The deep ocean is a complete global of alien thriller.While you get started diving deep, underneath the variety by which daylight can penetrate, complete ecosystems spread, glimmering, glittering, and feasting within the darkness.Working example: In a deep surroundings the place methane seeps from underneath the seafloor into the encompassing water, a shimmering new bug has been came upon.It is been named Pectinereis strickrotti, and it marks the forty eighth new species came upon thriving round methane seeps off the coast of Costa Rica – an atmosphere as soon as regarded as too inhospitable for lifestyles to live to tell the tale.The invention, says a workforce led by means of marine biologist Greg Rouse of the Scripps Establishment of Oceanography, finds simply how little we perceive Earth’s oceans, and the wild variety that may be discovered therein.”We have now spent years seeking to identify and describe the biodiversity of the deep sea,” Rouse says. “At this level we have now discovered extra new species than we have now time to call and describe. It simply displays how a lot undiscovered biodiversity is available in the market. We wish to stay exploring the deep sea and to give protection to it.”The sea depths are totally antagonistic to people. Between the crushing force, the frigid temperatures, and the loss of mild, it is very tricky for us to get there.So there is a lot we do not know in regards to the deeper portions of the sea; we now have explored simply 5 % of the arena’s oceans, and cataloged simply an estimated 10 % of the lifestyles that may be discovered within the depths. The top of P. strickrotti. (Rouse et al., PLOS One, 2024)However, the place people concern to tread, we expand generation to move forth. Rouse and his colleague Bruce Strickrott, lead pilot for deep-sea submersible Alvin (for whom the bug was once named), first encountered the brand new species at a intensity of about 1,000 meters (3,280 ft) in 2009 all the way through a crewed dive off the coast of Costa Rica.”We noticed two worms close to each and every different a few sub’s duration away swimming simply off the ground,” Strickrott recollects. “We could not see them neatly and attempted to creep in for a better glance, however it is arduous to creep in a submarine and we spooked them.”And that was once that, till 2018, when the workforce was once ready to go back to the similar spot. To their wonder, they encountered the similar creature – no longer one person, however six, undulating expectantly within the water. This time, the submersible was once ready to means.The workforce gathered pictures, movies, or even specimens. This bounty received, they retreated to an environment surroundings to catalog and find out about their unearths.
The top of P. strickrotti. (Rouse et al., PLOS One, 2024)However, the place people concern to tread, we expand generation to move forth. Rouse and his colleague Bruce Strickrott, lead pilot for deep-sea submersible Alvin (for whom the bug was once named), first encountered the brand new species at a intensity of about 1,000 meters (3,280 ft) in 2009 all the way through a crewed dive off the coast of Costa Rica.”We noticed two worms close to each and every different a few sub’s duration away swimming simply off the ground,” Strickrott recollects. “We could not see them neatly and attempted to creep in for a better glance, however it is arduous to creep in a submarine and we spooked them.”And that was once that, till 2018, when the workforce was once ready to go back to the similar spot. To their wonder, they encountered the similar creature – no longer one person, however six, undulating expectantly within the water. This time, the submersible was once ready to means.The workforce gathered pictures, movies, or even specimens. This bounty received, they retreated to an environment surroundings to catalog and find out about their unearths. Video of P. strickrotti filmed from Alvin. (Rouse et al., PLOS One, 2024)The gathering printed that what that they had was once a brand new species of marine bug belonging to the Nereididae circle of relatives, sometimes called ragworms. Like different family members, P. strickrotti is a segmented polychaete bug with an extended frame whose facets are bristling with leg-like appendages referred to as parapodia, and hidden jaws that emerge for feeding.In different very attention-grabbing techniques, P. strickrotti is not like different recognized ragworms. For a get started, maximum recognized ragworms inhabit a lot shallower waters. As it lives within the bathypelagic darkness, P. strickotti is blind. As well as, maximum recognized ragworms take in oxygen via their parapodia with out assistance from gills, the place P. strickrotti’s parapodia are coated with gills.Generally, Nereididae have two lifestyles phases: the immature atoke degree wherein they spend maximum in their lives in a burrow at the seafloor; and the grownup epitoke degree that emerges and swims freely to reproduce ahead of loss of life.
