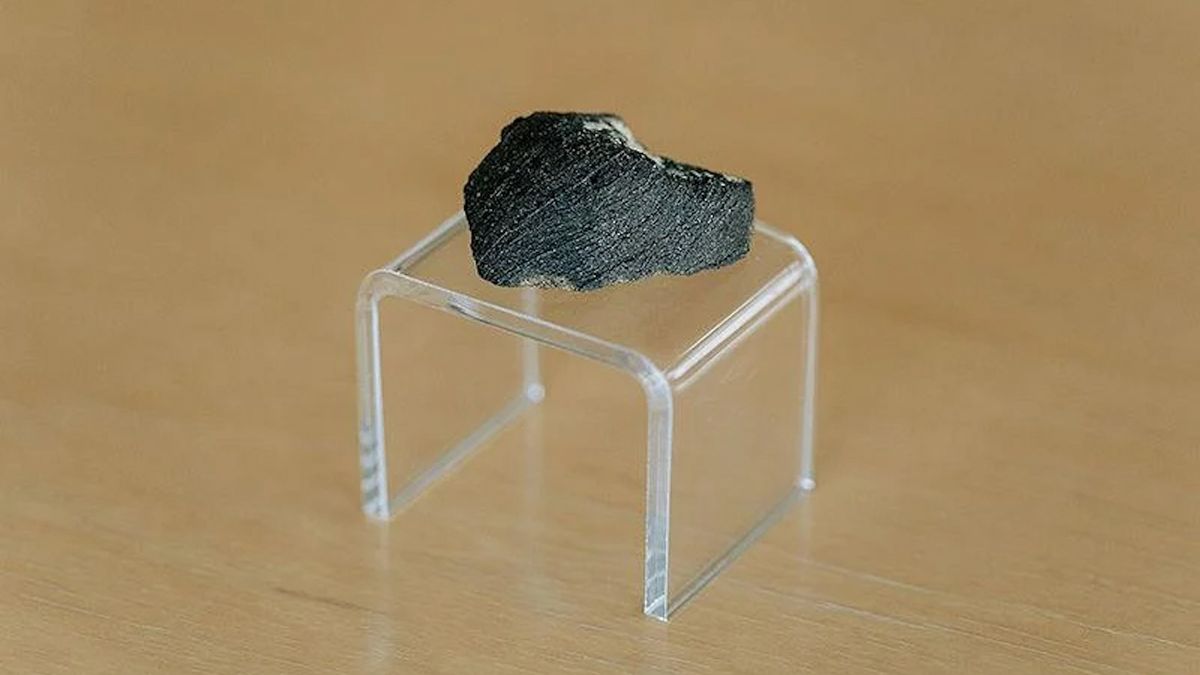
The explosive finish of non-avian dinosaurs is probably the most notorious blow to lifestyles on Earth. However there may be lengthy been hints that the asteroid is probably not the principle perpetrator in the back of this mass extinction, simply probably the most impressive remoted contribution.Earlier than this dramatic match, 66 million years in the past, poisonous winds of trade have been already brewing within the air.A brand new research through a global group of researchers has added proof to claims that the sector previous to the asteroid blow was once the rest however paradise, with measures of sulfur within the surroundings achieving essential ranges.Along with different research on ranges of mercury, the analysis supplies a signature of volcanic task sturdy sufficient to motive important local weather disruptions.In 1991, the timing of this volcanic task have been pushed aside as too early to be in the back of the mass extinction match however newer research reveal it is conceivable the timing was once shut sufficient to be important.”Our information counsel that volcanic sulfur degassing from such task will have led to repeated short-lived world drops in temperature,” College of Oslo geoscientist Sara Callegaro and associates write of their paper.The group tested rocks from the Deccan Traps – one of the most greatest volcanic options – in what is now West India. They implemented a brand new method they evolved for measuring sulfur concentrations.Fashions counsel sustained sulfur emissions from the Deccan Traps have been sufficient to considerably modify the worldwide local weather. This volcanic area by myself launched a staggering 1,000,000 cubic kilometers of molten rock.What is extra, formation of the extremely concentrated sulfur containing lava at Thakurvadi to Bushe, inside the area, coincides with the cooling Cretaceous local weather, the group notes.Whilst a lot of the basalt within the space is in most cases low in sulfur, this would point out the local weather – cooling molecule was once slowly launched into the ambience from the hardened magma following eruptions.In consequence world temperatures will have plummeted in bouts of as much as 10°C, between speedy restoration sessions, inside 100,000 years ahead of the Chicxulub meteor delivered that ultimate blow.”Our analysis demonstrates that climatic prerequisites have been nearly indisputably volatile, with repeated volcanic winters that will have lasted many years, previous to the extinction of the dinosaurs, ” explains McGill College geochemist Don Baker.”This instability would have made lifestyles tricky for all crops and animals and set the level for the dinosaur extinction match.”Fossilized bone fragments and 1000’s of eggshell remnants have steered a world decline in non-avian dinosaur species over this type of extended time frame.However those declines had been contradicted through different research, proceeding a long-standing and infrequently sour clinical debate between the asteroid and volcano theories. Some researchers counsel the asteroid can have prompted larger task from the Deccan Traps, others declare the volcanic task can have even helped lifestyles get well from the asteroid strike.The argument for pulses of eruptions does appear to be stacking up and volcanoes are, in any case, what introduced 3 quarters of all lifestyles on Earth to an finish throughout the former mass extinction.”Deccan Traps volcanism set the level for a world biotic disaster, time and again deteriorating environmental prerequisites through forcing habitual brief volcanic winters,” the group concludes.Their analysis was once revealed in Science Advances.
Even With out a Meteorite, The Level Was once Set For Dinosaurs to Cross Extinct








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1253767680-1d3e98f5bad047c4b780006342597af5.jpg)