Abstract: A contemporary learn about unearths that seniors who’re extra liable to “emotional contagion”—feeling feelings from others—are considerably much more likely to revel in anxiousness or melancholy. Researchers discovered that emotional sensitivity, when unmanaged, may just building up the chance of mental misery in seniors by means of as much as tenfold. Emotional contagion, continuously caused unconsciously, is helping foster empathy however would possibly pressure psychological well being in communal residing settings.This learn about means that working out emotional contagion can assist in creating enhance programs for seniors. Equipment to assist set up emotional sensitivity may just give a boost to resilience and cut back mental misery. Addressing those emotional dangers would possibly give a boost to seniors’ high quality of lifestyles in social environments.Key Details:Greater Chance: Extremely emotionally delicate seniors are 8.5–10 instances much more likely to revel in anxiousness or melancholy signs.Emotional Contagion Outlined: Emotional contagion is the subconscious adoption of others’ feelings, really helpful for empathy however difficult for psychological resilience.Attainable Interventions: Growing emotional leadership equipment for delicate seniors may just reinforce resilience and well-being.Supply: College of MontrealMadeleine and Paul are sitting on a park bench. As she tells Paul about her monetary worries and the way she’s been suffering for months to make ends meet, Madeleine’s eyes effectively with tears. Paul is moved by means of her misery; her woes resonate with him and heighten his personal fears. His middle grows heavy and his personal eyes develop into wet, too.What’s happening? A type of behavioural mirroring, what psychologists name “emotional contagion.”“Simply as some individuals are much more likely to catch a breathing virus via shut touch, others are extra liable to ‘catching’ the sentiments of the folk round them,” defined Marie-Josée Richer, a psychoeducator on the Institut universitaire de gériatrie de Montréal, affiliated with Université de Montréal, who did doctoral analysis at the matter within the aged.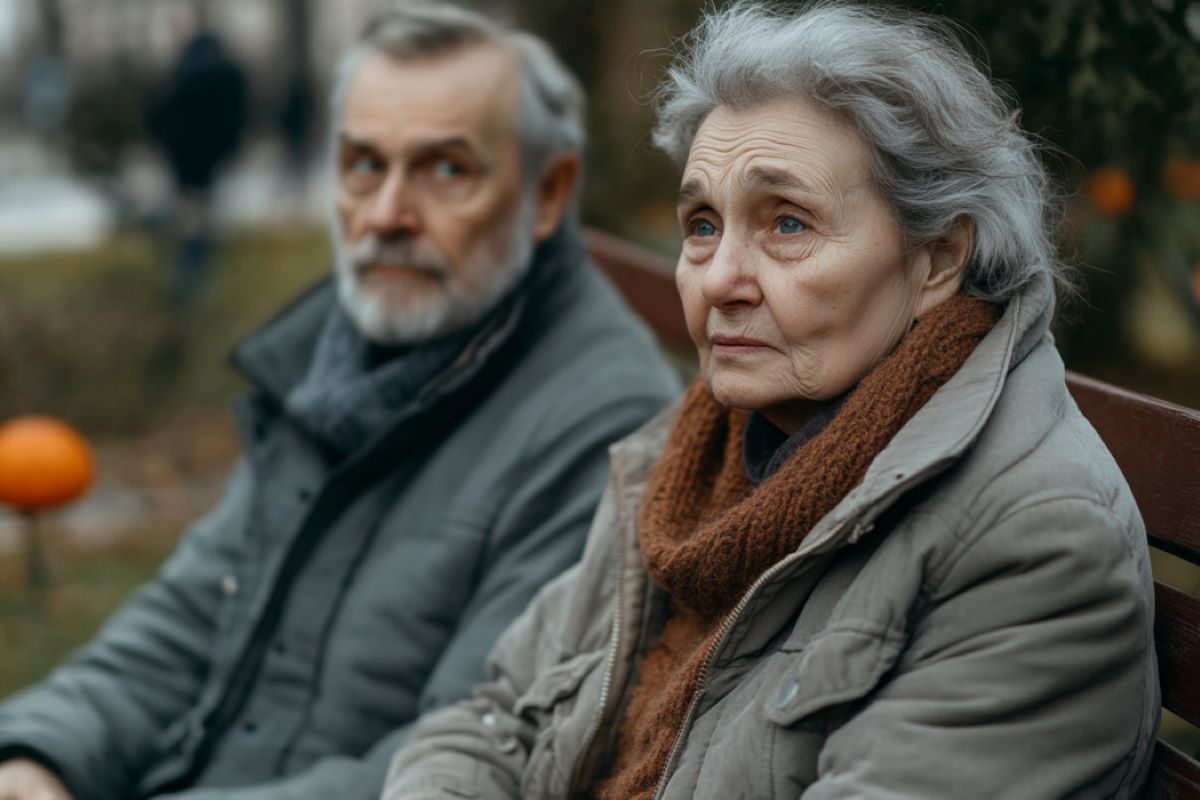  The learn about marks the primary time that vulnerability to emotional contagion has been tested as a determinant of mental misery in seniors, the researchers say. Credit score: Neuroscience Information“An individual susceptible to emotional contagion is particularly delicate to the sentiments of others,” added Pierrich Plusquellec, a professor in UdeM’s College of Psychoeducation and co-director of the Centre for Research on Human Pressure.“It’s an adaptive reaction that happens unconsciously via mimicry of facial expressions, gestures and postures, resulting in the sentiments convergencing.”For instance, he stated, “an individual with this sensitivity would possibly really feel bodily nerve-racking when seeing indignant folks on TV, tear up when seeing somebody cry, or really feel extra cheerful when involved with a contented particular person.To measure vulnerability to emotional contagion, we have a look at a spread of feelings: pleasure, love, anger, worry. Emotional contagion performs an very important position in a society, as it’s the foundation of empathy.”However this vulnerability generally is a double-edged sword. In a brand new learn about co-supervised by means of Plusquellec and UdeM psychology professor Sébastien Grenier and revealed in PLOS Psychological Well being, Richer discovered that vulnerability to emotional contagion is bigger amongst seniors affected by mental misery.