A contemporary find out about of the Ciomadul volcano in Romania highlights simply how temporarily – and the way powerfully – long-dormant volcanoes can erupt.One of the most youngest volcanoes in eastern-central Europe, Ciomadul hasn’t erupted for some 30,000 years. Thru a complicated geological research, a workforce of Eu scientists has shed extra gentle at the cycle of volcanic process that Ciomadul has long past via over the millennia.Specifically, the workforce sought after to have a look at the trade in eruption kind over a long time period, from the extra mild effusive (a gradual downhill go with the flow of lava) to the extra bad explosive (a surprising free up of gases and lava underneath intense power).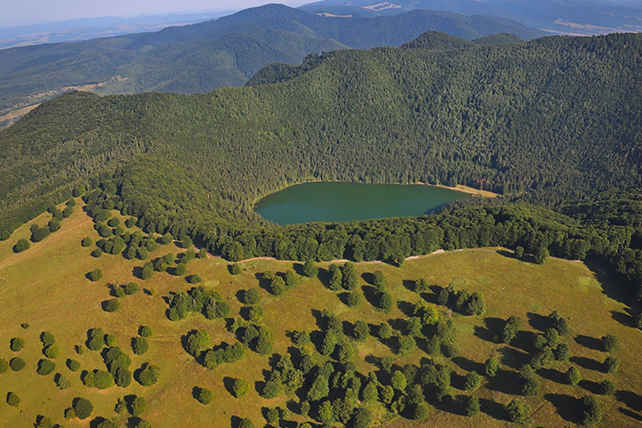 The Ciomadul volcano crater. (István Fodor)”There were a number of lengthy sessions of dormancy within the virtually million-year lifetime of the volcano, however even after tens of hundreds, every now and then much more than 100,000 years of quiescence, volcanic eruptions began once more,” says geochemist Szabolcs Harangi from Eötvös Loránd College in Hungary.The workforce undertook a cautious find out about of the crystals and minerals inside of volcanic rocks round Ciomadul: the chemical composition and water content material of those rocks give professionals clues as to the eruption stipulations that shape them, and once they have been created.Having up to now established that there was once an precedent days of effusive eruptions, right here the workforce focused on the newest, explosive eruption duration – from kind of 56,000 years in the past to kind of 30,000 years in the past.
The Ciomadul volcano crater. (István Fodor)”There were a number of lengthy sessions of dormancy within the virtually million-year lifetime of the volcano, however even after tens of hundreds, every now and then much more than 100,000 years of quiescence, volcanic eruptions began once more,” says geochemist Szabolcs Harangi from Eötvös Loránd College in Hungary.The workforce undertook a cautious find out about of the crystals and minerals inside of volcanic rocks round Ciomadul: the chemical composition and water content material of those rocks give professionals clues as to the eruption stipulations that shape them, and once they have been created.Having up to now established that there was once an precedent days of effusive eruptions, right here the workforce focused on the newest, explosive eruption duration – from kind of 56,000 years in the past to kind of 30,000 years in the past.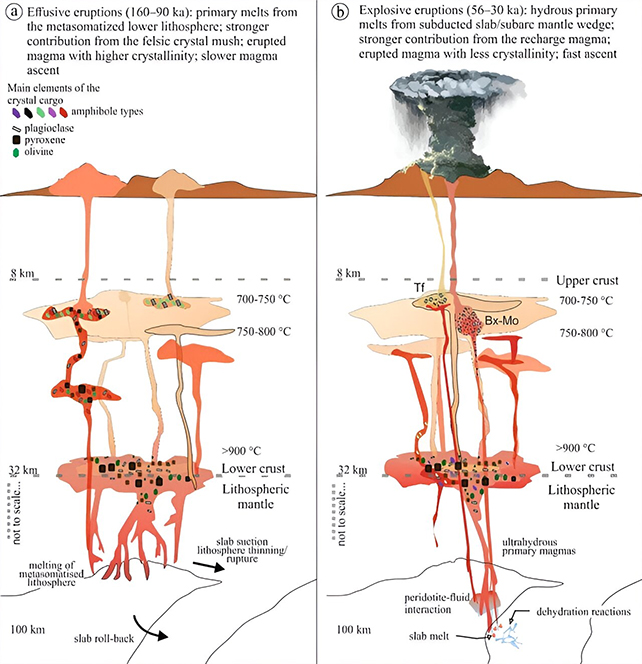 Variations within the underlying magma have been known as explaining the other eruptions. (Cserép et al, Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2023)The research printed two magma zones, an higher zone (8 to twelve kilometers or 5 to 7 miles) deep and a decrease zone (16 to 40 kilometers) deep. How the magma enters the skin seems to rely at the origins of this recharge magma.If it is most commonly composed of melted lithosphere then the chemical substances permit for a gradual free up, but when oceanic slab enters the combo the chemistry turns into extra explosive.In keeping with the researchers, the crystallinity and larger water content material of the magma rising from the recharge zone can have performed a vital position within the transfer from effusive to explosive eruptions after a smash of a few 10,000 years or so.”[The most recent eruptions] have been shaped by means of extra bad, explosive eruptions in comparison to the former lively episode,” says geochemist Barbara Cserép from Eötvös Loránd College.”So, you will need to know what should be blamed for this alteration in eruption taste.”It is widely recognized that explosive eruptions can blast out of volcanoes which have been quiet for a protracted, very long time – so it is the most important to grasp extra about that procedure. Whilst Ciomadul does not appear to be erupting anytime quickly, it is nonetheless an invaluable case find out about.One of the most tactics through which the analysis may also be helpful is in serving to to identify the indicators of an drawing close eruption. Relating to the 1,350 or so probably lively volcanoes on Earth, our very best means of staying secure is getting early warnings.”Eruption of volcanoes – regardless of their magnitude – poses a vital, however regularly underrated possibility on trendy society,” write the researchers of their printed paper.The analysis has been printed in Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology.
Variations within the underlying magma have been known as explaining the other eruptions. (Cserép et al, Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2023)The research printed two magma zones, an higher zone (8 to twelve kilometers or 5 to 7 miles) deep and a decrease zone (16 to 40 kilometers) deep. How the magma enters the skin seems to rely at the origins of this recharge magma.If it is most commonly composed of melted lithosphere then the chemical substances permit for a gradual free up, but when oceanic slab enters the combo the chemistry turns into extra explosive.In keeping with the researchers, the crystallinity and larger water content material of the magma rising from the recharge zone can have performed a vital position within the transfer from effusive to explosive eruptions after a smash of a few 10,000 years or so.”[The most recent eruptions] have been shaped by means of extra bad, explosive eruptions in comparison to the former lively episode,” says geochemist Barbara Cserép from Eötvös Loránd College.”So, you will need to know what should be blamed for this alteration in eruption taste.”It is widely recognized that explosive eruptions can blast out of volcanoes which have been quiet for a protracted, very long time – so it is the most important to grasp extra about that procedure. Whilst Ciomadul does not appear to be erupting anytime quickly, it is nonetheless an invaluable case find out about.One of the most tactics through which the analysis may also be helpful is in serving to to identify the indicators of an drawing close eruption. Relating to the 1,350 or so probably lively volcanoes on Earth, our very best means of staying secure is getting early warnings.”Eruption of volcanoes – regardless of their magnitude – poses a vital, however regularly underrated possibility on trendy society,” write the researchers of their printed paper.The analysis has been printed in Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology.
Even Napping Volcanoes Can Disguise an Explosive Marvel Deep Inside of