HELSINKI — Ecu-Chinese language cooperation in lunar exploration may just come to an finish in spite of a success collaboration within the ongoing Chang’e-6 project.
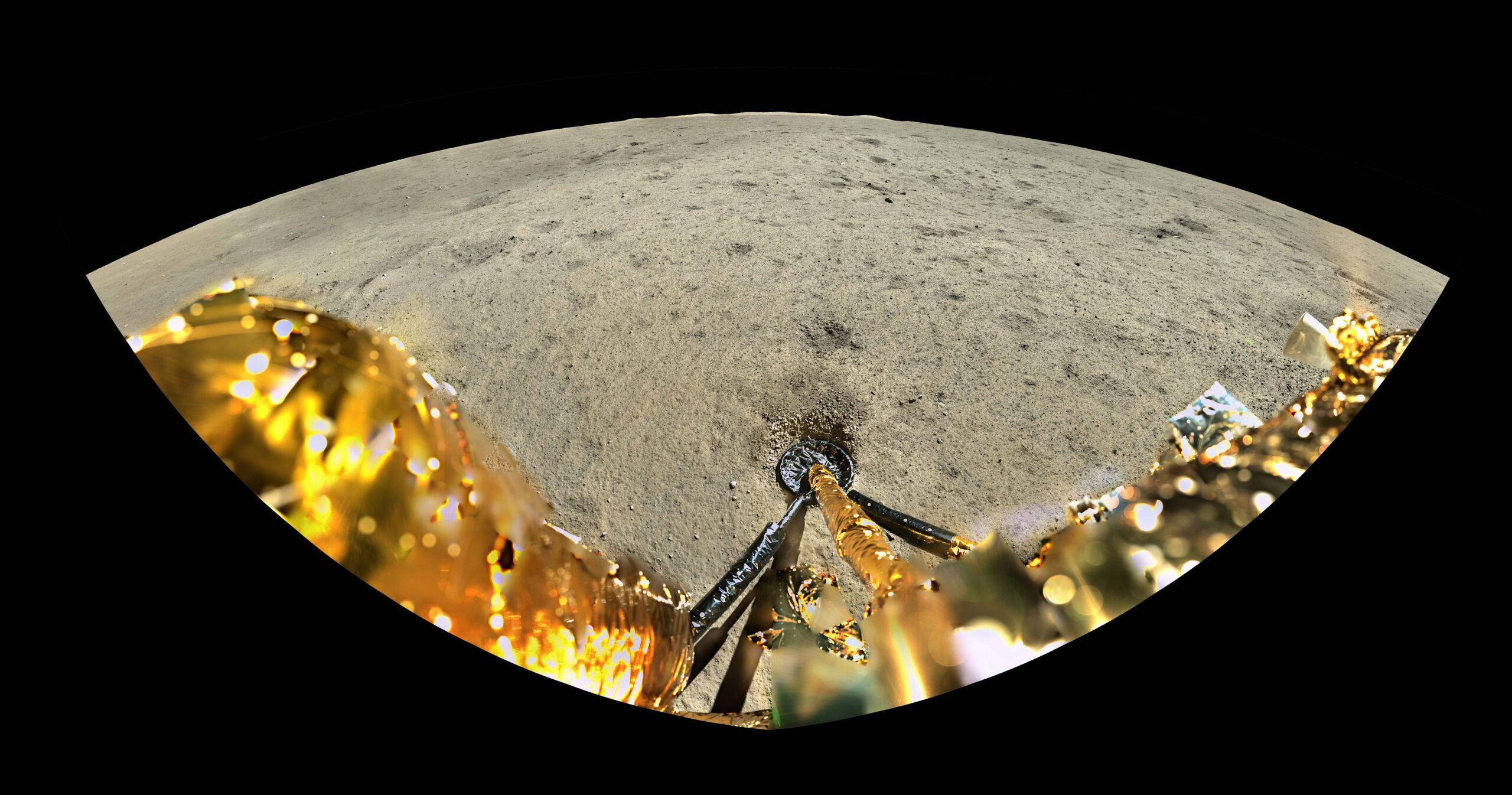
ESA supplied a payload for China’s Chang’e-6 advanced lunar a long way facet pattern go back project which introduced Might 3. The project goals to assemble and go back samples from the lunar a long way facet, offering exceptional insights into the moon’s composition and historical past.
