The usage of the Euclid house telescope, scientists have found out a staggering 1.5 trillion orphan stars drifting via a large cluster of hundreds of galaxies, some of the biggest constructions within the cosmos. Those orphan stars, ripped unfastened from their very own galaxies, are filling the gap between the galaxies of the Perseus cluster with ghostly blue mild. This so-called “intracluster” mild is so faint that it’s many hundreds of instances darker than the night time sky over Earth. Through staring at this intracluster mild within the Perseus cluster, which is positioned 240 million light-years clear of Earth and has a mass an identical to round 650 trillion suns, Euclid would possibly lend a hand scientists higher perceive the place the faint mild part from galaxy clusters comes from and the origins of the cosmic orphans that emit it.Comparable: The Euclid ‘darkish universe detective’ telescope has printed new photographs of the cosmos — and they’re remarkableEuclid introduced from Cape Canaveral in Florida atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on July 1, 2023. Euclid’s number one challenge is to analyze darkish power, the mysterious drive accelerating the growth of the universe, and darkish subject, an “invisible” substance that does not have interaction with mild and is not made up of atoms just like the “on a regular basis” stuff that surrounds us. On the other hand, regardless of being designed to look into the invisible “darkish universe,” the telescope was once additionally in a position to discover mild emanating from between galaxies within the Perseus galaxy cluster. “We had been stunned by means of our talent to look to this point into the outer areas of the cluster and discern the delicate colours of this mild,” workforce chief and College of Nottingham scientist Nina Hatch mentioned in a commentary. “This mild can lend a hand us map darkish subject if we perceive the place the intracluster stars got here from. Through learning their colours, luminosity, and configurations, we discovered they originated from small galaxies.” Breaking house information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!