Do micro organism mutate randomly, or do they mutate for a goal? Researchers had been puzzling over this conundrum for over a century.In 1943, microbiologist Salvador Luria and physicist became biologist Max Delbrück invented an experiment to argue that micro organism mutated aimlessly. The usage of their check, different scientists confirmed that micro organism may achieve resistance to antibiotics they hadn’t encountered earlier than.The Luria–Delbrück experiment has had an important impact on science. The findings helped Luria and Delbruck win the Nobel Prize in body structure or medication in 1969, and scholars as of late be informed this experiment in biology school rooms. I’ve been learning this experiment in my paintings as a biostatistician for over twenty years.Many years later, this experiment provides courses nonetheless related as of late, as it means that micro organism can expand resistance to antibiotics that have not been advanced but.Slot machines and a eureka momentImagine a check tube containing micro organism dwelling in nutrient broth. The broth is cloudy because of the top focus of micro organism inside it. Including an endemic that infects micro organism, often referred to as a phage, into the tube kills lots of the micro organism and makes the broth transparent.Then again, conserving the check tube underneath prerequisites favorable for bacterial enlargement will flip the broth cloudy once more over the years. This means that the micro organism advanced resistance towards the phages and had been ready to proliferate.What position did the phages play on this exchange?Some scientists idea the phages incited the micro organism to mutate for survival. Others prompt that micro organism automatically mutate randomly, and the improvement of phage-resistant variants used to be merely a fortunate result. Luria and Delbrück have been operating in combination for months to resolve this conundrum, however none in their experiments have been a success.At the evening of Jan. 16, 1943, Luria were given a touch about the way to crack the thriller whilst gazing a colleague hit the jackpot at a slot system. The following morning, he moved quickly to his lab.Luria’s experiment consisted of a couple of tubes and dishes. Each and every tube contained nutrient broth that may lend a hand the micro organism E. coli multiply, whilst each and every dish contained subject material covered with phages.A couple of micro organism had been positioned into each and every tube and given two alternatives to generate phage-resistant variants. They might both mutate within the tubes within the absence of phages, or they might mutate within the dishes within the presence of phages.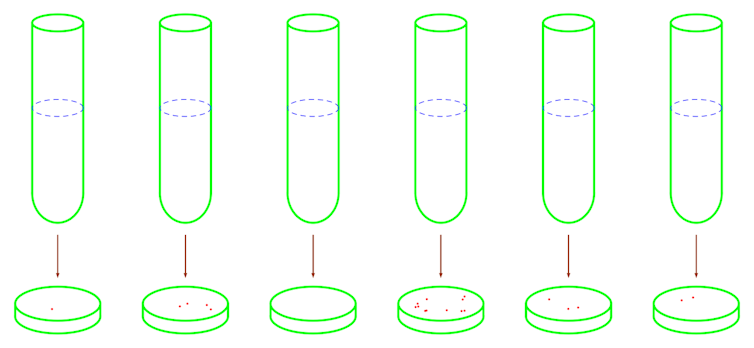 This diagram of the Luria-Delbrück experiment depicts colonies of phage-resistant variants of E. coli (purple) growing in petri dishes. (Qi Zheng, CC BY-SA)The next day to come, Luria transferred the micro organism in each and every tube right into a dish stuffed with phages. The day after that, he counted the collection of resistant bacterial colonies in each and every dish.If micro organism expand resistance towards phages through interacting with them, not one of the micro organism within the tubes must have mutations. However, simplest some of the micro organism – say, 1 out of 10 million micro organism – must spawn resistant variants when they’re transferred right into a dish containing phages. Each and every phage-resistant variant would develop right into a colony, however the remainder micro organism would die from an infection.If micro organism expand resistance independently of interacting with phages, one of the most micro organism within the tubes may have mutations. It is because each and every time a bacterium divides in a tube, it has a small likelihood of spawning a resistant variant.If the beginning era of micro organism is the primary to mutate, no less than part of the micro organism will likely be resistant in later generations. If a bacterium in the second one era is the primary to mutate, no less than an 8th of the micro organism will likely be resistant in later generations.