“This analysis was once a part of my paintings on mental resilience in older adults,” she stated. “The primary purpose was once to higher perceive the criteria that affect resilience amongst seniors so as to assist save you mental misery, which will have critical results at the total well being of seniors, together with higher chance of heart problems, cognitive decline and untimely demise.”The learn about discovered that vulnerability to emotional contagion varies from individual to individual, simply as character characteristics do, and is one thing that’s continuously overpassed in research of psychological well being, particularly a number of the aged.170 adults studiedThe UdeM researchers studied a bunch of 170 adults elderly 55 or over residing in retirement properties or the usage of the products and services of neighborhood organizations, and who had been coping with some form of adversity. Adversity was once outlined as demanding situations, stumbling blocks or tricky stipulations that a person would possibly face, akin to bereavement or battle with a liked one (specific adversity) or vulnerability to emotional contagion (implicit adversity).The learn about was once a part of a bigger undertaking comparing the results of a program to control strain and strain contagion. To be integrated, individuals needed to are living in a metropolitan space and be all in favour of team stress-management tactics.The researchers sought a wide pattern, together with folks with various ranges of mental misery and bodily obstacles, in an effort to be consultant of the overall inhabitants.Information had been accumulated between September 2018 and September 2019. Lots of the individuals – 85 consistent with cent – had been ladies. They ranged in age from 56 to 96, with a median of 76.1. Maximum had been born in Canada and lived by myself.Individuals had been divided into 3 teams in keeping with degree of mental misery:Just about 45 consistent with cent are compatible the anxiousness profile, with scientific or subclinical signs of tension most effective.Round 20 consistent with cent had been categorised within the nervous melancholy profile, with scientific or subclinical signs of each anxiousness and melancholy. The closing team, the no-distress profile, consisted of people and not using a important signs of tension or melancholy.“We classify signs of various depth which might be sturdy sufficient to intrude with an individual’s day by day lifestyles as ‘subclinical’ or ‘scientific’,” Grenier defined.“Signs are scientific in the event that they meet the standards for a proper analysis of tension or melancholy. For instance, an individual with scientific anxiousness may revel in common panic assaults, problem leaving the home and social isolation.“An individual with subclinical anxiousness should not have a proper analysis however would possibly revel in bodily signs and worries that have an effect on their day by day functioning.”As much as 10 instances extra symptomaticThe researchers analyzed ranges of mental misery relating to elements akin to intercourse, age, source of revenue, residing state of affairs, independence, delight with one’s social community and one’s means of dealing with adversity, and relating to an emotional contagion scale that measured topics’ vulnerability on this regard.The consequences display that the seniors who had been maximum susceptible to emotional contagion had been 8.5 to ten instances much more likely to provide signs of tension or nervous melancholy than those that had been much less inclined. This discovering was once unbiased of alternative elements, akin to a person’s social enhance or coping methods.The learn about marks the primary time that vulnerability to emotional contagion has been tested as a determinant of mental misery in seniors, the researchers say.Regardless that they didn’t determine a cause-and-effect dating between vulnerability to emotional contagion and mental misery, their learn about does spotlight the significance of bearing in mind each specific and implicit adversity to spot seniors in peril for mental misery.In communal residing environments, akin to seniors’ apartments, and in caregiving eventualities, the hazards of emotional contagion want to be addressed proactively, the researchers argue.They suggest creating equipment to assist the folks maximum susceptible to emotional contagion higher set up this sensitivity. This may fortify their mental resilience and assist give a boost to their high quality of lifestyles.Additionally they recommend long run analysis on moderators of vulnerability to emotional contagion so as to give a boost to our working out of its have an effect on on psychological well being and assist cut back mental misery in older folks.About this psychological well being analysis newsAuthor: Julie Gazaille
