Up to date 12:45 p.m. Japanese with affirmation of touch with satellite tv for pc after deployment.
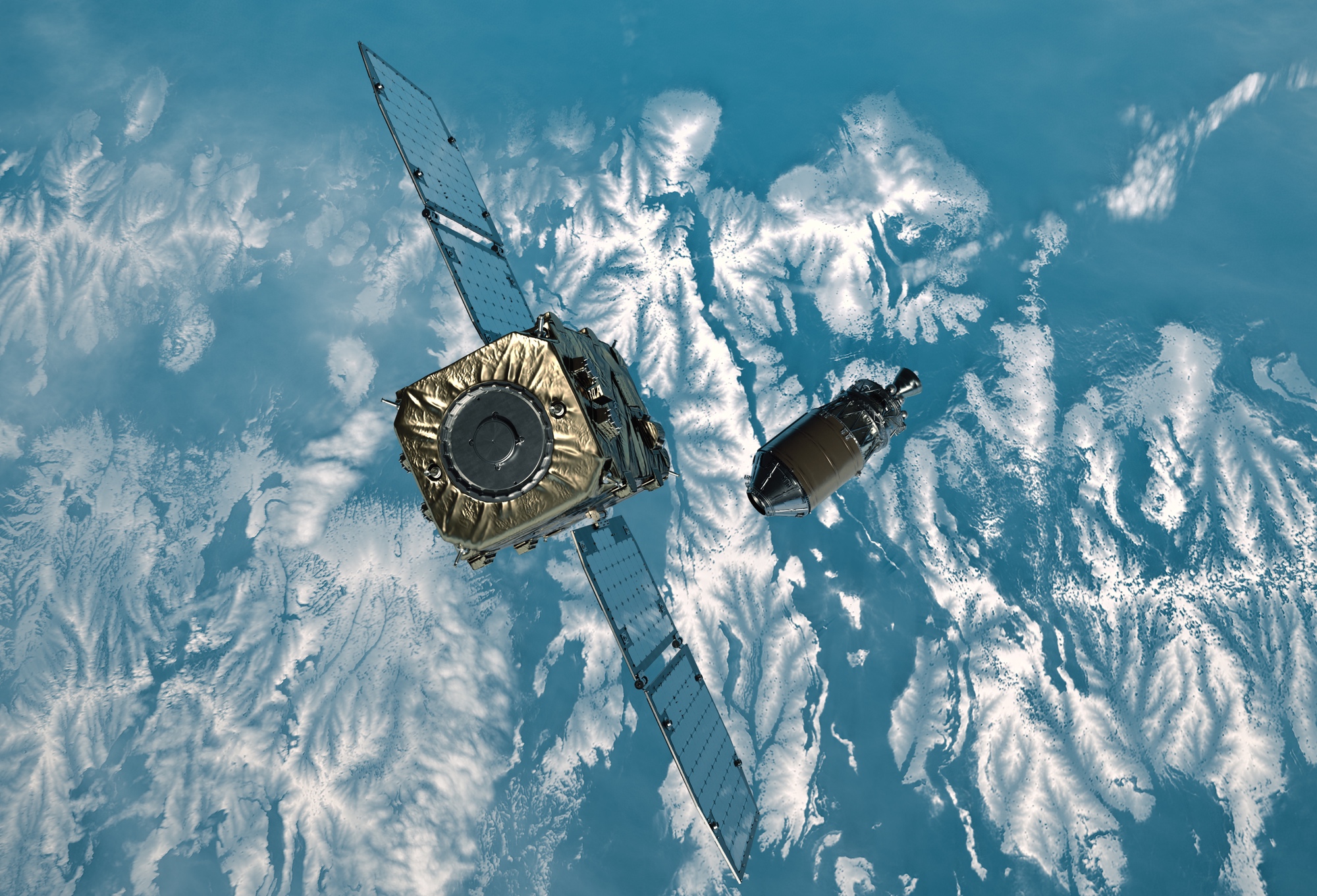
WASHINGTON — A Rocket Lab Electron introduced an Astroscale spacecraft that can rendezvous with and check up on a spent higher degree in low Earth orbit as a precursor to getting rid of it.