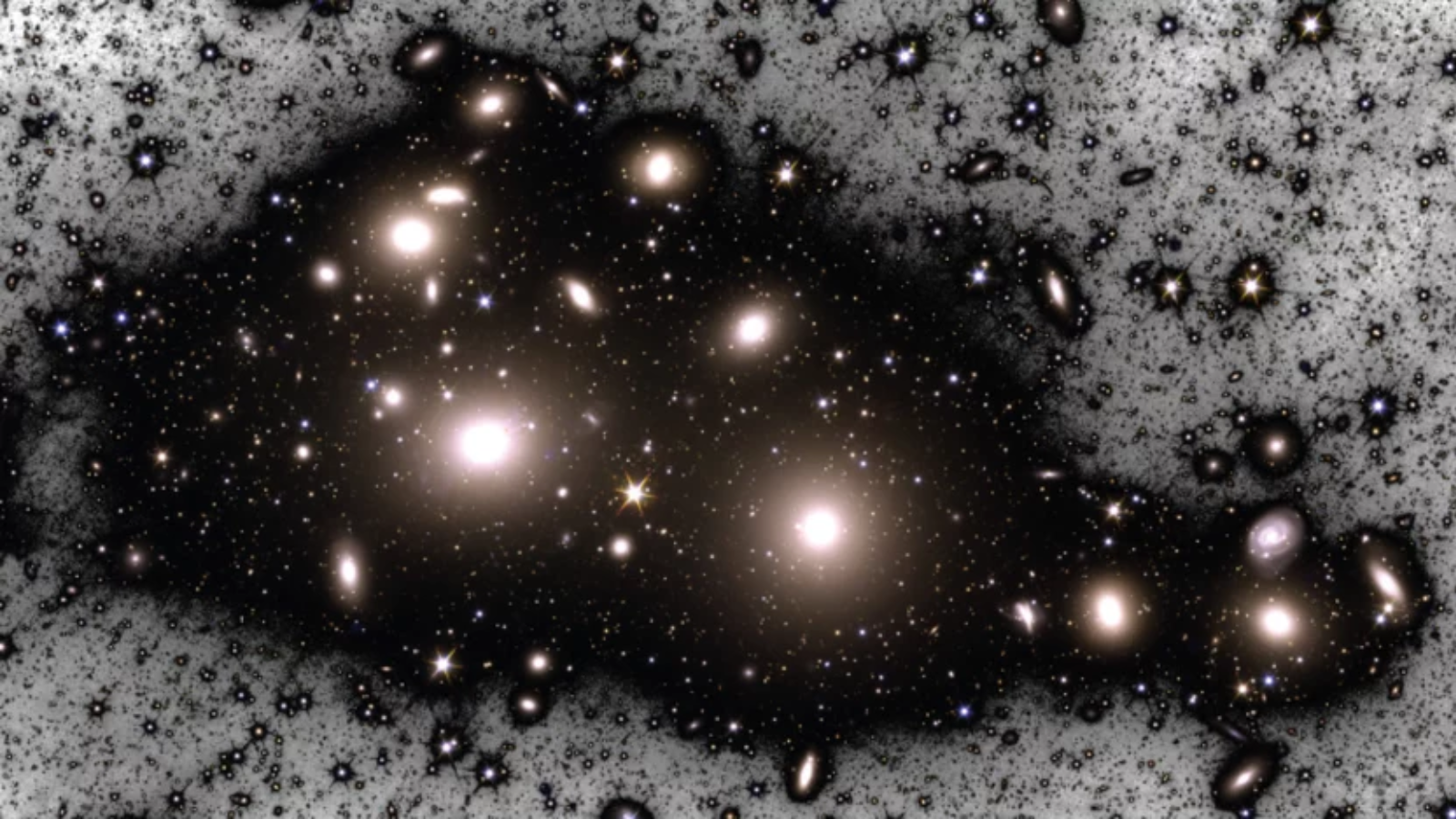 A manipulated symbol of the Perseus cluster appearing the 2 brightest galaxies brightest galaxies within the cluster, NGC 1275 (left) and NGC 1272 (proper) at ist middle (Symbol credit score: Euclid consortium, MPE)Orphan stars have the bluesThe key to figuring out orphan stars in Perseus was once Euclid’s talent to look the faintest mild within the cluster, the intracluster mild, which comes now not from its galaxies however from between them.”This diffuse mild is greater than 100,000 instances fainter than the darkest night time sky on Earth,” workforce member and Max-Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics Matthias Kluge mentioned. “However it’s unfold over this kind of huge quantity that once we upload all of it up, it accounts for roughly 20% of the luminosity of all of the cluster.”The orphan stars observed by means of Euclid within the Perseus cluster are distinguishable by means of their function blue color and their unfastened clustering. Those options allowed Hatch and associates to track their origins. The workforce made up our minds that a few of these free-wandering stars in intracluster house had been dragged clear of the outskirts of galaxies by the use of interactions with different galaxies. Different orphan stars they discovered got here from smaller dwarf galaxies within the Perseus cluster which were utterly disrupted.
A manipulated symbol of the Perseus cluster appearing the 2 brightest galaxies brightest galaxies within the cluster, NGC 1275 (left) and NGC 1272 (proper) at ist middle (Symbol credit score: Euclid consortium, MPE)Orphan stars have the bluesThe key to figuring out orphan stars in Perseus was once Euclid’s talent to look the faintest mild within the cluster, the intracluster mild, which comes now not from its galaxies however from between them.”This diffuse mild is greater than 100,000 instances fainter than the darkest night time sky on Earth,” workforce