however achieving depths of tens of meters or extra is a large process, Smith mentioned. Doing so could be very power in depth, he mentioned, and calls for numerous human intervention, even on Earth. “For the foreseeable long run, it’ll need to be accomplished through robots on Mars, almost certainly over lengthy sessions, requiring additional ranges of robustness, which provides value, and a few energy supply that we should not have but,” Smith mentioned. “It is possible in the long run, and Honeybee Robotics is almost certainly the corporate to construct it.”
Drilling for water ice on Mars: How shut are we to creating it occur?