The Electron lifted off from Rocket Lab’s Release Advanced 1 in New Zealand at 9:52 a.m. Japanese Feb. 18. The release was once the second one this 12 months for the corporate after the Jan. 31 release of 4 satellites for house situational consciousness corporate NorthStar Earth and House.
The only payload for this release was once the Energetic Particles Removing by way of Astroscale-Japan (ADRAS-J) spacecraft. The 150-kilogram satellite tv for pc was once launched into an orbit of about 600 kilometers 64 mins after liftoff.
Astroscale stated in a remark that it made touch with ADRAS-J after deployment. “This milestone alerts the beginning of our challenge, and we’re excited to survey and symbolize an actual piece of particles thru our leading edge rendezvous and proximity operations features,” stated Eijiro Atarashi, mission supervisor for ADRAS-J at Astroscale.
ADRAS-J was once advanced by way of Astroscale as the primary section of the Jap house Company JAXA’s Business Removing of Particles Demonstration, or CRD2, program. The function of ADRAS-J is to method the higher degree of an H-2A rocket, 11 meters lengthy and four meters in diameter, that introduced the GOSAT Earth commentary satellite tv for pc in 2009 and check up on it. A long term 2nd section of the CRD2 program will ship a spacecraft to the higher degree to try to deorbit it.
“This can be, to my wisdom, the primary challenge that can method and rendezvous with a real piece of house particles,” stated Mike Lindsay, leader generation officer of Astroscale, right through a panel dialogue on the House Particles Convention arranged by way of the Saudi House Company Feb. 12. “What we’re going to do is assess the state of this house particles, see the way it’s transferring, the way it’s tumbling, what’s its situation, in point of fact seeking to resolve if it’s secure to method with a follow-on challenge.”
Astroscale officers stated in a September briefing that the challenge had a number of milestones to show rendezvous and proximity operations (RPO), together with the facility to soundly method and function across the higher degree whilst accumulating details about it to help a long term challenge to grapple and deorbit it.
“The important thing to the challenge is demonstrating essentially the most difficult facets of RPO applied sciences,” Gene Fujii, leader engineer of Astroscale, stated at that briefing. He stated Astroscale anticipated the ADRAS-J challenge to ultimate 3 to 6 months.
ADRAS-J was once finished ultimate fall and deliberate to release in November, however was once not on time by way of a September Electron release failure. Astroscale stated on the time it didn’t plan to modify release suppliers on account of the prolong, and Rocket Lab argued that the challenge was once most effective conceivable thru a devoted release like Electron that positioned the spacecraft into a particular orbit on the subject of the H-2A higher degree.
“Our subsequent challenge is an orbital rendezvous challenge,” stated Sandy Tirtey, director of worldwide industrial release products and services at Rocket Lab, right through a panel on the SmallSat Symposium Feb. 7, regarding the approaching ADRAS-J release. “There’s no manner you should do that on a rideshare.”
ADRAS-J is Astroscale’s 2nd challenge, after the Finish-of-Lifestyles Products and services by way of Astroscale demonstration (ELSA-d) challenge introduced in 2021. ELSA-d demonstrated rendezvous and seize applied sciences the usage of a servicer and consumer spacecraft, despite the fact that the ones exams have been difficult by way of the failure of 4 of 8 thrusters at the servicer spacecraft.
“We surely discovered so much from ELSA-d,” Fujii stated on the September briefing. That integrated no longer simply {hardware} design and instrument building but in addition operations, which featured a mixture of self sustaining operations and the ones passed by way of floor controllers. “To determine how one can steadiness between autonomy and floor interactions for protection was once a in point of fact tough factor to place in combination.”
Astroscale introduced Jan. 24 that it had finished challenge operations for the ELSA-d servicer and consumer spacecraft after appearing maneuvers by way of the servicer to decrease its orbit. The servicer spacecraft will reenter in about 3 and a part years, the corporate stated, whilst the buyer spacecraft, which lacks propulsion, is predicted to deorbit inside 5 years.
Comparable