Water from Earth’s floor can in finding its means deep into the planet, and new analysis explains the way it adjustments the outermost area of the metal liquid core.The discovering may give an explanation for the presence of a skinny layer of subject material within the planet that has mystified geologists for many years.Earth’s crust consists of tectonic plates that grind and slide underneath every different; over billions of years, those subduction zones have transported water to the decrease mantle.When this water reaches the core-mantle boundary, some 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles) underneath the skin, it units off a formidable chemical interplay. A group from South Korea, the USA, and Germany confirmed this creates a best core layer wealthy in hydrogen, and sends silica to the decrease mantle.”For years, it’s been believed that subject material change between Earth’s core and mantle is small,” says fabrics scientist Dan Shim from Arizona State College.”But, our contemporary high-pressure experiments divulge a unique tale. We discovered that once water reaches the core-mantle boundary, it reacts with silicon within the core, forming silica.”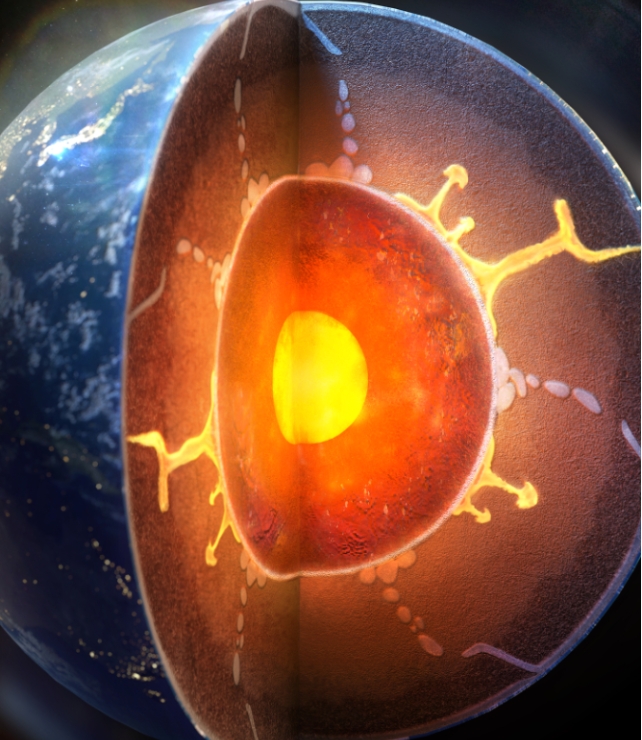 Representation of Earth’s internal revealing subducting water. (Yonsei College)The outer core’s mixture of iron and nickel performs a vital function in producing Earth’s magnetic box, which necessarily protects lifestyles on this planet from sun winds and radiation. So you have to know how Earth’s insides paintings and feature advanced through the years.Earth’s core-mantle boundary adjustments from silicate to steel relatively sharply, and now not a lot is understood concerning the chemical exchanges.A long time in the past, researchers recording seismic waves thru Earth’s gooey insides documented a skinny layer simply over a couple of hundred kilometers thick, however till now no person knew the place this proposed ‘E top’ layer got here from.”We propose that such chemical change between the core and mantle over gigayears of deep shipping of water will have contributed to the formation of the putative E top layer,” the group writes.Seismologists mapped out some odd options that recommend this modified liquid metal layer might be much less dense and feature slower seismic speeds. Those density variations are thought to be to contain other concentrations of sunshine parts, like hydrogen or silicon.However an building up within the focus of a unmarried gentle part would make the velocity move up whilst the density is going down, making it exhausting to reconcile the seismic remark and the dynamic balance of the E top layer.Expanding the focus of 1 gentle part whilst reducing the focus of some other has been put ahead as a conceivable rationalization. On the other hand, scientists weren’t conscious about such an change procedure.The group used laser-heated diamond-anvil cells to imitate pressure-temperature stipulations on the core-mantle boundary.They confirmed that water that was once subducted into Earth’s core may react chemically with the fabrics there to show the outer core right into a hydrogen-rich movie and disperse silica crystals that upward thrust and sign up for the mantle.