An software evolved through the Swedish Institute of Area physics was once aboard the Chang’e-6 lander which previous this month landed in and sampled the mid-latitude Apollo crater within the South Pole-Aitken Basin.
The Ecu staff operating with the Damaging Ions on the Lunar Floor (NILS) software showed the good fortune in their clinical project. The payload made the primary detection of destructive ions at the lunar floor.
“The invention of a brand new element of plasma on the floor of the moon opens a brand new window for house physics and for human and robot missions in an generation of renewed lunar exploration,” ESA mentioned.
China is making ready for 2 lunar south pole missions with Chang’e-7 round 2026 and the Chang’e-8 in-situ useful resource usage and generation project no previous than 2028.
The a success NILS experiment cooperation with Chang’e-6 might, alternatively, mark the tip of an generation of ESA-China lunar collaboration.
“For the instant there aren’t any choices to proceed the cooperation at the Chang’e-7 or -8,” Karl Bergquist, ESA’s global members of the family administrator, advised SpaceNews.
Additional forward, ESA might not be concerned within the China-led Global Lunar Analysis Station (ILRS).
“ESA is not going to cooperate on ILRS as it is a Sino-Russian initiative and house cooperation with Russia is at this time underneath embargo,” Bergquist mentioned.
It’s the most recent blow to Sino-Ecu house cooperation. ESA final yr additionally mentioned that it might not pursue alternatives to ship Ecu astronauts to the Tiangong house station. China and ESA had previous carried out coaching exchanges.
ILRS, companions and Russian ratification
China and Russia formally introduced a joint roadmap for the undertaking in St. Petersburg in June 2021. The moon base is to be to begin with robot, built by way of tremendous heavy-lift rocket launches within the 2030s. It is going to additionally host crewed missions.
Moscow and Beijing had eyed attracting ESA and its member states to take part within the undertaking. The Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 signaled an finish to any cooperation potentialities.
China has taken a number one position within the ILRS since 2022. The undertaking’s headquarters can be established in China. The China Nationwide Area Management (CNSA) and its Deep Area Exploration Laboratory (DSEL) were on the middle of efforts to draw companions, now and then omitting point out of Russia as a spouse. A lot of those efforts have, as with China’s broader diplomatic efforts, targeted at the “international south.”
There at the moment are 11 international locations signed up, in addition to different our bodies. Russian reviews state that Turkey has additionally carried out to sign up for ILRS. Russia President Vladimir Putin signed a legislation June 12 ratifying an intergovernmental settlement with China on advent of the ILRS.
The Ecu Area Company in the meantime is engaged within the Gateway and Artemis techniques. A variety of its member states have signed the Artemis Accords. 42 countries have now signed the Accords.
TArtemis and ILRS initiatives and comparable diplomatic efforts may also be gave the impression to be forming separate teams. There are alternatively a small stage of overlap. This comprises Bahrain, an Accords signatory, lately agreeing to cooperate with Egypt to expand a hyperspectral imager for Chang’e-7.
With regards to post-ISS plans for human spaceflight—which had previous integrated Tiangong—ESA has signed agreements at the Starlab and Huge business house stations.
Cooperation with China will proceed a minimum of within the close to long run. The samples accumulated through Chang’e-6 are lately in lunar orbit waiting for a go back to Earth, anticipated round June 25.
ESA will supply flooring station toughen for Chang’e-6, because it did for Chang’e-5 via its monitoring station community, ESTRACK.
The Maspalomas station in Gran Canaria, Spain, will monitor the Chang’e-6 spacecraft because it returns to Earth round June 25. Kourou station in French Guiana tracked the spacecraft for a number of hours after release to verify its orbit.
Comparable