Earth is beneath consistent bombardment by way of high-energy charged debris known as cosmic rays. We are usually protected against this barrage by way of Earth’s magnetic bubble, the magnetosphere. However what occurs when this protect weakens?Cosmic rays are basically hydrogen nuclei blasted into house by way of tough celestial occasions such because the supernova deaths of huge stars. Those extremely full of life debris are usually intercepted by way of the magnetosphere, which additionally protects us from harsh sun radiation from the solar.The magnetosphere isn’t a monolithic, unchanging entity, on the other hand. No longer handiest does magnetic north “wobble” relatively clear of geographic “true north,” however all the magnetosphere infrequently “flips.” This ends up in the sector’s north pole changing into south and vice versa, with the depth of the sector waning within the procedure.Along with this, there are different transient sessions right through which the 2 magnetic poles of the magnetosphere “disappear,” to get replaced by way of a mess of magnetic poles. All the way through those sessions, known as “magnetic box tours,” the power of magnetic poles additionally weakens, implying that our planet is much less well-protected from cosmic rays at those occasions.Comparable: The place do cosmic rays come from?The query is, Do sessions of low magnetosphere depth additionally correlate with main upheavals in Earth’s biosphere, your entire zone of our planet over which existence exists, starting from mountaintops to the private ocean trenches?”Figuring out those excessive occasions is vital for his or her prevalence at some point, house local weather predictions, and assessing the consequences at the surroundings and at the Earth machine,” Sanja Panovska, a scientist at GFZ Potsdam in Germany, stated in a observation.Breaking house information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!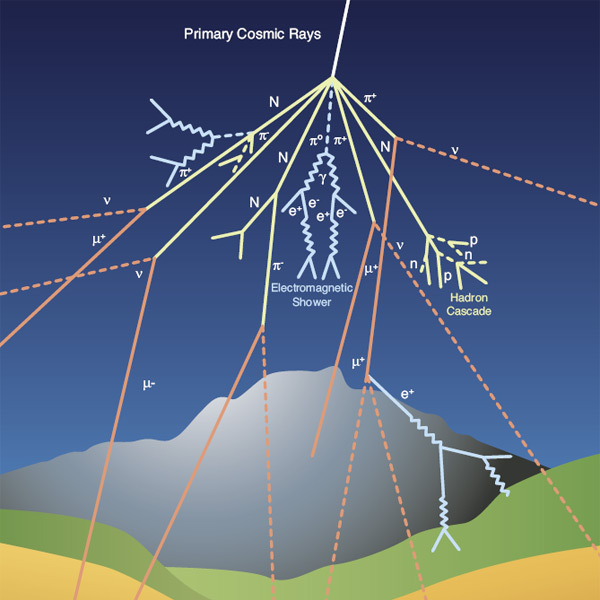 A demonstration of cosmic rays streaming into Earth’s setting, growing a bath of secondary debris. (Symbol credit score: CERN)To resolve the sessions right through which Earth has skilled a heavier than standard bombardment of cosmic rays, scientists can measure the abundances of various isotopes. Those are variants of a component that experience other numbers of neutrons of their atomic nuclei.When cosmic rays strike debris in Earth’s setting, they invent showers of isotopes known as “cosmogenic radionuclides” that rain right down to our planet’s floor. Those building up through the years in sediments, which scientists can learn about after convalescing them from the ocean mattress and in ice cores drilled from areas like Antarctica and Greenland.One well-studied instance of a magnetic box tour is the Laschamps tour, which passed off round 41,000 years in the past. Panovska has been learning the connection between the depth of Earth’s magnetosphere and the focus of cosmogenic radionuclides similar to beryllium-10 right through this tournament.She discovered that the common manufacturing charge of beryllium-10 doubled in comparison to the velocity at which this cosmogenic radionuclide is generated by way of cosmic ray bombardment nowadays. This means an overly low magnetosphere depth right through the Laschamps tour, resulting in massively extra cosmic rays achieving Earth’s setting and growing showers of secondary debris.Panovska used those measurements to reconstruct Earth’s magnetosphere, discovering that it shrank right through this tournament when its power lowered. She is hoping this reconstruction will lend a hand her and fellow scientists get additional info from cosmogenic radionuclide and cosmic ray bombardments. Panovska introduced the cosmic ray findings on the Eu Geosciences Union (EGU) Normal Meeting 2024 on Friday (April 19).
A demonstration of cosmic rays streaming into Earth’s setting, growing a bath of secondary debris. (Symbol credit score: CERN)To resolve the sessions right through which Earth has skilled a heavier than standard bombardment of cosmic rays, scientists can measure the abundances of various isotopes. Those are variants of a component that experience other numbers of neutrons of their atomic nuclei.When cosmic rays strike debris in Earth’s setting, they invent showers of isotopes known as “cosmogenic radionuclides” that rain right down to our planet’s floor. Those building up through the years in sediments, which scientists can learn about after convalescing them from the ocean mattress and in ice cores drilled from areas like Antarctica and Greenland.One well-studied instance of a magnetic box tour is the Laschamps tour, which passed off round 41,000 years in the past. Panovska has been learning the connection between the depth of Earth’s magnetosphere and the focus of cosmogenic radionuclides similar to beryllium-10 right through this tournament.She discovered that the common manufacturing charge of beryllium-10 doubled in comparison to the velocity at which this cosmogenic radionuclide is generated by way of cosmic ray bombardment nowadays. This means an overly low magnetosphere depth right through the Laschamps tour, resulting in massively extra cosmic rays achieving Earth’s setting and growing showers of secondary debris.Panovska used those measurements to reconstruct Earth’s magnetosphere, discovering that it shrank right through this tournament when its power lowered. She is hoping this reconstruction will lend a hand her and fellow scientists get additional info from cosmogenic radionuclide and cosmic ray bombardments. Panovska introduced the cosmic ray findings on the Eu Geosciences Union (EGU) Normal Meeting 2024 on Friday (April 19).
Earth were given hammered by way of cosmic rays 41,000 years in the past because of a vulnerable magnetic box








/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25833773/686325_20241217_Polestar_line_up.jpg)