Video of P. strickrotti filmed from Alvin. (Rouse et al., PLOS One, 2024)The gathering printed that what that they had was once a brand new species of marine bug belonging to the Nereididae circle of relatives, sometimes called ragworms. Like different family members, P. strickrotti is a segmented polychaete bug with an extended frame whose facets are bristling with leg-like appendages referred to as parapodia, and hidden jaws that emerge for feeding.In different very attention-grabbing techniques, P. strickrotti is not like different recognized ragworms. For a get started, maximum recognized ragworms inhabit a lot shallower waters. As it lives within the bathypelagic darkness, P. strickotti is blind. As well as, maximum recognized ragworms take in oxygen via their parapodia with out assistance from gills, the place P. strickrotti’s parapodia are coated with gills.Generally, Nereididae have two lifestyles phases: the immature atoke degree wherein they spend maximum in their lives in a burrow at the seafloor; and the grownup epitoke degree that emerges and swims freely to reproduce ahead of loss of life.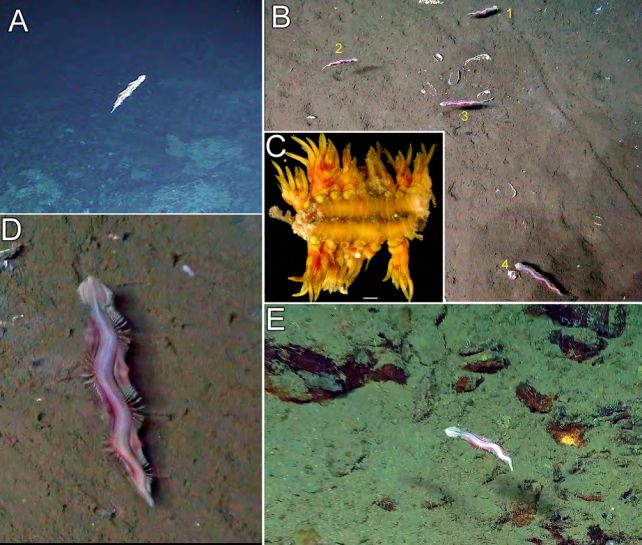 Photographs of P. strickrotti placing round in its herbal habitat. (Rouse et al., PLOS One, 2024)As many of the specimens gathered right here had been free-swimming men, and the one (partial) feminine pattern was once gathered from the sediment, the workforce suspect on this species it may well be best the men that transform epitokes.What is extra the men had atypical non-reproductive epitokous traits that seem to be distinctive amongst Nereididae. It’s going to take additional investigation to expose the way in which the bug lives, and why it wishes those traits.It is also no longer recognized what the creature eats, even though learning the chemosynthetic meals internet that emerges round methane seeps may lend a hand determine that out.Extra importantly, even though, the strange bug provides us a glimpse into the huge abyss of our personal unknowing, and the bizarre wonders of this global simply looking forward to us to search out them.A paper describing the brand new species has been revealed in PLOS One.
Photographs of P. strickrotti placing round in its herbal habitat. (Rouse et al., PLOS One, 2024)As many of the specimens gathered right here had been free-swimming men, and the one (partial) feminine pattern was once gathered from the sediment, the workforce suspect on this species it may well be best the men that transform epitokes.What is extra the men had atypical non-reproductive epitokous traits that seem to be distinctive amongst Nereididae. It’s going to take additional investigation to expose the way in which the bug lives, and why it wishes those traits.It is also no longer recognized what the creature eats, even though learning the chemosynthetic meals internet that emerges round methane seeps may lend a hand determine that out.Extra importantly, even though, the strange bug provides us a glimpse into the huge abyss of our personal unknowing, and the bizarre wonders of this global simply looking forward to us to search out them.A paper describing the brand new species has been revealed in PLOS One.
Eerie New Bug Species Discovered Slithering in Ocean's Darkest Depths