member and Max-Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics Matthias Kluge mentioned. “However it’s unfold over this kind of huge quantity that once we upload all of it up, it accounts for roughly 20% of the luminosity of all of the cluster.”The orphan stars observed by means of Euclid within the Perseus cluster are distinguishable by means of their function blue color and their unfastened clustering. Those options allowed Hatch and associates to track their origins. The workforce made up our minds that a few of these free-wandering stars in intracluster house had been dragged clear of the outskirts of galaxies by the use of interactions with different galaxies. Different orphan stars they discovered got here from smaller dwarf galaxies within the Perseus cluster which were utterly disrupted.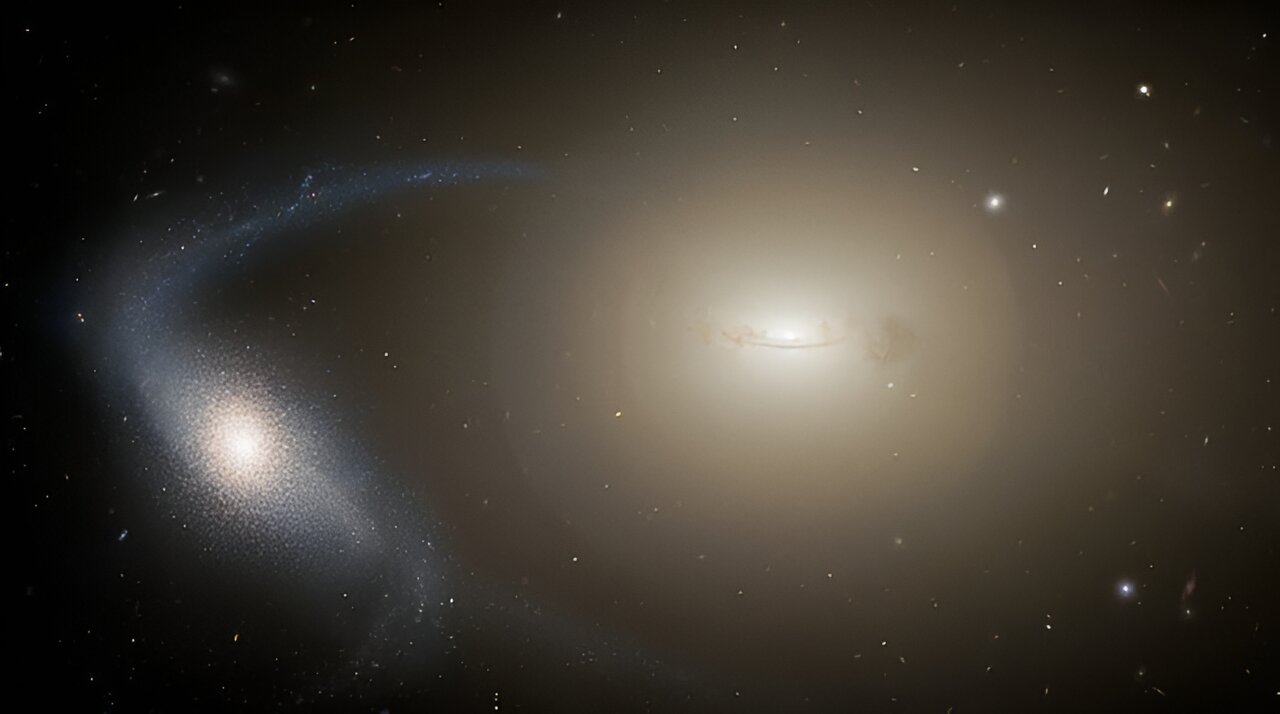  An indication of a dwarf galaxy being disrupted by means of a bigger galaxy which is ripping away its stars. (Symbol credit score: NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/M. Zamani)What the workforce found out subsequent took them by means of wonder. As soon as ripped from their house galaxies, intracluster stars are anticipated to start out orbiting the most important galaxies within the cluster they in finding themselves remoted in, virtually like a misplaced kid within the mall gravitating towards the closest grownup.Hatch and associates did not in finding that during Perseus with Euclid, on the other hand. As a substitute, they noticed that orphan stars orbited some extent between the cluster’s two brightest galaxies, NGC 1275 and NGC 1272.”This novel statement means that the large Perseus cluster can have lately passed through a merger with any other team of galaxies,” workforce member and College of Nottingham astronomer Jesse Golden-Marx mentioned. “This contemporary merger can have triggered a gravitational disturbance, inflicting both essentially the most large galaxy or the orphan stars to deviate from their anticipated orbits, thus ensuing within the noticed misalignment.”
