Geologists have made positive assumptions about how the crust making up our planet’s earliest floor shaped, however a brand new learn about has discovered that Earth’s first actual protocrust used to be unusually very similar to the shell of cast rock in position nowadays.
It’s going to imply an entire reconsider of the way Earth’s coat transitioned from a pores and skin of boiling magma to the transferring armor of tectonic plates we now survive, in line with the global group of researchers in the back of the learn about.
“Scientists have lengthy idea that tectonic plates had to dive underneath every different to create the chemical fingerprint we see in continents,” says geochemist Simon Turner, from Macquarie College in Australia.
“Our analysis displays this fingerprint existed in Earth’s first actual crust, the protocrust – that means the ones theories want to be reconsidered.”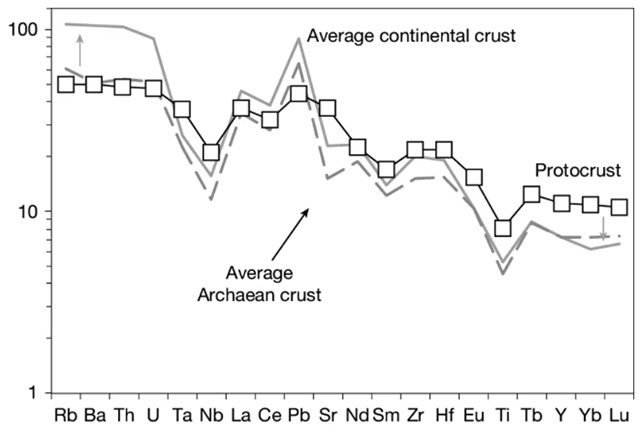 The group discovered that the modeled protocrust used to be similar to nowadays’s continental crust. (Turner et al., Nature, 2025)The chemical fingerprint Turner and his colleagues had been searching for used to be a loss of the component niobium. That is a method of figuring out rocks at subduction zones, the place one plate slides beneath any other – it is idea that the magma forming those rocks loses niobium because the component will get trapped additional down.
The group discovered that the modeled protocrust used to be similar to nowadays’s continental crust. (Turner et al., Nature, 2025)The chemical fingerprint Turner and his colleagues had been searching for used to be a loss of the component niobium. That is a method of figuring out rocks at subduction zones, the place one plate slides beneath any other – it is idea that the magma forming those rocks loses niobium because the component will get trapped additional down.
In finding the primary proof of low ranges of niobium within the geological file, it used to be idea, and also you to find the purpose when continental plates first gave the impression and began slamming into every different. On the other hand, this speculation of a differing early crust composition has been known as into query sooner than.
Right here the researchers took a recent way. They used mathematical fashions to determine the composition of Earth’s earliest masking of laborious rock, some 4 to 4.5 billion years in the past (the Hadean eon). The modeling confirmed that niobium can be drawn to Earth’s core, without a plate tectonics required.
It manner continental crust formation could have been part of the unique means of layer formation on Earth, now not one thing that got here after. The speculation is subsidized up through the habits of alternative siderophile components within the style – components drawn to iron, such because the iron in Earth’s core because it took form.
“I noticed there may well be a connection between early core formation, prime siderophile component patterns, and the notorious detrimental niobium anomaly noticed in continental crust,” says Turner.
Within the many millennia since, it kind of feels continental crust has retained that authentic chemical signature, much less suffering from the heavy bombardment of meteorites that modified the composition of Earth’s mantle, and ended round 3.8 billion years in the past.
All of this wishes additional investigation, after all, however it is an intriguing selection tackle how Earth first turned into the planet we acknowledge nowadays, and the way that may follow to different planets. It additionally solutions one of the maximum baffling questions in geological historical past.
“This discovery totally adjustments our figuring out of Earth’s earliest geological processes,” says Turner.
“It additionally provides us a brand new approach to take into consideration how continents may shape on different rocky planets around the Universe.”The analysis has been printed in Nature.
Earth’s First Crust Would possibly Have Seemed Strangely Like The One We Have These days