This newsletter has been reviewed in keeping with Science X’s editorial procedure
and insurance policies.
Editors have highlighted the next attributes whilst making sure the content material’s credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed newsletter
relied on supply
proofread
Good enough!
A cushy summer time night within the Paleoproterozoic, as envisioned through DALL-E. Credit score: DALL-E / Harrison Tasoff
× shut
A cushy summer time night within the Paleoproterozoic, as envisioned through DALL-E. Credit score: DALL-E / Harrison Tasoff
The solar has simply set on a quiet mudflat in Australia’s Northern Territory; it’s going to set once more in every other 19 hours. A tender moon looms huge over the desolate panorama. No animals scurry within the waning mild. No leaves rustle within the breeze. No lichens encrust the uncovered rock. The one trace of existence is a few scum in a couple of puddles and ponds. And amongst it lives a various microbial neighborhood of our historic ancestors.
In a brand new account of exquisitely preserved microfossils, researchers at UC Santa Barbara and McGill College divulge that eukaryotic organisms had already advanced into a various array of paperwork even 1.64 billion years in the past. The paper, printed within the magazine Papers in Paleontology, recounts an assemblage of eukaryotic fossils from an technology early within the team’s evolutionary historical past. The authors describe 4 new taxa, in addition to proof of a number of complicated traits already found in those early eukaryotes.
“Those are a number of the oldest eukaryotes that experience ever been came upon,” defined lead writer Leigh Anne Riedman, an assistant researcher in UCSB’s Division of Earth Science. “But, even in those first data we are seeing a large number of range.”
Eukarya paperwork one of the most primary domain names of existence, encompassing the plant, animal and fungi clades, in addition to all different teams whose cells have a membrane-bound nucleus, like protists and seaweeds. Many scientists had concept early eukaryotes have been all rather an identical right through the overdue Paleoproterozoic, and that diversification came about round 800 million years in the past. However Riedman and her co-authors discovered fossils of a delightfully various, and complicated, forged of characters in rock just about two times as previous.
Scientists knew from earlier research that eukaryotes had advanced through this time, however their range on this technology was once poorly understood. So Riedman headed to the outback in overdue 2019. Inside one week, she had accrued about 430 samples from 8 cores drilled through a prospecting corporate; they now are living within the library of the Northern Territory Geological Survey. The 2 cores used for this learn about spanned kind of 500 meters of stratigraphy, or 133 million years, with round 15 million years of important deposition.
Riedman returned to the USA with shale and mudstone, remnants of an historic coastal ecosystem that alternated between shallow, subtidal mudflats and coastal lagoons. A dip in hydrofluoric acid dissolved the matrix rock, concentrating the dear microfossils that she then analyzed beneath the microscope.
“We have been hoping to seek out species with fascinating and other traits to their cellular partitions,” Riedman stated. She was hoping that those options may make clear what was once going down inside the cells right through this period of time. Attaining any conclusions in regards to the mobile internal will require a substantial amount of sleuthing, despite the fact that, for the reason that fossils maintain handiest the outside of the cells.
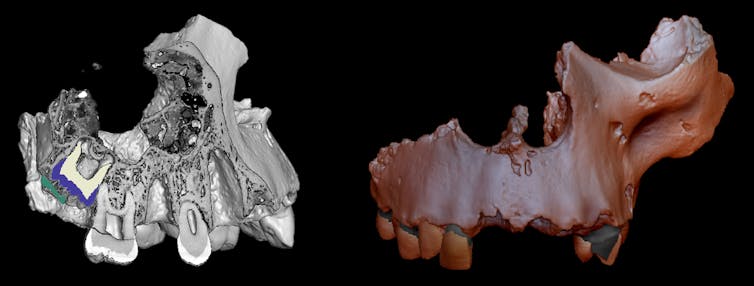
Limbunyasphaera operculata is a brand new species that presentations a small door opening into the cellular. Credit score: Riedman et al.
× shut
Limbunyasphaera operculata is a brand new species that presentations a small door opening into the cellular. Credit score: Riedman et al.
The researchers have been shocked through the range and complexity preserved in those fossils. They recorded 26 taxa, together with 10 up to now undescribed species. The staff discovered oblique proof of cytoskeletons, in addition to platy constructions that counsel the presence of interior vesicles through which the plates have been shaped—possibly ancestral to Golgi our bodies, found in fashionable eukaryotic cells. Different microbes had cellular partitions product of sure fibers, in a similar way suggestive of the presence of a fancy cytoskeleton.
The authors additionally discovered cells with a tiny lure door, proof of a point of class. Some microbes can shape a cyst to attend out detrimental environmental prerequisites. As a way to emerge, they want so that you could etch a gap of their protecting shell. Making this door is a specialised procedure.
“If you will produce an enzyme that dissolves your cellular wall, you want to be truly cautious about how you utilize that enzyme,” Riedman stated. “So in one of the most earliest data of eukaryotes, we are seeing some beautiful spectacular ranges of complexity.”
Many of us within the box had concept this skill emerged later, and the proof for it on this assemblage additional emphasizes how various and complicated eukaryotes have been even at this early juncture. “The belief has all the time been that that is across the time that eukaryotes gave the impression. And now we predict that folks simply have not explored older rocks,” stated co-author Susannah Porter, an Earth science professor at UC Santa Barbara.
This paper is a part of a bigger mission investigating early eukaryote evolution. Riedman and Porter wish to know in what environments early eukaryotes have been diversifying, why they have been there, once they migrated to different puts, and what diversifications they wanted with a view to fill the ones new niches.
A large a part of this effort comes to figuring out when other traits of eukaryotes first arose. As an example, the authors are slightly to be told whether or not those organisms have been tailored to oxygenated or anoxic environments. The previous would counsel that they’d an cardio metabolism, and in all probability mitochondria. Each and every fashionable eukaryote that is been discovered descends from ancestors that possessed mitochondria. This means that eukaryotes received the organelle very early on, and that it equipped an important merit.
Riedman and Porter are lately operating on a contemporary account of eukaryote range thru time. They have got additionally accrued even older samples from Western Australia and Minnesota. In the meantime, their geochemist collaborators at McGill are spearheading a learn about on oxygen ranges and most popular eukaryote habitats, facets that would make clear their evolution.
“Those effects are a directive to move search for older subject material, older eukaryotes, as a result of that is obviously no longer the start of eukaryotes on Earth,” Riedman stated.
Additional information:
Leigh Anne Riedman et al, Early eukaryotic microfossils of the overdue Palaeoproterozoic Limbunya Crew, Birrindudu Basin, northern Australia, Papers in Palaeontology (2023). DOI: 10.1002/spp2.1538
Magazine knowledge:
Papers in Palaeontology