An indication of a dwarf galaxy being disrupted by means of a bigger galaxy which is ripping away its stars. (Symbol credit score: NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/M. Zamani)What the workforce found out subsequent took them by means of wonder. As soon as ripped from their house galaxies, intracluster stars are anticipated to start out orbiting the most important galaxies within the cluster they in finding themselves remoted in, virtually like a misplaced kid within the mall gravitating towards the closest grownup.Hatch and associates did not in finding that during Perseus with Euclid, on the other hand. As a substitute, they noticed that orphan stars orbited some extent between the cluster’s two brightest galaxies, NGC 1275 and NGC 1272.”This novel statement means that the large Perseus cluster can have lately passed through a merger with any other team of galaxies,” workforce member and College of Nottingham astronomer Jesse Golden-Marx mentioned. “This contemporary merger can have triggered a gravitational disturbance, inflicting both essentially the most large galaxy or the orphan stars to deviate from their anticipated orbits, thus ensuing within the noticed misalignment.”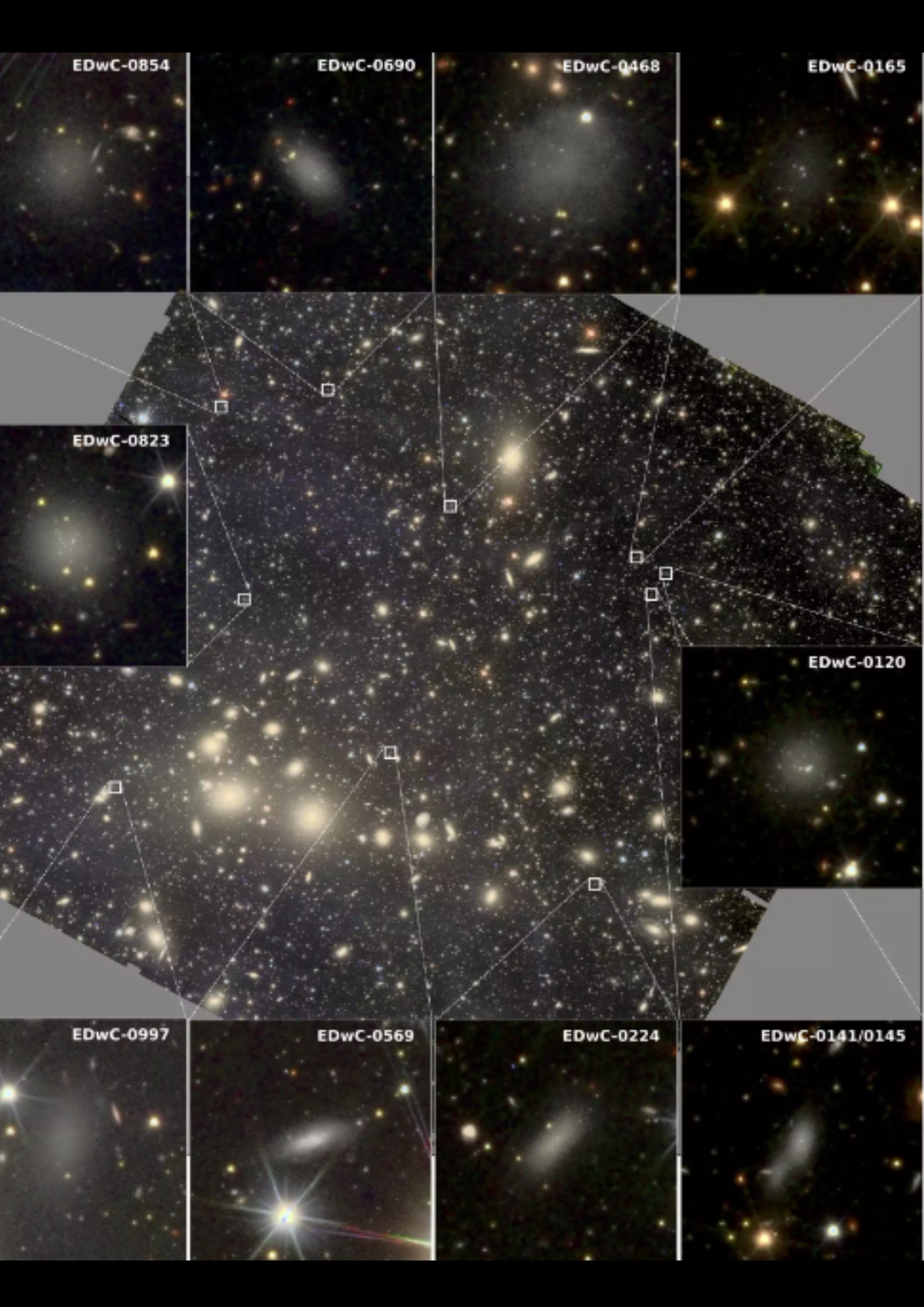 Zoomed in photographs of the Perseus cluster as observed by means of Euclid display dwarf galaxies that experience survived interactions with higher galaxies. (Symbol credit score: Euclid consortium, LMU, MPE)The similar researchers extensively utilized Euclid’s delicate visual mild functions to identify 50,000 free-flying densely packed and round collections of tens of hundreds to thousands and thousands of stars referred to as “globular clusters” within the Perseus galaxy cluster. The diffuse intracluster mild appears to be disbursed similarly to the globular clusters in Perseus, so those conglomerations of stars seem to be the supply of no less than a few of this mild. The celebs in those globular clusters lack prime concentrations of “metals,” a time period that astronomers use for parts heavier than hydrogen and helium. This means to the workforce that the globular clusters within the Perseus galaxy cluster have made their method inwards from the huge number of galaxies’ outer edges, which can be additionally “metal-poor.”Globular clusters contain a dominant consider dwarf galaxies, which means that one of the most intracluster mild would possibly originate from the stays of such small galaxies which were ripped aside by means of tidal forces generated all over encounters with extra large galaxies. The workforce additionally found out from the Euclid statement of Perseus that the small dwarf galaxies on this galactic cluster build up in quantity as one strikes clear of the cluster’s heart. The analysis is helping check Euclid’s capacity to