Representation of Earth’s internal revealing subducting water. (Yonsei College)The outer core’s mixture of iron and nickel performs a vital function in producing Earth’s magnetic box, which necessarily protects lifestyles on this planet from sun winds and radiation. So you have to know how Earth’s insides paintings and feature advanced through the years.Earth’s core-mantle boundary adjustments from silicate to steel relatively sharply, and now not a lot is understood concerning the chemical exchanges.A long time in the past, researchers recording seismic waves thru Earth’s gooey insides documented a skinny layer simply over a couple of hundred kilometers thick, however till now no person knew the place this proposed ‘E top’ layer got here from.”We propose that such chemical change between the core and mantle over gigayears of deep shipping of water will have contributed to the formation of the putative E top layer,” the group writes.Seismologists mapped out some odd options that recommend this modified liquid metal layer might be much less dense and feature slower seismic speeds. Those density variations are thought to be to contain other concentrations of sunshine parts, like hydrogen or silicon.However an building up within the focus of a unmarried gentle part would make the velocity move up whilst the density is going down, making it exhausting to reconcile the seismic remark and the dynamic balance of the E top layer.Expanding the focus of 1 gentle part whilst reducing the focus of some other has been put ahead as a conceivable rationalization. On the other hand, scientists weren’t conscious about such an change procedure.The group used laser-heated diamond-anvil cells to imitate pressure-temperature stipulations on the core-mantle boundary.They confirmed that water that was once subducted into Earth’s core may react chemically with the fabrics there to show the outer core right into a hydrogen-rich movie and disperse silica crystals that upward thrust and sign up for the mantle.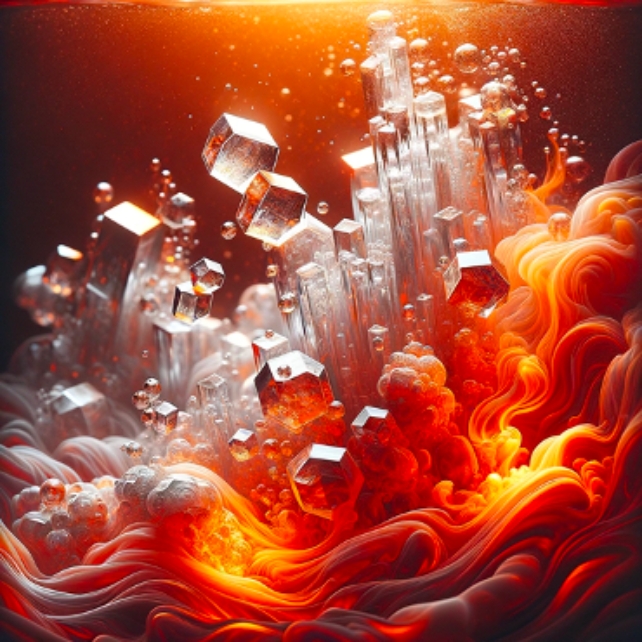 Representation of silica crystals popping out from the liquid steel of Earth’s outer core because of subducted water triggering a chemical response. (Dan Shim/ASU)The layer of hydrogen-rich, silicon-poor subject material that bureaucracy on the best of the core would have much less density and not more velocity, matching seismic wave observations.The altered core movie may in flip have a vital have an effect on at the deep water cycle, and the group says their effects recommend a extra complicated world water cycle than we idea.”This discovery, at the side of our earlier remark of diamonds forming from water reacting with carbon in iron liquid underneath excessive stress,” Shim says, “issues to a much more dynamic core-mantle interplay, suggesting considerable subject material change.”The find out about has been printed in Nature Geoscience.
Representation of silica crystals popping out from the liquid steel of Earth’s outer core because of subducted water triggering a chemical response. (Dan Shim/ASU)The layer of hydrogen-rich, silicon-poor subject material that bureaucracy on the best of the core would have much less density and not more velocity, matching seismic wave observations.The altered core movie may in flip have a vital have an effect on at the deep water cycle, and the group says their effects recommend a extra complicated world water cycle than we idea.”This discovery, at the side of our earlier remark of diamonds forming from water reacting with carbon in iron liquid underneath excessive stress,” Shim says, “issues to a much more dynamic core-mantle interplay, suggesting considerable subject material change.”The find out about has been printed in Nature Geoscience.
Earth’s Core Is Converting: Little-Identified Phenomenon Is Making a Mysterious New Layer






/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25807125/2100335117.jpg)