This diagram of the Luria-Delbrück experiment depicts colonies of phage-resistant variants of E. coli (purple) growing in petri dishes. (Qi Zheng, CC BY-SA)The next day to come, Luria transferred the micro organism in each and every tube right into a dish stuffed with phages. The day after that, he counted the collection of resistant bacterial colonies in each and every dish.If micro organism expand resistance towards phages through interacting with them, not one of the micro organism within the tubes must have mutations. However, simplest some of the micro organism – say, 1 out of 10 million micro organism – must spawn resistant variants when they’re transferred right into a dish containing phages. Each and every phage-resistant variant would develop right into a colony, however the remainder micro organism would die from an infection.If micro organism expand resistance independently of interacting with phages, one of the most micro organism within the tubes may have mutations. It is because each and every time a bacterium divides in a tube, it has a small likelihood of spawning a resistant variant.If the beginning era of micro organism is the primary to mutate, no less than part of the micro organism will likely be resistant in later generations. If a bacterium in the second one era is the primary to mutate, no less than an 8th of the micro organism will likely be resistant in later generations.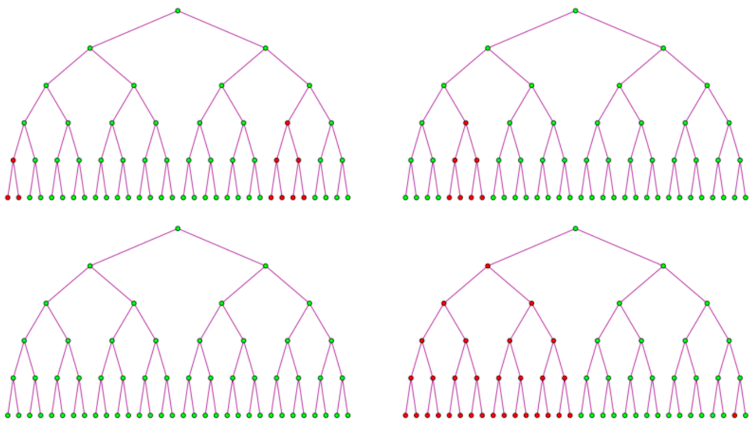 Mutations that confer resistance towards phages (purple) early on will spawn a lot of phage-resistant variants, whilst mutations that happen afterward will spawn only some resistant variants. (Qi Zheng, CC BY-SA)Like small-prize cash-outs in slot machines, late-generation mutations happen extra ceaselessly however give fewer resistant variants. Like jackpots, early-generation mutations happen hardly ever however give massive numbers of variants. Early-generation mutations are uncommon as a result of early on there are just a small collection of micro organism to be had to mutate.As an example, in a 20-generation experiment, a mutation happening on the tenth era of micro organism would give 1,024 phage-resistant variants. A mutation happening on the seventeenth era would give simplest 4 phage-resistant variants.The collection of resistant colonies in Luria’s experiments confirmed a identical development to that of slot system cash-outs. Maximum dishes contained no or small numbers of mutant colonies, however a number of contained a lot of mutant colonies that Luria thought to be jackpots. This supposed that the micro organism advanced resistant variants earlier than they interacted with the phages within the dishes.An experiment’s legacyLuria despatched a be aware to Delbrück after his experiment used to be finished, asking him to test his paintings. The 2 scientists then labored in combination to jot down a vintage paper describing the experimental protocol and a theoretical framework to measure bacterial mutation charges.Different scientists carried out identical experiments through changing phages with penicillin and with tuberculosis medicine. In a similar fashion, they discovered that micro organism didn’t wish to stumble upon an antibiotic to procure resistance to it.Micro organism have depended on random mutations to deal with harsh, continuously converting environments for tens of millions of years. Their incessant, random mutations will cause them to inevitably expand variants which might be proof against the antibiotics of the long run.Drug resistance is a truth of existence we will be able to have to simply accept and proceed to battle towards.
Mutations that confer resistance towards phages (purple) early on will spawn a lot of phage-resistant variants, whilst mutations that happen afterward will spawn only some resistant variants. (Qi Zheng, CC BY-SA)Like small-prize cash-outs in slot machines, late-generation mutations happen extra ceaselessly however give fewer resistant variants. Like jackpots, early-generation mutations happen hardly ever however give massive numbers of variants. Early-generation mutations are uncommon as a result of early on there are just a small collection of micro organism to be had to mutate.As an example, in a 20-generation experiment, a mutation happening on the tenth era of micro organism would give 1,024 phage-resistant variants. A mutation happening on the seventeenth era would give simplest 4 phage-resistant variants.The collection of resistant colonies in Luria’s experiments confirmed a identical development to that of slot system cash-outs. Maximum dishes contained no or small numbers of mutant colonies, however a number of contained a lot of mutant colonies that Luria thought to be jackpots. This supposed that the micro organism advanced resistant variants earlier than they interacted with the phages within the dishes.An experiment’s legacyLuria despatched a be aware to Delbrück after his experiment used to be finished, asking him to test his paintings. The 2 scientists then labored in combination to jot down a vintage paper describing the experimental protocol and a theoretical framework to measure bacterial mutation charges.Different scientists carried out identical experiments through changing phages with penicillin and with tuberculosis medicine. In a similar fashion, they discovered that micro organism didn’t wish to stumble upon an antibiotic to procure resistance to it.Micro organism have depended on random mutations to deal with harsh, continuously converting environments for tens of millions of years. Their incessant, random mutations will cause them to inevitably expand variants which might be proof against the antibiotics of the long run.Drug resistance is a truth of existence we will be able to have to simply accept and proceed to battle towards.![]()
Qi Zheng, Professor of Biostatistics, Texas A&M UniversityThis article is republished from The Dialog underneath a Inventive Commons license. Learn the unique article.
Easy Experiment Finds Why Your Subsequent Antibiotics Would possibly Turn out Pointless