know the evolution of galaxies and galaxy clusters and, thus, how the universe got here to seem how it does to us as of late. Excitingly, those findings are a few of the first clinical effects from Euclid’s Early Liberate Observations, representing simply the primary 24 hours of Euclid’s observations earlier than it all started staring at its primary clinical goals, billions of galaxies throughout greater than a 3rd of the sky on Feb. 14 2024.The workforce’s analysis is featured at the paper repository web page arXiv.
Zoomed in photographs of the Perseus cluster as observed by means of Euclid display dwarf galaxies that experience survived interactions with higher galaxies. (Symbol credit score: Euclid consortium, LMU, MPE)The similar researchers extensively utilized Euclid’s delicate visual mild functions to identify 50,000 free-flying densely packed and round collections of tens of hundreds to thousands and thousands of stars referred to as “globular clusters” within the Perseus galaxy cluster. The diffuse intracluster mild appears to be disbursed similarly to the globular clusters in Perseus, so those conglomerations of stars seem to be the supply of no less than a few of this mild. The celebs in those globular clusters lack prime concentrations of “metals,” a time period that astronomers use for parts heavier than hydrogen and helium. This means to the workforce that the globular clusters within the Perseus galaxy cluster have made their method inwards from the huge number of galaxies’ outer edges, which can be additionally “metal-poor.”Globular clusters contain a dominant consider dwarf galaxies, which means that one of the most intracluster mild would possibly originate from the stays of such small galaxies which were ripped aside by means of tidal forces generated all over encounters with extra large galaxies. The workforce additionally found out from the Euclid statement of Perseus that the small dwarf galaxies on this galactic cluster build up in quantity as one strikes clear of the cluster’s heart. The analysis is helping check Euclid’s capacity to know the evolution of galaxies and galaxy clusters and, thus, how the universe got here to seem how it does to us as of late. Excitingly, those findings are a few of the first clinical effects from Euclid’s Early Liberate Observations, representing simply the primary 24 hours of Euclid’s observations earlier than it all started staring at its primary clinical goals, billions of galaxies throughout greater than a 3rd of the sky on Feb. 14 2024.The workforce’s analysis is featured at the paper repository web page arXiv.
Euclid house telescope reveals 1.5 trillion orphan stars wandering the Perseus cluster (photographs)











/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25462005/STK155_OPEN_AI_CVirginia_B.jpg)