The learn about marks the primary time that vulnerability to emotional contagion has been tested as a determinant of mental misery in seniors, the researchers say. Credit score: Neuroscience Information“An individual susceptible to emotional contagion is particularly delicate to the sentiments of others,” added Pierrich Plusquellec, a professor in UdeM’s College of Psychoeducation and co-director of the Centre for Research on Human Pressure.“It’s an adaptive reaction that happens unconsciously via mimicry of facial expressions, gestures and postures, resulting in the sentiments convergencing.”For instance, he stated, “an individual with this sensitivity would possibly really feel bodily nerve-racking when seeing indignant folks on TV, tear up when seeing somebody cry, or really feel extra cheerful when involved with a contented particular person.To measure vulnerability to emotional contagion, we have a look at a spread of feelings: pleasure, love, anger, worry. Emotional contagion performs an very important position in a society, as it’s the foundation of empathy.”However this vulnerability generally is a double-edged sword. In a brand new learn about co-supervised by means of Plusquellec and UdeM psychology professor Sébastien Grenier and revealed in PLOS Psychological Well being, Richer discovered that vulnerability to emotional contagion is bigger amongst seniors affected by mental misery.“This analysis was once a part of my paintings on mental resilience in older adults,” she stated. “The primary purpose was once to higher perceive the criteria that affect resilience amongst seniors so as to assist save you mental misery, which will have critical results at the total well being of seniors, together with higher chance of heart problems, cognitive decline and untimely demise.”The learn about discovered that vulnerability to emotional contagion varies from individual to individual, simply as character characteristics do, and is one thing that’s continuously overpassed in research of psychological well being, particularly a number of the aged.170 adults studiedThe UdeM researchers studied a bunch of 170 adults elderly 55 or over residing in retirement properties or the usage of the products and services of neighborhood organizations, and who had been coping with some form of adversity. Adversity was once outlined as demanding situations, stumbling blocks or tricky stipulations that a person would possibly face, akin to bereavement or battle with a liked one (specific adversity) or vulnerability to emotional contagion (implicit adversity).The learn about was once a part of a bigger undertaking comparing the results of a program to control strain and strain contagion. To be integrated, individuals needed to are living in a metropolitan space and be all in favour of team stress-management tactics.The researchers sought a wide pattern, together with folks with various ranges of mental misery and bodily obstacles, in an effort to be consultant of the overall inhabitants.Information had been accumulated between September 2018 and September 2019. Lots of the individuals – 85 consistent with cent – had been ladies. They ranged in age from 56 to 96, with a median of 76.1. Maximum had been born in Canada and lived by myself.Individuals had been divided into 3 teams in keeping with degree of mental misery:Just about 45 consistent with cent are compatible the anxiousness profile, with scientific or subclinical signs of tension most effective.Round 20 consistent with cent had been categorised within the nervous melancholy profile, with scientific or subclinical signs of each anxiousness and melancholy. The closing team, the no-distress profile, consisted of people and not using a important signs of tension or melancholy.“We classify signs of various depth which might be sturdy sufficient to intrude with an individual’s day by day lifestyles as ‘subclinical’ or ‘scientific’,” Grenier defined.“Signs are scientific in the event that they meet the standards for a proper analysis of tension or melancholy. For instance, an individual with scientific anxiousness may revel in common panic assaults, problem leaving the home and social isolation.“An individual with subclinical anxiousness should not have a proper analysis however would possibly revel in bodily signs and worries that have an effect on their day by day functioning.”As much as 10 instances extra symptomaticThe researchers analyzed ranges of mental misery relating to elements akin to intercourse, age, source of revenue, residing state of affairs, independence, delight with one’s social community and one’s means of dealing with adversity, and relating to an emotional contagion scale that measured topics’ vulnerability on this regard.The consequences display that the seniors who had been maximum susceptible to emotional contagion had been 8.5 to ten instances much more likely to provide signs of tension or nervous melancholy than those that had been much less inclined. This discovering was once unbiased of alternative elements, akin to a person’s social enhance or coping methods.The learn about marks the primary time that vulnerability to emotional contagion has been tested as a determinant of mental misery in seniors, the researchers say.Regardless that they didn’t determine a cause-and-effect dating between vulnerability to emotional contagion and mental misery, their learn about does spotlight the significance of bearing in mind each specific and implicit adversity to spot seniors in peril for mental misery.In communal residing environments, akin to seniors’ apartments, and in caregiving eventualities, the hazards of emotional contagion want to be addressed proactively, the researchers argue.They suggest creating equipment to assist the folks maximum susceptible to emotional contagion higher set up this sensitivity. This may fortify their mental resilience and assist give a boost to their high quality of lifestyles.Additionally they recommend long run analysis on moderators of vulnerability to emotional contagion so as to give a boost to our working out of its have an effect on on psychological well being and assist cut back mental misery in older folks.About this psychological well being analysis newsAuthor: Julie Gazaille
Supply: College of Montreal
Touch: Julie Gazaille – College of Montreal
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Open get admission to.
“The contribution of vulnerability to emotional contagion to the expression of mental misery in older adults” by means of Marie-Josée Richer et al. PLOS Psychological HealthAbstractThe contribution of vulnerability to emotional contagion to the expression of mental misery in older adultsThis learn about examines the differential weight of a variety of elements—sociodemographic elements, signs of autonomy, social enhance, coping types, vulnerability to emotional contagion, and empathy—within the presence of 2 profiles of mental misery and of their absence.This cross-sectional learn about integrated 170 older adults. As assessed by means of the Medical institution Nervousness and Melancholy Scale (HADS), 65.9% of the folks within the pattern had a scientific or subthreshold degree of tension and melancholy (rating > 1).In keeping with the HADS’s scientific cutoff rankings for the anxiousness and melancholy subscales, 3 profiles had been created for the no misery, anxiousness, and concerned melancholy teams.The profiles didn’t range on demographic signs with the exception of for intercourse. Vulnerability to emotional contagion, delight with the social community and coping types emerged as elements weighing the possibility of being in both of the mental misery teams relative to folks and not using a misery.After controlling for adversity and psychotropic remedy, vulnerability to emotional contagion had the most powerful dating with each mental misery profiles.Long term analysis, akin to a potential longitudinal learn about, would possibly provide a chance to provide an explanation for the path of the connection between mental misery and the criteria studied, in particular vulnerability to emotional contagion.
Emotional Sensitivity Connected to Nervousness and Melancholy Dangers – Neuroscience Information